Why is Sports Nutrition Important?
Sports nutrition is important for maintaining the health of those who do sports, increasing endurance, good concentration and attention skills. Energy and nutrient requirements vary according to age, gender, weight, height, sport practice and frequency. The main goal with sports nutrition; The health of the athlete should be protected and their performance should be increased. It is seen that an athlete who is adequate and well nourished has higher performance than a poorly nourished athlete, his growth and development curves are smooth, his body weight is at the desired limit and his concentration is higher.
What is the meaning of sports nutrition?
Sports nutrition is the nutrition, diet study and practice to improve athletic performance to support athletes to achieve the highest performance in physical activity.
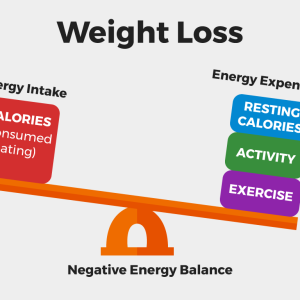
The nutrition of the athlete should include the necessary energy and sufficient fluid intake. The body spends more calories during exercise than at rest. Therefore, the energy and nutrient needs of athletes are higher. The diet of athletes in general; It should be rich in carbohydrates, normal in protein and slightly below normal in fat content. Since the fluid loss of athletes is higher than normal individuals, the amount of water drunk should be increased. In general, the daily calorie needs of athletes can be between 2000-5000 calories on average. The calorie requirement of each athlete differs.
What should be the ideal body weight and fat percentage of the athletes?
The weight of the athlete affects the amount of fat in his body, the amount of lean tissue, fluid mass, his success in sports, speed, strength and endurance. It is not correct to evaluate only the weight of athletes; body fat amount and muscle mass should also be measured and evaluated. For example, body weight may be high in some sports such as bodybuilding and weightlifting. This is because although the fat ratio is normal, the muscle mass is high.
The amount of fat effective in body weight varies according to gender and the sports branch. For example, the body fat percentage of the male athlete who is engaged in bodybuilding is 6%; 15% of the male athlete who deals with basketball. Body fat percentage of female athletes can rise up to 20%. The minimum percentage of fat in athletes’ body is 5% for men; in women it should be 12%.
Body Fat Calculator
BODY FAT PERCENTAGE CATEGORIES
| CLASSIFICATION | WOMAN (% FAT) | MEN (% FAT) |
| Essential Fat | 10-12 % | 2-4 % |
| Athletes | 14-20 % | 6-13 % |
| Fitness | 21-24 % | 14-17 % |
| Acceptable | 25-31 % | 18-25 % |
| Obese | 32 % | 25 % |
How Should Sports Nutrition Be?
The intensity, duration and type of exercise directly affect your nutritional needs. The body spends more calories during exercise than during rest. Therefore, the energy and nutrient needs of athletes are higher.
In order to avoid problems such as fatigue, weakness and weight loss, calories should be taken into the body as much as the daily energy spent and the sports diet should be prepared accordingly. Carbohydrate, protein, fat, vitamin and mineral values required with the sports nutrition program should be provided to the body through foods. The main energy source of the body is carbohydrates. Therefore, the consumption of carbohydrates should be higher than protein and fat sources.
Energy
- The energy that each athlete should take varies according to his age, height, weight, health condition and the sport he is engaged in.
- Insufficient energy intake can cause weight loss and weakness. Therefore, a sufficient amount of calories should be provided to the body.
- The energy intake of athletes during the day may vary between 2000-5000 calories. This value may be higher in endurance sports.
Carbohydrate
- Carbohydrate source foods are the main energy source especially for athletes.
- Carbohydrates taken with food are stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. Complex carbohydrate sources such as rice, pasta, bread, vegetables and legumes must be included in the nutrition program of athletes.
- Thanks to a high-carbohydrate diet, athletes can increase these glycogen stores 1.5-2 times. Having more glycogen stores in athletes means an increase in endurance times. Therefore, carbohydrate sources make up most of the daily energy intake. 60-65% of the daily energy intake of athletes should come from carbohydrate source foods. In endurance sports, this value can be up to 70%. The amount of carbohydrate to be taken can also be calculated according to body weight.
In sports that require endurance such as marathon running, increasing the carbohydrate intake one week before the sport and reducing the training duration and frequency is called carbohydrate loading. With carbohydrate loading, muscle glycogen stores can be increased by 50-100%.
Protein
- Protein has an important role especially in protecting the body from external microbes and repairing worn-out tissues and exercise-related muscle damage. The amount of protein required by the athlete; It varies according to gender, condition level, type of exercise, body weight, total daily energy requirement and carbohydrate consumption.
- During exercise, especially when carbohydrate stores are very low, protein is also used as an energy source, which is important for athletes due to its duties. Protein sources do not provide energy to the body in short-term exercises. It only contributes 2-5% energy in long-term exercises.
