Dumbbell Deadlift Overview
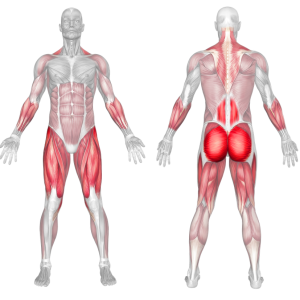
The dumbbell deadlift is a compound exercise, working the lower back, glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps. It’s like the barbell deadlift but uses dumbbells. It’s great for athletes, powerlifters, and those aiming to boost fitness.
How to do:
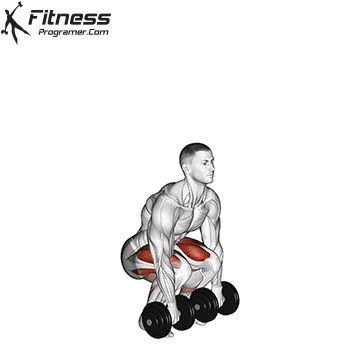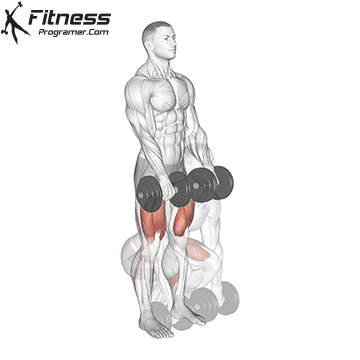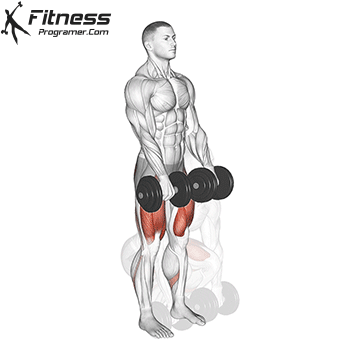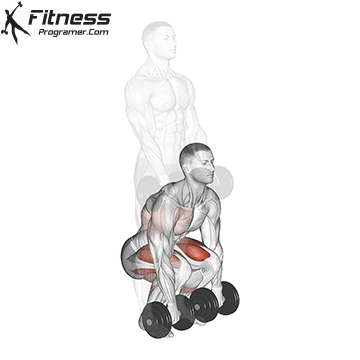
Here’s how to perform a dumbbell deadlift:
- Setup:
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart. Place a dumbbell on each side of your feet.
- The dumbbells should be positioned parallel to your feet, so the handles are perpendicular to your body.
- Stance:
- Bend at your hips and knees to lower yourself down.
- Keep your back straight, chest up, and shoulders back.
- Hold onto the dumbbells with a firm grip, palms facing your body. Your hands should be just outside your knees.
- Lift:
- Push through your heels and lift the dumbbells by straightening your hips and knees.
- Maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement. Do not round your back.
- Keep the dumbbells close to your body as you lift them.
- Stand fully upright with your chest out and shoulders back.
- Lower:
- Reverse the movement by pushing your hips back first, then bending your knees to lower the dumbbells back to the ground.
- Keep the dumbbells close to your body and maintain good form.
- Repetition:
- Repeat the lift for the desired number of repetitions.
- Exhale as you lift the dumbbells and inhale as you lower them.
Tips:
- Start with a light weight to practice proper form, and gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable and stronger.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your spine throughout the exercise.
- Keep your head in a neutral position, looking forward or slightly upward.
- Avoid jerky or fast movements; focus on controlled and smooth lifting and lowering.
- If you have any pre-existing back or lower-body issues, consult a fitness professional or medical expert before attempting this exercise.
Benefits of Dumbbell Deadlift
Here are some key advantages of incorporating dumbbell deadlifts into your workout routine:
- Strength Development: The dumbbell deadlift is a strength training exercise that works multiple muscle groups simultaneously. It targets the lower back, glutes, hamstrings, quadriceps, and forearms. This, in turn, enhances lower body strength and grip strenght.
- Functional Fitness: This exercise mirrors everyday actions like lifting heavy objects. It strengthens key muscles and enhances lifting technique, making daily tasks easier.
- Posterior Chain Development: Dumbbell deadlifts focus on the posterior chain, including the lower back, glutes, and hamstrings. Strengthening these areas improves posture, prevents lower back pain, and boosts athletic performance.
- Improved Core Stability: Engaging the core is crucial for a safe deadlift. This lift strengthens the core, providing better spinal support and lowering the risk of back injuries.
- Increased Metabolism: Dumbbell deadlift is a great exercise that you can use in a full-body workout to burn excess calories. It can boost your metabolism and aid in fat loss when paired with a healthy diet.
Dumbbell Deadlift Muscles Worked