You’ve probably heard that drinking coffee before a workout can improve performance. But does that same cup of coffee help you burn more fat after your workout ends? The answer lies in a physiological process called EPOC—Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption—commonly referred to as the “afterburn effect.” In this article, we’ll explore what EPOC is, how […]
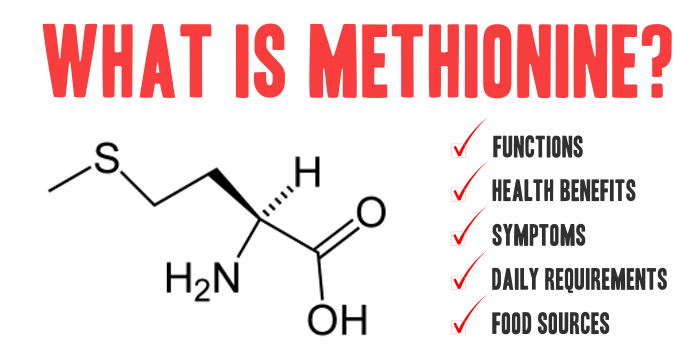
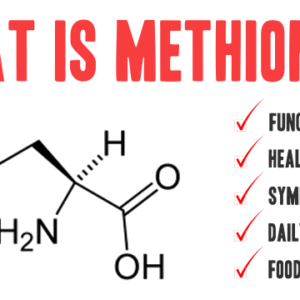
What Is Methionine? Methionine is one of the nine essential amino acids—nutrients the body cannot produce on its own and must obtain from food. It is a sulfur-containing amino acid, playing a foundational role in protein synthesis, methylation, and cellular detoxification processes. Methionine is a precursor to cysteine, glutathione (the body’s master antioxidant), and important […]
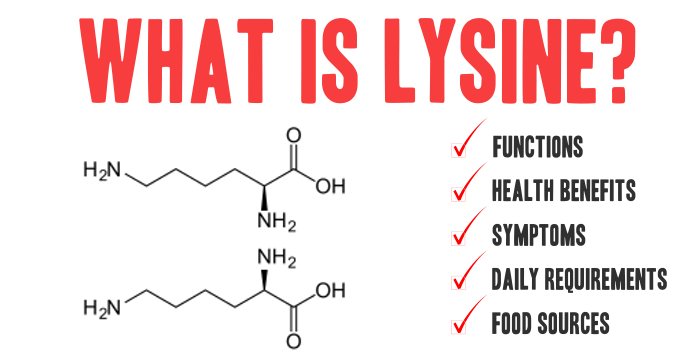
What Is Lysine? Lysine (L-lysine) is one of the nine essential amino acids—nutrients that the human body cannot produce and must obtain through dietary sources. It is a basic (positively charged) amino acid involved in protein synthesis, tissue repair, collagen formation, and calcium absorption. Unlike branched-chain amino acids, lysine plays a central role in immunity, […]
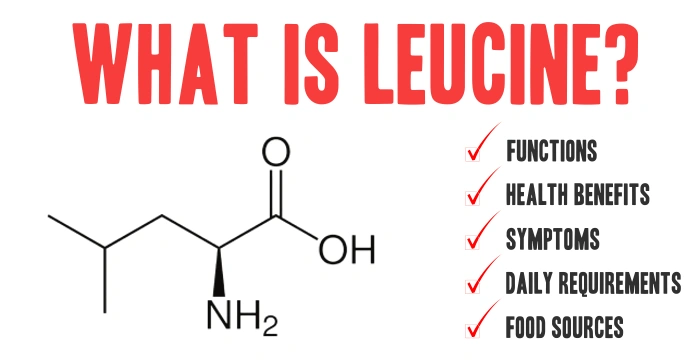
What Is Leucine? Leucine is one of the nine essential amino acids that the human body cannot produce on its own. It must be obtained from food or supplementation. It is also one of the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), alongside isoleucine and valine, known for their crucial roles in muscle metabolism. Among the BCAAs, […]
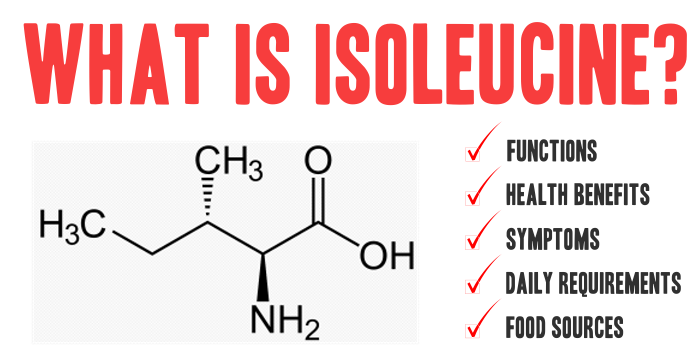
What Is Isoleucine? Isoleucine is one of the nine essential amino acids that the human body cannot synthesize and must be obtained through diet. It belongs to the group of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), along with leucine and valine, and plays a central role in muscle metabolism, energy production, immune regulation, and hemoglobin synthesis. Unlike […]
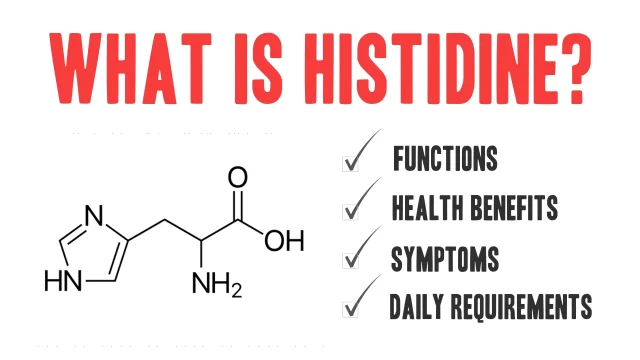
What Is Histidine? Histidine is one of the nine essential amino acids, meaning it cannot be synthesized by the human body and must be obtained through diet. It plays a vital role in multiple physiological processes, including immune response, tissue repair, growth, and neurotransmitter regulation. Although often overlooked compared to more well-known amino acids like […]