Contents
If you’re seeking a swift and efficient path to building muscle, a dumbbell full body workout could be precisely what you need. Unlike gym memberships or expensive exercise machines, a good set of dumbbells is a one-time investment that can last for years. With a well-structured routine, you can engage multiple muscle groups in a single session, optimizing your workout time. You’re ready to start your fitness journey with this dumbbell full body workout for beginners. So, grab those dumbbells, and let’s get started on the path to a healthier, stronger you!
| Dumbbell Full Body Workout | Home and Gym |
| Training Type | Full-body, Upper/Lower Split |
| Goal | Muscle Gain, Strength |
| Program Duration | 8-12 weeks |
| Frequency | Per week 3-4 Days |
| Equipment | Dumbbells |
| Levels | Beginner to Intermediate |
| Suitable For | Men and Women |
Understanding Muscle Gain
Before we get into the workouts, let’s briefly discuss the science behind muscle gain. Muscle growth, or hypertrophy, occurs when your muscles are subjected to progressive overload, typically through resistance training. This process involves small muscle fiber tears that, when repaired, result in stronger and larger muscles.
1. Progressive Overload: At the heart of muscle gain is the concept of progressive overload. This principle dictates that for your muscles to grow, you must continually subject them to increased levels of resistance or stress during your workouts. In the context of resistance training, this means gradually increasing the weight, repetitions, or intensity of your exercises over time. By doing so, you challenge your muscles to adapt and become stronger.
2. Muscle Fiber Tears: During dumbbell training, particularly when lifting weights, your muscles undergo stress and tension. This stress can lead to the formation of tiny micro-tears within the muscle fibers. These micro-tears are a natural part of the muscle-building process. They signal your body to initiate the repair and recovery process.
3. Muscle Protein Synthesis: Muscle repair and growth are primarily driven by a process called muscle protein synthesis (MPS). After a workout, your body begins synthesizing new proteins to repair and strengthen the damaged muscle fibers. This is where the growth happens. Protein intake through your diet plays a crucial role in supporting this process, as it provides the necessary building blocks (amino acids) for muscle repair and growth.
4. Rest and Recovery: While dumbbell training and muscle fiber tears are essential for muscle growth, it’s during the recovery phase that your muscles actually become stronger and larger. Adequate rest and recovery time are critical because they allow your body to repair the damaged muscle fibers, adapt to the stress, and build new muscle tissue. Overtraining or not allowing enough recovery time can hinder muscle growth and increase the risk of injury.
5. Nutrition’s Role: Proper nutrition is a key component of muscle gain. Consuming a diet rich in high-quality protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats provides your body with the energy and nutrients it needs to support muscle repair and growth. Protein, in particular, is essential as it provides the amino acids necessary for muscle protein synthesis. Remember, muscle gain is not just about exercise; nutrition and recovery are equally important. Consume a balanced diet rich in protein to support muscle repair and growth.
6. Consistency and Patience: Muscle gain is a gradual process that requires consistency and patience. It’s essential to stick to a structured dumbbell full body workout routine, progressively increase the resistance, and maintain a balanced diet. Results may not be immediate, but with time and dedication, you’ll notice significant improvements in muscle size and strength.
In summary, muscle gain is the result of subjecting your muscles to progressive overload, leading to micro-tears in muscle fibers. These tears trigger the body’s repair and growth process through muscle protein synthesis, supported by proper nutrition and sufficient rest. Consistency and patience are key to achieving your muscle gain goals in a safe and effective manner.
Why Dumbbell Workouts for Muscle Gain?
Dumbbells offer several advantages for muscle growth:
- Isolation and Control: Dumbbells allow you to isolate specific muscle groups and control each repetition, ensuring you’re effectively targeting the muscles you want to develop.
- Variety of Exercises: Dumbbells provide a wide range of exercise options, allowing you to hit all major muscle groups, from chest and back to legs and arms.
- Stabilization and Balance: Using dumbbells engages stabilizer muscles, promoting balanced muscle development and functional strength.
- Flexibility and Convenience: Dumbbell workouts can be done at home or in the gym, offering the flexibility to integrate fitness into your daily
Options for Dumbbell Full Body Workout
When engaging in a dumbbell full body training regimen, you have two distinct options to choose from, each tailored to different fitness goals and preferences. These options provide versatility in your workout routine, allowing you to cater to either muscle preservation and overall fitness or a more intense approach focused on muscle development and growth.
Opsion 1: Muscle Maintenance and Functional Strength
This particular option is tailored to individuals who prioritize the maintenance of their current muscle mass, overall fitness, and functional strength. With just one exercise targeting all major muscle groups, you can get a comprehensive workout in a shorter amount of time.
Within Option 1, a three-day weekly workout schedule is adopted, allowing all major muscle groups to be engaged three times a week.
While it employs one exercise per major muscle group, it’s true that this approach may not provide the intensity and volume required for substantial muscle growth. Instead, Option 1 is well-suited for individuals who value a well-rounded, time-efficient workout that promotes muscle maintenance and overall functional strength.