- Protein needs of high-level exercisers and athletes are approximately 1.5-2 times higher than inactive individuals. According to body weight; The recommended amount for endurance athletes is 1.2-1.4 g/kg per day, and the recommended amount for strength athletes is 1.6-1.7 g/kg.
- Protein needs can be met from animal products such as milk and dairy products, meat, eggs, fish, chicken, and legumes.
While the daily protein requirement of a normal person who does not do sports is 0.8-1 g/kg/day, it is calculated as 1.2-1.8 g/kg/day for athletes. It is recommended that people who are new to sports increase their protein intake for the first 3-4 weeks to increase their muscle mass. By using only protein, muscle mass does not increase, training is of great importance. Unnecessarily excessive protein intake tires the liver and kidney, causes calcium loss and causes dehydration. 12-15% of daily calorie needs should be provided from proteins.
Oil
- In order for the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K to be taken into the body and to avoid digestive problems, fat source foods should be taken into the body.
- Fats can be used as an energy source for the body, especially in long-term aerobics. That’s why even the weakest athlete must have fat in their body.
- 20-25% of the daily energy in athletes should come from fat.
- Since excessive fat consumption may suppress carbohydrate intake, these values should not be exceeded in the sports diet program and sports nutrition scheme.
- Studies have found that fat intake below 15% of daily energy can negatively affect performance. Therefore, very high and low oil consumption should be avoided.
If fat consumption is increased and carbohydrate consumption is reduced, performance will be adversely affected. Athletes should avoid consuming excessively fatty foods (mayonnaise, cream, butter, chips), prefer liquid oils instead of solid fats, and use low-fat dairy products.
Vitamins
- Especially the importance of B group vitamins is more in athletes.
- B group vitamins such as thiamine, riboflavin, niacin and biotin help build energy during exercise.
- Folic acid and vitamin B12 are important for protein synthesis, tissue building and repair.
A healthy diet contains enough vitamins and minerals. While fat-soluble vitamins are vitamins A, D, E, and K, vitamins of group B and C are water-soluble vitamins. Each vitamin has very important functions in the body. Some water-soluble vitamins are necessary for the formation of energy during sports, while others help the oxygen transport by taking part in the structure of red blood cells. Vitamins are also essential for protein synthesis and tissue repair. Therefore, vitamins are very important for athletes. An athlete with a sufficient and balanced diet does not need to take external vitamins. Taking too many vitamins does not increase performance. While excess water-soluble vitamins are excreted in the urine, excess of fat-soluble vitamins can lead to vitamin excess called “hypervitaminosis”.
Minerals
- Mineral resources are effective in nerve conduction, muscle contraction and oxygen transport in athletes. The most important minerals for athletes are calcium and iron.
- Calcium is involved in controlling blood coagulation, nerve conduction and heart rate. Milk, yoghurt, cheese, oilseeds, legumes and green leafy vegetables are among the calcium source foods.
- Iron mineral is responsible for carrying oxygen to the muscles. Oxygen is needed during energy production. If there is insufficient iron mineral in the blood, the athlete can get tired quickly. Therefore, iron mineral is important for athletes. Liver, red meat, green leafy vegetables, molasses, dried fruits and legumes are among the foods that contain iron mineral.
- If the athlete is a vegan, has a bad nutritional habit, is pregnant, has anemia, has menstrual bleeding, and consumes too much smoking and alcohol, vitamin and mineral supplements can be used.
Liquid
- Water constitutes 55-70% of the weight, depending on the amount of muscle in the body. It has been observed that the performance of athletes who maintain their body fluid balance during exercise is also higher.
- In the event of fluid insufficiency, ie dehydration, performance is also negatively affected.
- In order to maintain body fluid balance, athletes should consume 400-600 ml of fluid 2-3 hours before exercise; It is recommended that they drink 150-350 ml of water at the beginning of the exercise and every 15-20 minutes afterwards.
- This liquid can be water or a sports drink. Sports drinks contain some carbohydrates, as well as minerals lost through sweat. Preferred sports drinks should contain 4-8% carbohydrates and these drinks should be consumed over 1 hour of exercise.
Nutrition Rules Before and After Sports
The purpose of nutrition before sports is to eliminate hunger, provide energy and provide fluid needs. Many athletes prefer to eat 2-4 hours before sports. Some athletes consume carbohydrate foods 60 minutes before sports. It has been observed that performance increases if the carbohydrate content is high in the diet before sports. Athletes should under no circumstances start sports hungry. Foods that have not been tried before should not be eaten before the sport. The pre-workout meal should be high in carbohydrates, moderate in protein and low in fat. Adequate fluid is included in this meal. Foods that are difficult to digest before sports should not be consumed. It is necessary to avoid raw vegetables and fruits and dried legumes. Gas-producing foods should also not be consumed.
If the sport will take too long, the athlete can consume something with carbohydrates in the second hour of the sport. At the end of the exercise, it should not be forgotten that getting enough carbohydrates and protein is important for recovery.
What Should We Eat for Fast Muscle Development?
