Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) is an important water-soluble vitamin that our body needs but cannot produce. It is naturally found in animal foods, but can be industrially produced and added to some foods, such as breakfast cereals. It has an important role in the formation of red blood cells, the production of DNA, and the healthy functioning of the brain and nervous system. B12 deficiency, which can be seen especially in the elderly, vegan diets, or people with digestive system disorders that affect the absorption of nutrients, can lead to anemia, psychiatric and neurological health problems.
What is vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is a vitamin that plays a fundamental role in red blood cell formation, cell metabolism, nerve function, and DNA production. The most important feature that distinguishes it from other B group vitamins is that it is the only vitamin containing cobalt, one of the minerals our body needs. Since our body cannot produce vitamin B12, it can be obtained naturally from animal foods.
It is almost non-existent in plant foods. It can also be produced industrially through bacterial fermentation synthesis as a food supplement. And it is added to many foodstuffs, especially cereals.
What does vitamin B12 do?
Vitamin B 12 is vital for DNA formation and regulation, nervous tissue health, brain function, and the production of red blood cells. The metabolism of every cell in the body needs vitamin B12 as it plays a role in the synthesis of fatty acids and energy production.
Since it is a water-soluble vitamin like other B vitamins, it can travel through the bloodstream. By helping our body absorb vitamin B9 (folic acid), it enables the synthesis and release of energy.
The human body produces millions of red blood cells every minute. These cells cannot reproduce properly without vitamin B12. When vitamin B 12 levels are too low, the production of red blood cells decreases. Anemia can occur if the red blood cell count drops.
This vitamin cannot be produced by the body, but can be stored in the liver (mostly) and kidneys for about four years. Excess need is excreted in urine. Getting enough Vitamin B 12 is very beneficial for the overall health of the body.
Benefits of vitamin B12
- It creates DNA, one of the building blocks of cells.
- It contributes to the protein synthesis process.
- It ensures the production of new cells and prevents aging.
- Converts carbohydrates to glucose, reduces fat and increases energy
- Strengthens the central nervous system, repairs nerve cells
- Strengthens the immune system
- May prevent Forgetful, Alzheimer’s and Dementia
- Helps prevent anemia
- May prevent major birth defects
- May support bone health and prevent osteoporosis
- May reduce risk of macular degeneration (yellow spot) eye disease
- Prevents or reduces the effects of depression
- Beneficial for the digestive system
- Protects the body against cardiovascular diseases
- Helps regulate blood pressure and lower cholesterol
- Prevents the risk of stroke
- It is one of the basic needs of hair, skin and nail health.
- May protect against breast, colon, prostate, lung cancers

Vitamin B12 Foods
Vitamin B12 is not found in fruits and vegetables. The only natural source for B12-containing foods is some protein-heavy animal foods. These:
- Shellfish such as lobster and mussels
- Oily fish such as sardines, anchovies, haddock, tuna, salmon
- Poultry such as chicken, turkey
- Red meat such as beef and sheep
- Especially sheep offal such as liver, kidney
- Dairy products such as milk, cheese, yogurt, kefir
- Eggs


How much vitamin B12 should be taken per day?
- Teenagers and adults over 14 years old 2.4 mcg
- pregnant women 2.6 mcg
- Breastfeeding women 2.8 mcg
How can the daily need for vitamin B12 be met?
You should take care to include one of the foods containing vitamin B12 in one of your meals every day.
Breakfast cereals fortified with vitamin B12 are both practical and ideal. It can be eaten by mixing with milk and honey and optionally adding nuts.
Vegans can include some fortified soy products in their diet, along with some foods containing yeast extract (extract).
Although some plant milks or cereals, such as almond milk, are fortified with vitamin B12, they cannot adequately meet a vegan woman’s B12 needs, and this can lead to deficiency problems over time.
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Since our body has an average of 4 years of vitamin B12 storage capacity, its deficiency can be seen rarely or years later. However, if you do not consume enough B12-containing foods or if you have any digestive system conditions such as gastritis, you may develop a vitamin B12 deficiency.
Who gets vitamin B12 deficiency?
- in the elderly
- Those who do not eat any animal products, such as vegans
- In people with anemia
- Diabetic patients using drugs containing metformin
- Especially in people with certain digestive disorders such as Celiac or Crohn’s disease
- Taking long-term anti-acid medications against heartburn
- in people who are HIV positive
- People who have had gastrointestinal surgery
- Long-term drug users
- Those who consume large amounts of alcohol
People who experience symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency should definitely see a doctor. If it is not taken care of, it can lead to bigger diseases as well as cause permanent damage to the body.
Vitamin B12 test
Vitamin B12 tests can be done for three different purposes:
1- Vitamin B12 deficiency test
It is the first test you may be asked for when you go to a doctor with symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency. Because this test is only done to measure the level of vitamin B12 in the blood. You may be asked not to eat for about 6-8 hours before your blood is drawn. The normal level range is 200-800 pg/L. 199 pg/L and below indicate B12 deficiency, 1500 pg/L and above indicate excess. The normal level in people 50 years of age and older is 500-800 pg/L. Some lab results may give different results. Therefore, your doctor will make the correct evaluation.
2- Causes of vitamin B12 deficiency test
The main challenge of this test is to detect vitamin B12 deficiency at a stage when its complications can be prevented with treatment. Because in some cases, there may be false deficiency and false height. This may indicate that there is a background condition that causes them to appear deficient or elevated when B12 values are normal.
- Conditions where false deficiency can be seen: It is a sign of active liver disease, lymphoma, autoimmune diseases and bone marrow diseases.
- Situations where false elevation can be seen: B9 (folate) deficiency, pregnancy, multiple myeloma (a type of cancer that develops in the white blood cell), excessive vitamin C intake.
3- Vitamin B12 control tests
10-14 days after drug supplements and nutritional therapy, the doctor may ask you for another blood test for control purposes. The goal is to control the course of treatment.
Diseases caused by vitamin B12 deficiency
Neurological changes
Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause neurological (affecting your nervous system) problems:
- vision problems
- Loss of memory
- numbness and tingling
- Loss of physical coordination (ataxia) that can affect your whole body and cause difficulty speaking or walking
- Damage to nerves, especially in the legs
Infertility
Vitamin B12 deficiency can sometimes lead to temporary infertility. This can usually be corrected with appropriate vitamin B12 therapy.
Gastric cancer
You may have an increased risk of stomach cancer if you have a vitamin B12 deficiency caused by pernicious anemia (a condition in which your immune system attacks healthy cells in your stomach).
Birth defect
If you’re pregnant and don’t get enough vitamin B12, you may increase your baby’s risk of developing a serious birth defect known as a neural tube defect. The neural tube is a narrow canal that forms the brain and spinal cord.
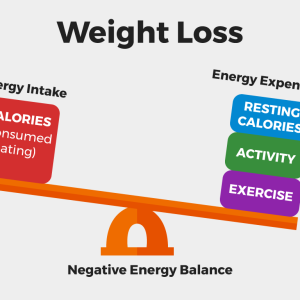
Does vitamin B12 help weight loss?
There is no evidence that taking pills or particularly injection supplements will help with weight loss. Those who enter such a sphere do not need to worry, because excess B12 is excreted through urine, so it does not accumulate in the body and cause damage. Approach all supplements that are said to help you lose weight with caution.