Dumbbell Sumo Deadlift | 3×12-15 | 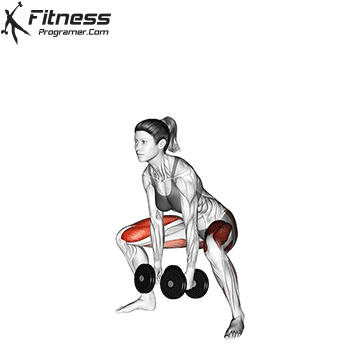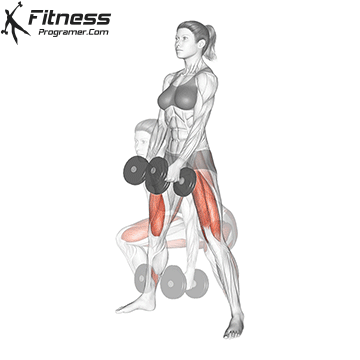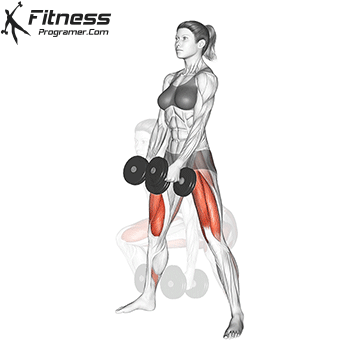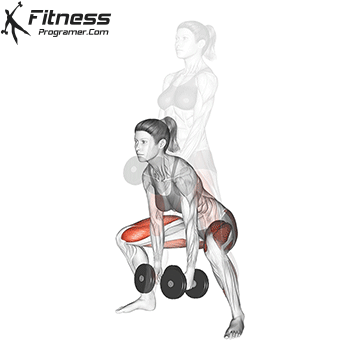 |
Dumbbell Curtsey Lunge | 3×12-15 | 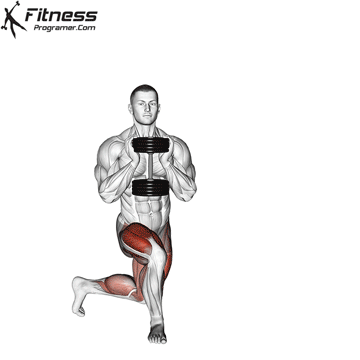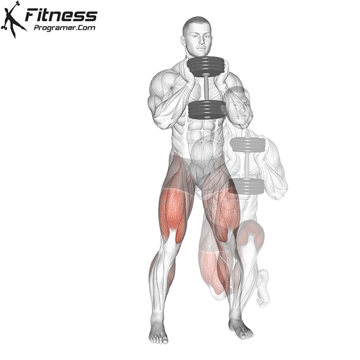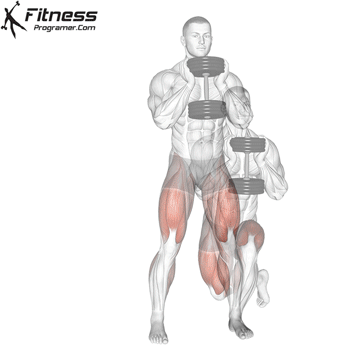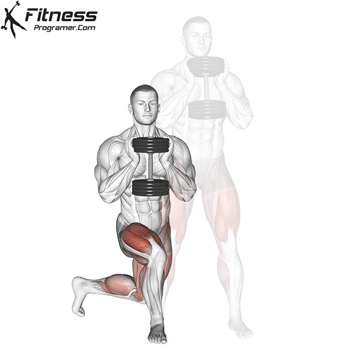 |
Dumbbell Bench press | 4×10-12 | 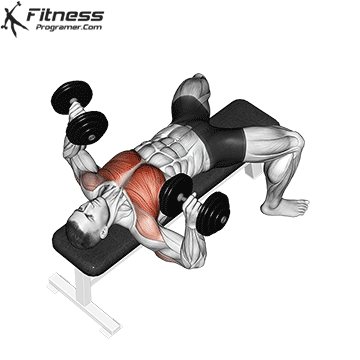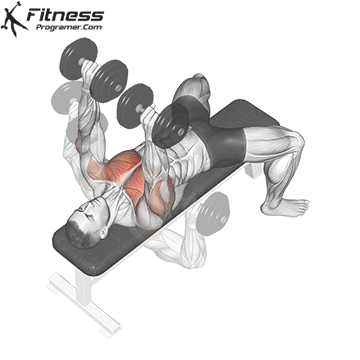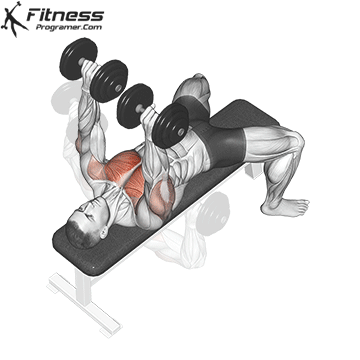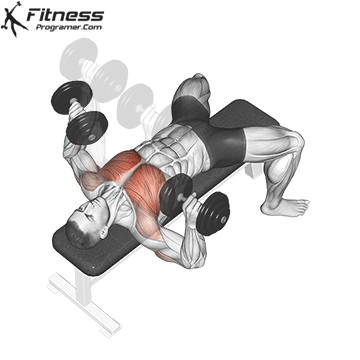 |
Dumbbell Overhead Press | 4×10-12 | 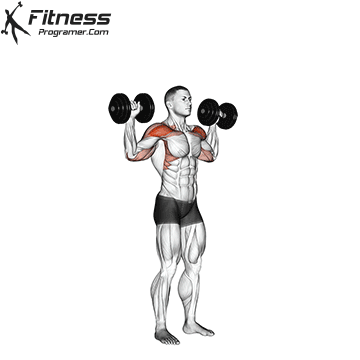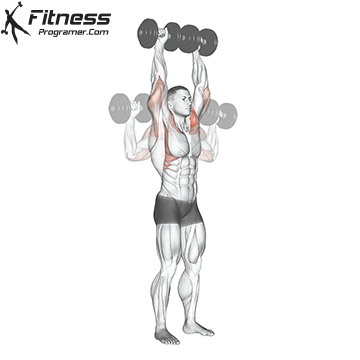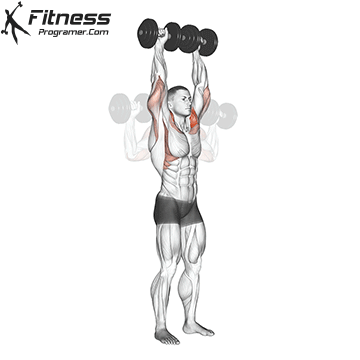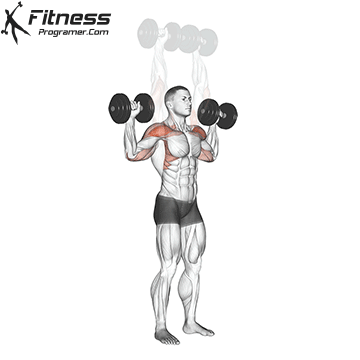 |
Dumbbell Bent Over Row | 4×10-12 | 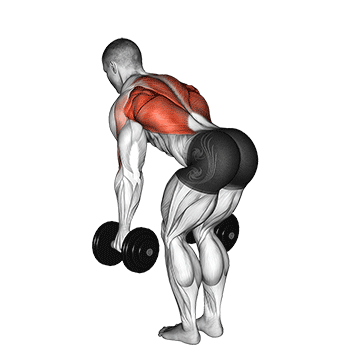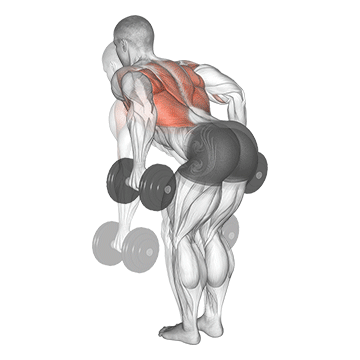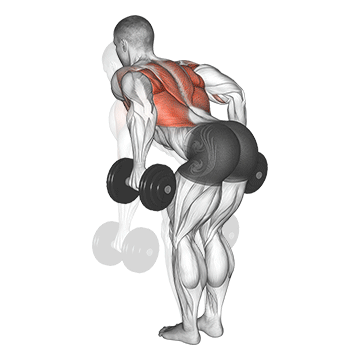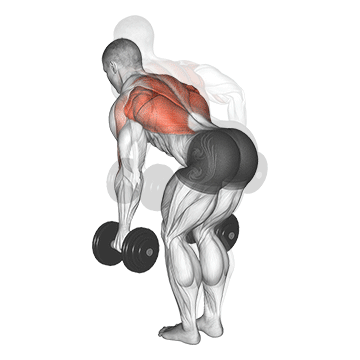 |
Dumbbell Curl | 4×10-12 | 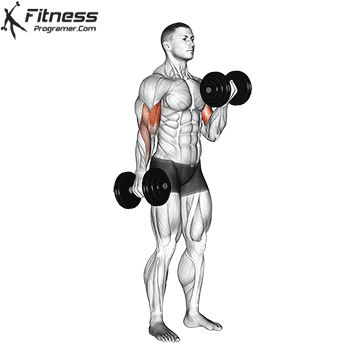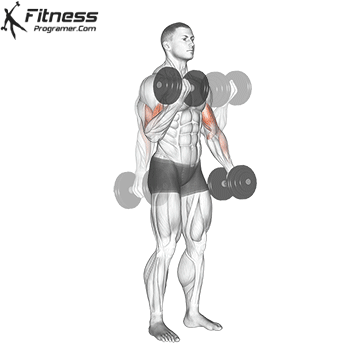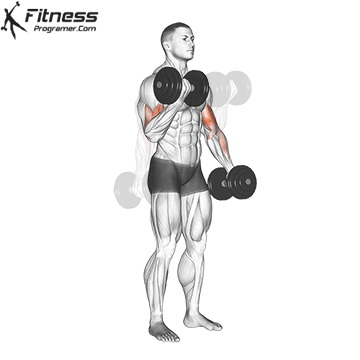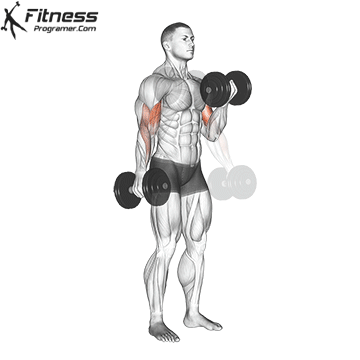 |
Dumbbell Tricep Kickback | 4×10-12 | 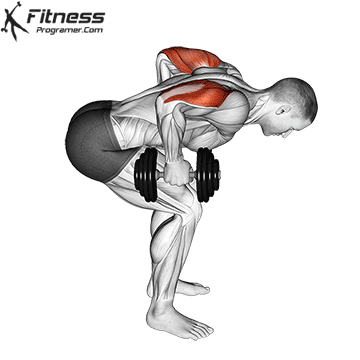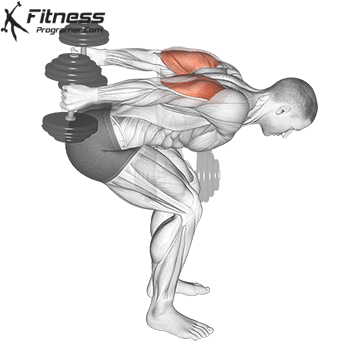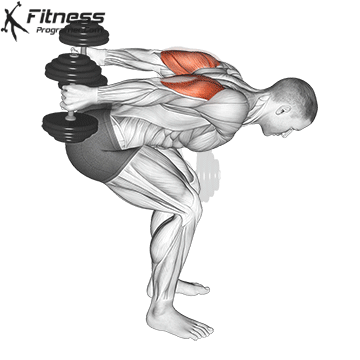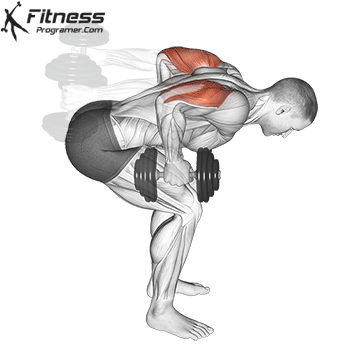 |
Dumbbell V-up | 3×10-15 | 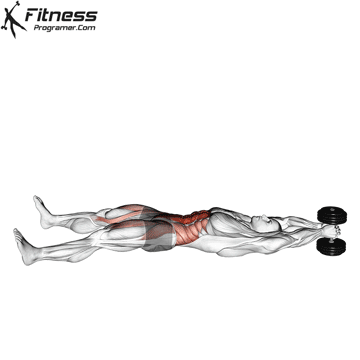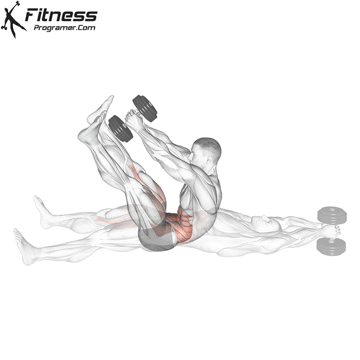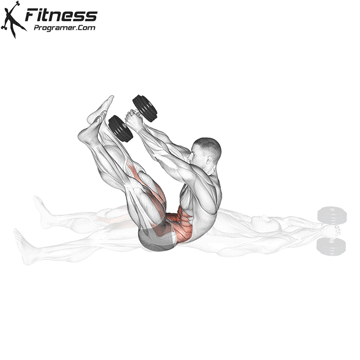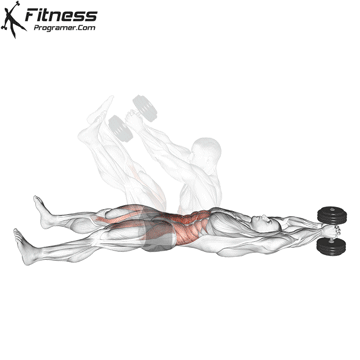 |
Option 2: Comprehensive Dumbbell Full Body Workout