The most important nutrients that provide muscle growth are amino acids and protein sources. Protein sources are important for muscle development in the first 3-4 weeks of starting sports. The protein sources required in this process are naturally; should be met with nutrients. The increase in muscle growth occurs when athlete diet and exercise are done together.
In order to ensure muscle development, foods containing high quality protein should be consumed in the sports nutrition program. Lean meat, fish, poultry, milk, yogurt, eggs, and legumes are foods rich in protein. Egg, which is one of the most important foods after breast milk, is a quality source of protein and should be consumed at breakfast.
Excessive protein consumption does not mean that there will be an increase in muscle mass at the same rate. It should be kept in mind that high protein consumption can cause damage to the kidney and liver.
Should Athletes Consume Ergogenic Products?
Today, athletes, whether at the amateur or professional level, prefer supportive products to compensate for their lost energy or to support muscle growth. There are many ergogenic products on the market such as athletic products, creatine, protein powder, ginseng and vitamins. Before these products are consumed, attention should be paid to many features such as age, gender, sports branch of interest, whether the athlete is an amateur or a professional.
Products should be evaluated in terms of their health and performance effects before consumption. In order for ergogenic products to have a positive effect on performance increase, the right product should be selected and used at the right time and amount. Therefore, professional help should be taken. A doctor and dietician should be consulted before using the products in order to avoid adverse health effects.
How Right Is Using Protein Powder for Muscle Building?
Body building; It is the method of developing body muscles, which is becoming increasingly common in the world, especially preferred by men. These individuals usually have the highest levels of muscle mass; They aim to keep the fat percentage at the minimum level. The frequency of use of commercial products used for this purpose has increased worldwide.
The most preferred of these commercial products are protein powders, creatine and steroid hormones. Before using these products that aim to increase muscle mass, one should have information about their effects on the body. The best known product among the people and especially preferred by weight trainers are protein powders. By increasing the amount of protein taken with diet, protein powders may not be needed.
However, in some cases, especially during heavy training periods, the amount of protein needed may not be met by foods and these products are needed. The protein that needs attention should be met with foods first; If insufficient is to try these products. Even during intense training periods, a maximum of 2 g / kg of protein per day is required.
4 Nutrition Tips for Athletes
1) Increase your carbohydrate consumption
Carbohydrate is the body’s main source of energy and the energy required during training is supplied from glycogen stores. Glycogen storages should be sufficient in order for the performance to be higher, to prevent fatigue quickly and to prolong the endurance period of the athlete. With the sports diet, an average of 60-65% of the daily energy should come from carbohydrate sources. Especially in sports diet and sports nutrition program; complex carbohydrate sources, brown bread varieties, whole wheat pasta, bulgur pilaf, legumes and vegetables can be preferred.
2) Eat 3-4 hours before training
Carbohydrate-based foods such as pasta, vegetables, bread and fruit can be added to meals before training to maximize endurance and performance. Before training, foods that cause gas and indigestion such as cabbage, radish, cauliflower and dry beans should not be consumed. A food that has not been consumed before should not be tried before training.
3) get enough protein
Excessive protein intake can cause serious damage, especially to the kidneys. Therefore, a sufficient amount of protein suitable for body weight and gender should be calculated and consumed, especially in sports nutrition and athlete diet program. Protein sources such as red meat, chicken meat, legumes, eggs and milk should be preferred instead of supplementary products. It would be more ideal to choose those with fat-free or reduced fat of these foods.
4) Increase fluid consumption
Adequate fluid intake is important to avoid dehydration problems and to replace electrolytes lost through sweating. Insufficient fluid consumption can be understood from the color of the urine. Pale yellow urine indicates sufficient fluid intake; Bright yellow and dark urine is an indicator of insufficient fluid consumption. At the same time, a weight loss of 1.5-2 kg during the day is an indication of fluid decrease and insufficient amount of fluid in the body. With a sports diet, care should be taken to drink 400-600 ml of liquid 2-3 hours before exercise.
Example Athlete Diet and Sports Nutrition Program
The sports diet list prepared is an average of 2200 calories. The portions and food types may differ according to the physical characteristics of the person. The list below is a sample athlete diet list nutrition program. It is recommended that you consult a Dietitian for personalized diet lists.
In the morning:
- 2 glasses of water
Breakfast:
- Mushroom / curd omelet made with 1 whole egg + 2 egg whites
- 2-3 slices of whole wheat bread
- 50 g low-fat feta cheese
- 5-6 olives
Snack:
- 1 portion fruit + 15 raw almonds or hazelnuts
Noon:
- Salad made with 200g grilled chicken or boiled chicken
- 1 bowl of yogurt
- 2-3 slices of whole wheat bread
Snack:
- 200 ml milk or kefir + 2 dried figs
Evening:
- 150 g grilled lean beef or meatballs
- Grilled vegetables or 1 serving of olive oil vegetable meal
- 1 serving whole wheat pasta
Night:
- 200 ml light milk