When your primary fitness goal revolves around significant muscle gain and sculpting a more toned, muscular physique, it’s imperative to increase the workload. This is precisely where Option 2, with its comprehensive muscle-building program, shines. Let’s delve deeper into why Option 2 is the optimal choice for individuals determined to achieve substantial muscle gains:
The concept of splitting your full body workout into upper and lower body sessions involves focusing on different muscle groups on different days. Typically, you’ll dedicate specific workout sessions to exercises that primarily target your upper body on some days and lower body on others.
In Option 2, you have the flexibility to progressively challenge your muscles by lifting heavier weights, performing more repetitions, or advancing to more challenging exercises. This incremental approach is essential for stimulating muscle growth.
Scientific studies have shown that training muscle groups more than once a week can lead to greater increases in muscle size and strength compared to training them only once a week. This is often referred to as increased training frequency.
When you split your full body workout into upper and lower body days, you inherently increase the frequency at which you train each muscle group. For example, if you train four days a week, you’ll effectively target the same muscle groups twice in that week. Just like PPL Workout Routine..
Dumbbell Full Body Workout Overview
Before diving into the workouts, let’s talk about weight load, an essential aspect of any effective strength training program. The weight you choose should be challenging enough to complete the prescribed sets and reps with proper form, but it should also provide enough resistance to stimulate muscle hypertrophy (growth). Aim for 8 to 12 reps per set for compound exercises (such as the bench press and squat) to focus on hypertrophy. For isolation exercises (like curls and kickbacks), a range of 10 to 15 reps is effective.
Frequency: 4 Days a Week
To optimize muscle growth and allow for adequate recovery, perform these workouts four days a week. For example, you can follow this schedule:
- Monday: Workout A
- Tuesday: Rest or active recovery
- Wednesday: Workout B
- Thursday: Rest or active recovery
- Friday: Workout A
- Saturday: Rest or active recovery
- Sunday: Workout B
This schedule ensures that you hit all major muscle groups while providing sufficient rest between sessions.
Warm-up: Begin with a 5-10 minute warm-up, incorporating activities like jumping jacks or light cardio to increase blood flow and prepare your muscles for the upcoming workout.
Cool-down: After your workout, allocate 5-10 minutes to stretch major muscle groups. This will enhance flexibility, mitigate post-workout stiffness, and support recovery.
Dumbbell Full Body Workout A
Dumbbell Bench press (3×10-12)
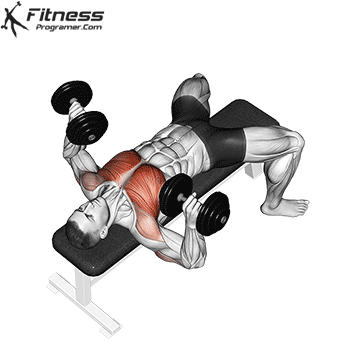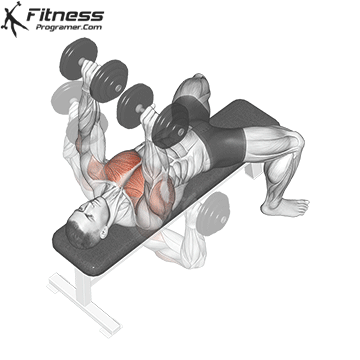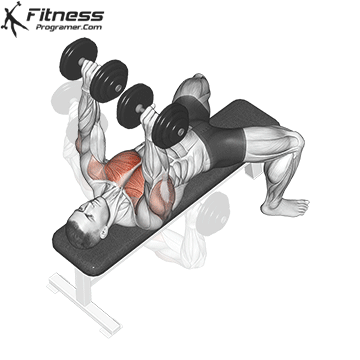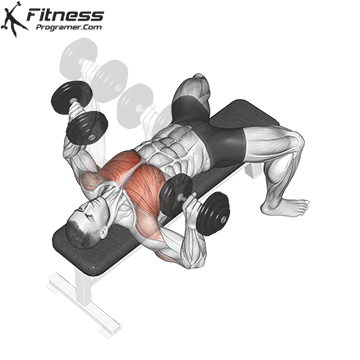
This exercise primarily targets the chest muscles (pectoralis major) and also engages the shoulders and triceps. It helps increase upper body strength and is a fundamental compound movement for chest development.
Lie flat on a bench with a dumbbell in each hand. Press the dumbbells upward until your arms are fully extended, then lower them to chest level.
Dumbbell Fly (3×12-15)
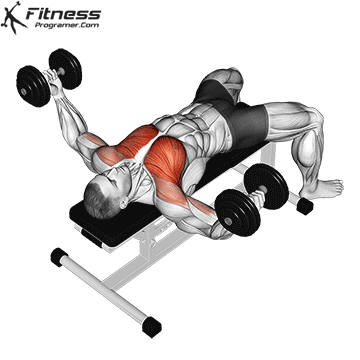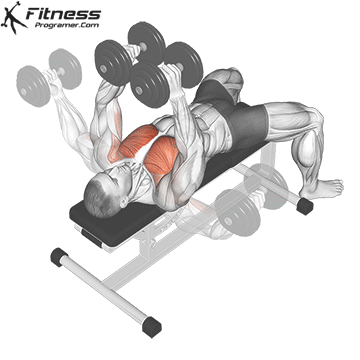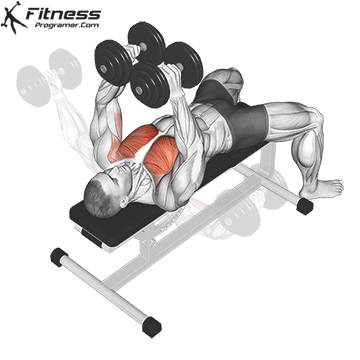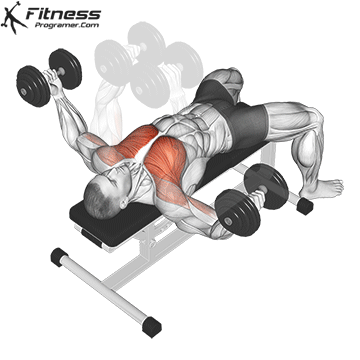
Dumbbell flies isolate and stretch the chest muscles, enhancing muscle definition and promoting chest development.
Lie on a bench with a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing each other. Lower your arms outward until you feel a stretch in your chest, then return to the starting position.
Dumbbell Overhead Press (3×10-12)

The overhead press primarily targets the shoulders (deltoids) and triceps. It builds shoulder strength and stability, enhancing upper body aesthetics and functional strength.
Sit or stand with a dumbbell in each hand at shoulder height. Press the weights overhead until your arms are fully extended, then lower them back down.
Bent Over Lateral Raise (3×12-15)
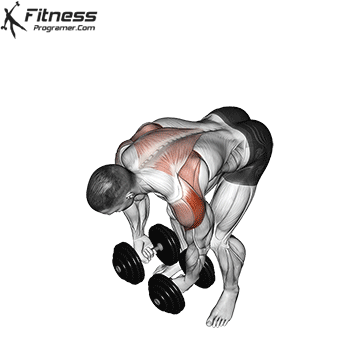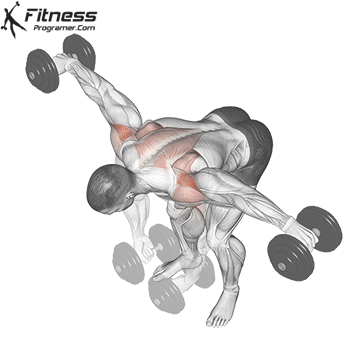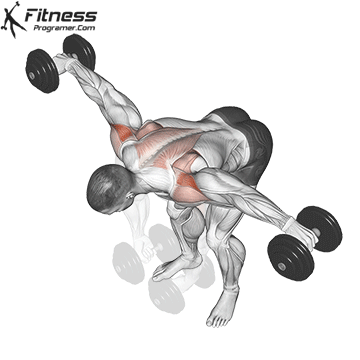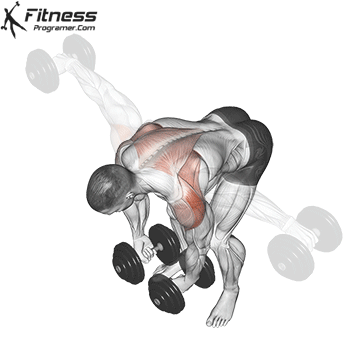
This exercise focuses on the traps, lateral and rear deltoid muscles, improving shoulder aesthetics and posture. It also helps prevent shoulder imbalances.
Bend at the waist with a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing each other. Raise your arms outward to shoulder height, then lower them.
Bent Over Dumbbell Row (3×10-12)

The bent-over row targets the back muscles, particularly the latissimus dorsi and rhomboids. It enhances upper back strength and posture.
Bend at the waist with a dumbbell in each hand. Pull the dumbbells toward your hips, squeezing your shoulder blades together, then lower them.
Single-Arm Dumbbell Row (3×12-15)
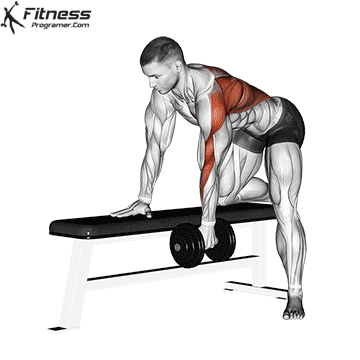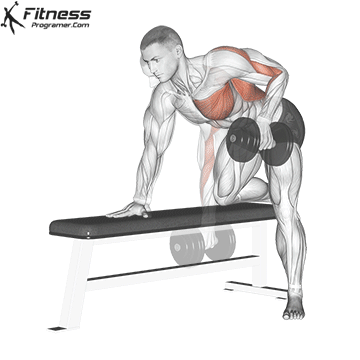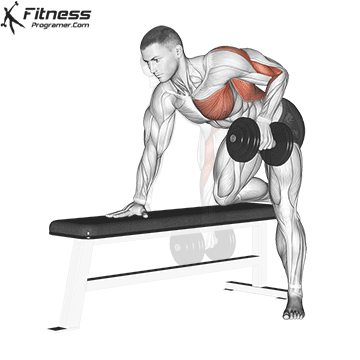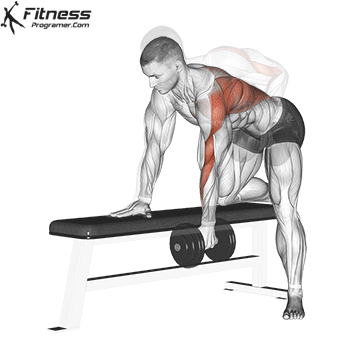
This unilateral exercise improves muscle balance and symmetry in the back and can help correct muscle imbalances.
Place one knee and hand on a bench, opposite leg on the floor. Hold a dumbbell in one hand and row it toward your hip, then lower it.
Double-Arm Dumbbell Curl (4×10-12)
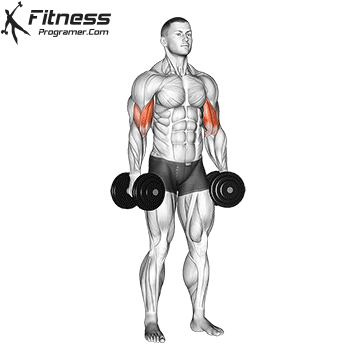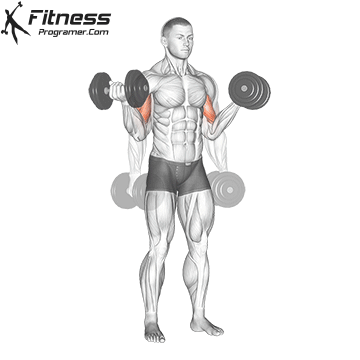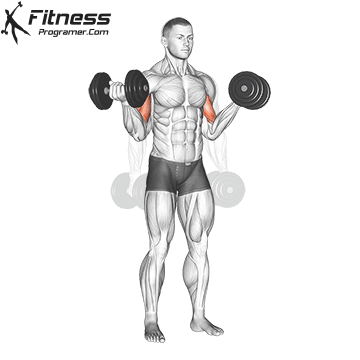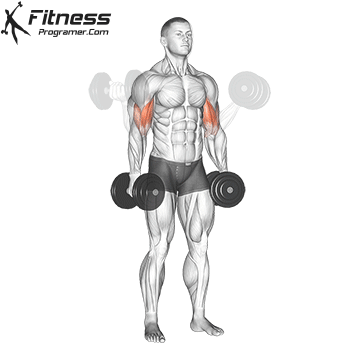
Dumbbell curls target the biceps, helping build arm strength and size. They also improve arm aesthetics.
Stand with a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing forward. Curl the dumbbells upward toward your shoulders, then lower them.
Dumbbell Kickback (4×10-12)
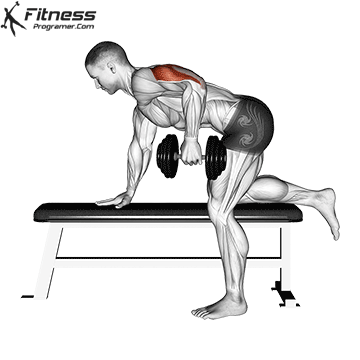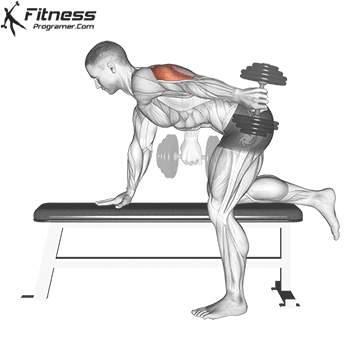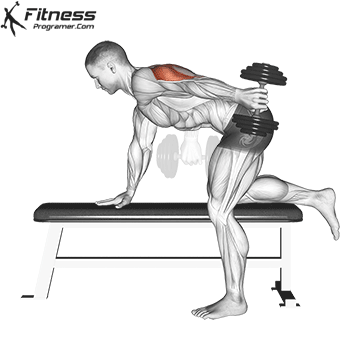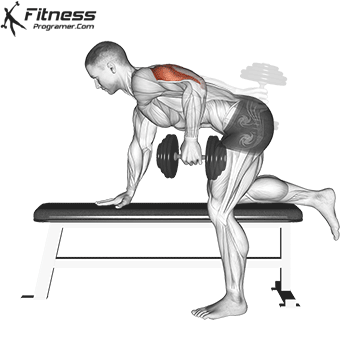
Dumbbell kickbacks isolate the triceps, promoting arm definition and strength.
For triceps development, extend the dumbbell behind you while keeping your upper arm steady. Focus on squeezing the triceps at the top of the movement.
Dumbbell Full Body Workout B
Dumbbell Goblet Squat (3×12)
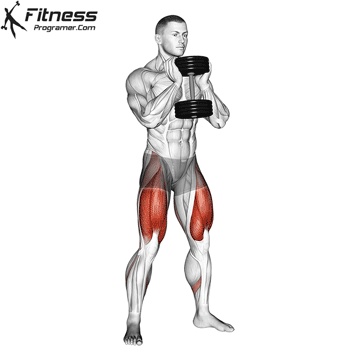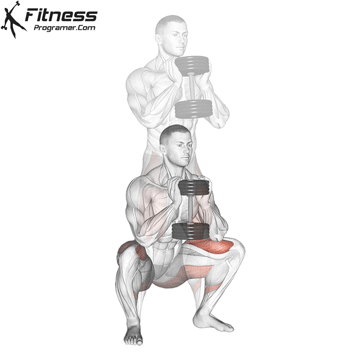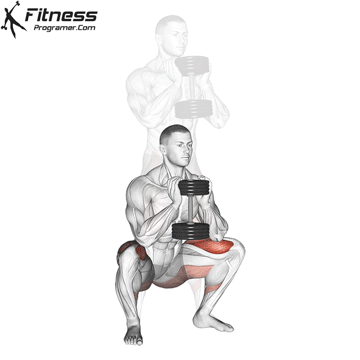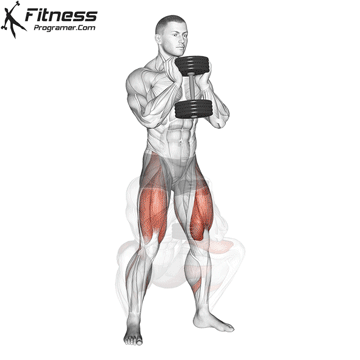
Goblet squats target the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and core muscles, improving lower body strength and stability.
Hold a dumbbell close to your chest and squat down, keeping your back straight. Push through your heels to return to a standing position.
Dumbbell Deadlift (3×12)
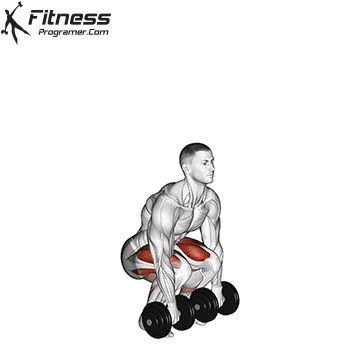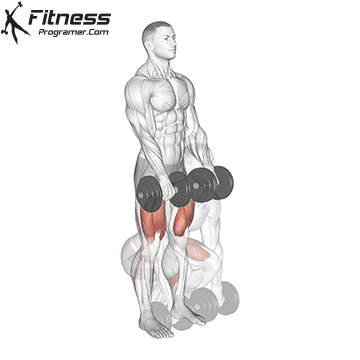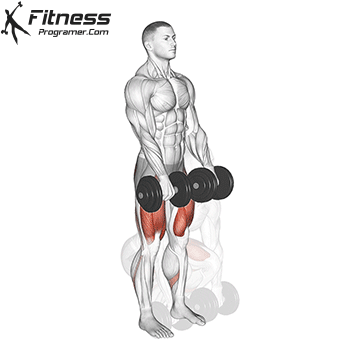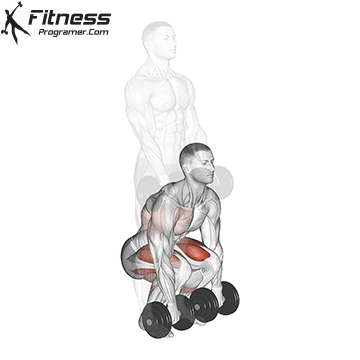
Dumbbell deadlifts engage the entire posterior chain, including the lower back, glutes, and hamstrings. They promote overall strength and posture.
Hold a dumbbell in each hand with a hip-width stance. Hinge at the hips and lower the weights while keeping your back straight, then return to a standing position.
Dumbbell Glute Bridge (3×12-15)
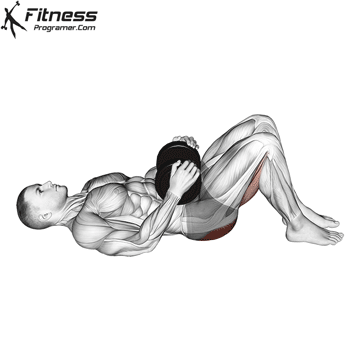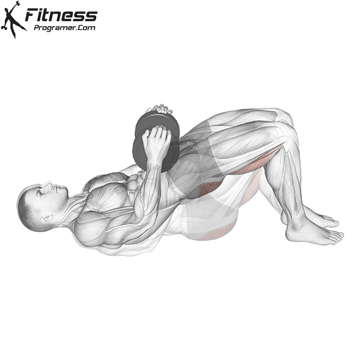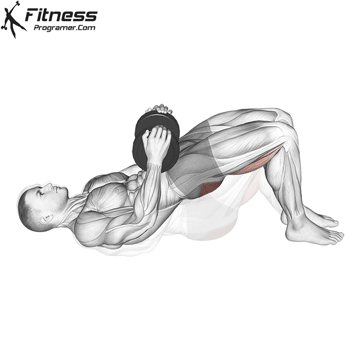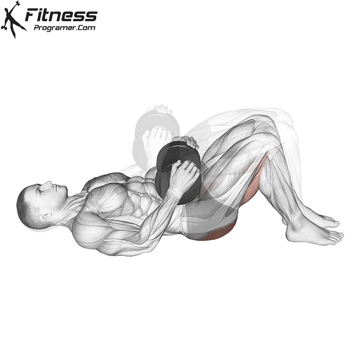
Glute bridges are an excellent exercise for targeting the gluteus maximus, the largest muscle in your buttocks.This exercise also engages the core muscles to a certain extent, promoting overall core stability.
Lie on your back with a dumbbell on your hips. Lift your hips toward the ceiling, squeezing your glutes, then lower them.
Lying Dumbbell Leg Curl (3×12-15)
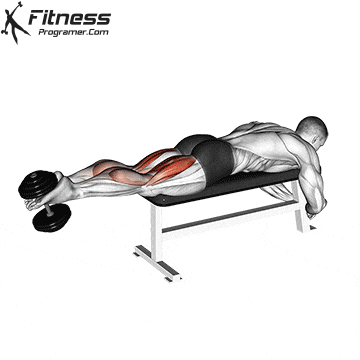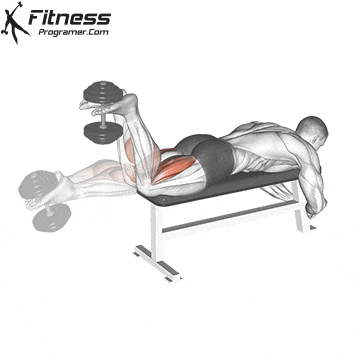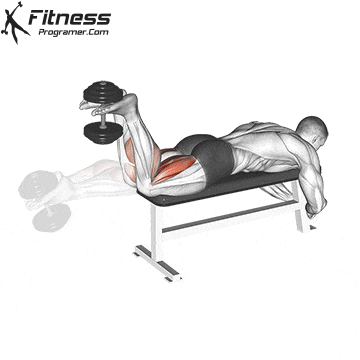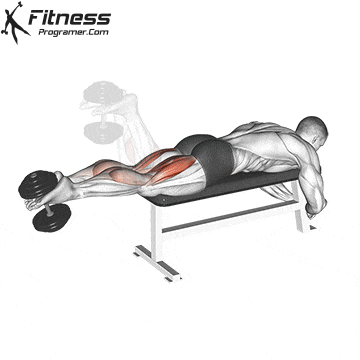
The lying dumbbell leg curl is a highly effective exercise for isolating and strengthening the hamstrings, which are the muscles on the back of your thighs. Strong hamstrings contribute to improved athletic performance, including running, jumping, and cycling.
Lie face down on a bench with a dumbbell between your ankles. Curl your legs upward, squeezing your hamstrings, then lower them.
Dumbbell Calf Raise (3×12-15)
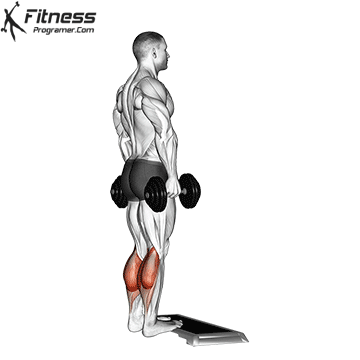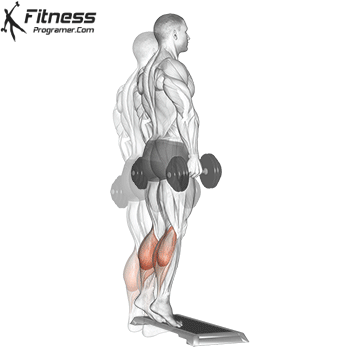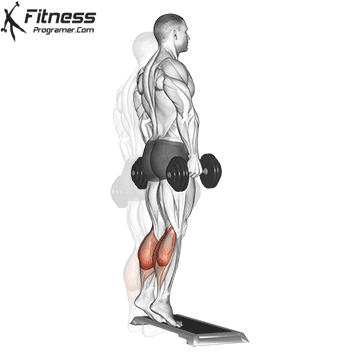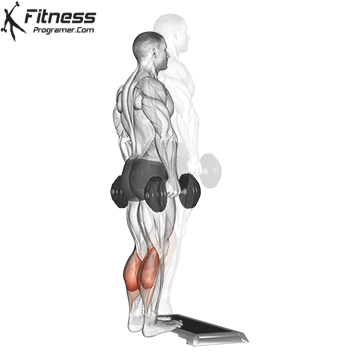
Calf raises target the calf muscles, improving lower leg strength and aesthetics.
Stand on a step or flat surface with a dumbbell in each hand. Raise your heels as high as possible, then lower them.
Dumbbell Side Bend (3×12-15)
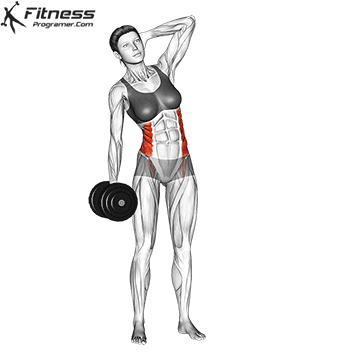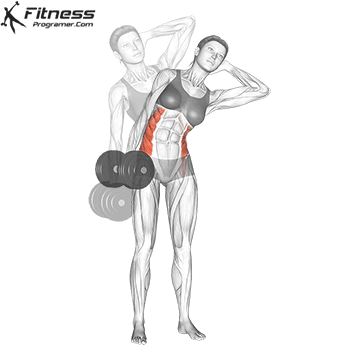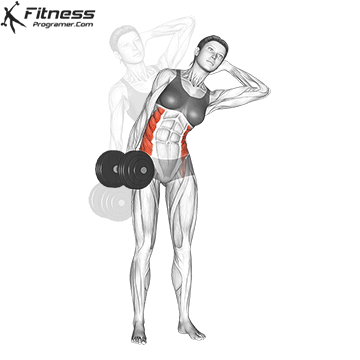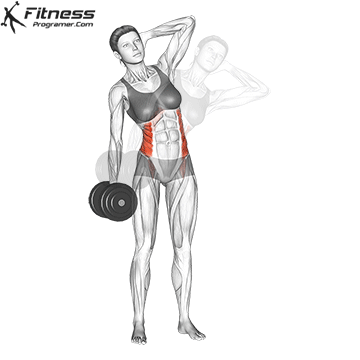
Dumbbell side bends primarily target the oblique muscles on the sides of your abdomen. Strengthening your obliques can improve core stability and posture.
Hold a dumbbell in one hand, stand tall, and bend to the side, then return to an upright position.
Dumbbell V-up (3×12-15)

Dumbbell V-ups are an advanced core exercise that engages all the muscles of the core, including the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis. By challenging your core, this exercise helps improve abdominal strength and definition.
Lie on your back with a dumbbell in your hands. Lift your upper body and legs simultaneously, forming a “V” shape, then lower them.
Tips:
- Warm up before each workout with some light cardio and dynamic stretches.
- Use proper form and technique to prevent injuries.
- Start with weights that allow you to complete the desired reps and sets with good form.
- Gradually increase the weight as you get stronger.
- Rest for 48 hours between each workout to allow for muscle recovery.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet to support muscle growth and recovery.
- Listen to your body and adjust the workout as needed based on your fitness level and goals.
Remember that consistency is key to seeing progress. Adjust the workout as needed to match your fitness level and goals, and consider consulting with a fitness professional to create a personalized plan if necessary.
References:
- Sports Med. 2016 Effects of Resistance Training Frequency on Measures of Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis PMID: 27102172
- Med Sci Sports Exerc 2009 Mar. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults



