Contents
- Anatomy of the Quadriceps
- Training Frequency and Volume for Quad Development
- Compound Exercises for Quadriceps Mass
- Isolation Exercises for Bigger Quads
- Progressive Overload Techniques for Quad Training
- Quad Workout Routines
- Incorporating Mobility and Flexibility for Quad Workouts
- The Importance of Nutrition in Building Massive Quads
When it comes to leg development, the quadriceps are often in the spotlight. These powerful muscles, located at the front of your thighs, play a crucial role in various leg movements, from walking and running to squatting and jumping. Building massive quadriceps requires more than just lifting weights; it’s a holistic journey that encompasses a deep understanding of anatomy, nutrition, training techniques, and quadriceps exercises. Let’s begin with a detailed exploration of the anatomy of the quadriceps, the foundation of your leg development.
Anatomy of the Quadriceps
The quadriceps, often referred to as the quads, is a group of four large muscles located in the front of the thigh. These muscles are essential for various leg movements and play a significant role in activities such as walking, running, jumping, and squatting. Let’s take a closer look at the four primary muscles that make up this group and how they function in various leg movements:
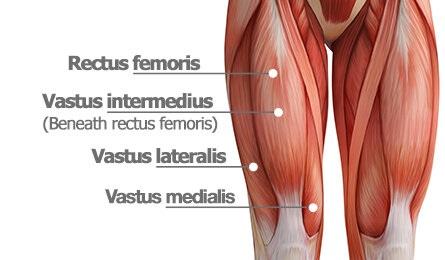
- Rectus Femoris
- Vastus Intermedius
- Vastus Lateralis
- Vastus Medialis
Additionally, the tensor vastus intermedius (TVI) is a newly recognized component of the quadriceps femoris group. Although not yet widely included in all anatomy textbooks, emerging anatomical and imaging studies support its classification as a separate muscle belly within the anterior thigh.
The quadriceps muscles are responsible for several crucial functions in leg movements:
- Knee Extension: All four quadriceps muscles work together to extend the knee joint, allowing you to straighten your leg.
- Hip Flexion: The rectus femoris, in particular, is involved in lifting the thigh toward the torso, a movement known as hip flexion.
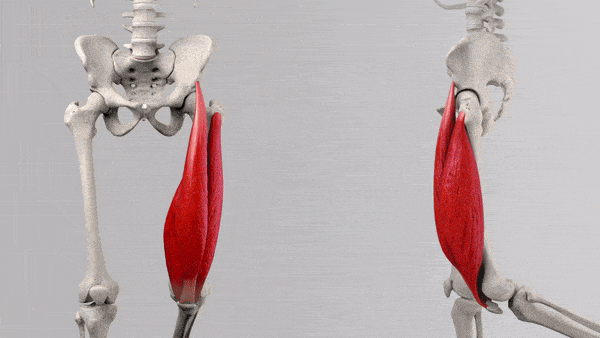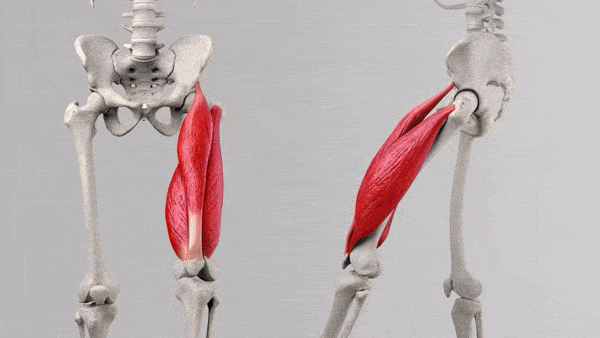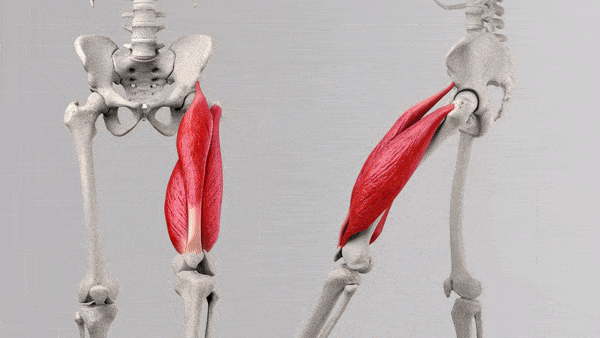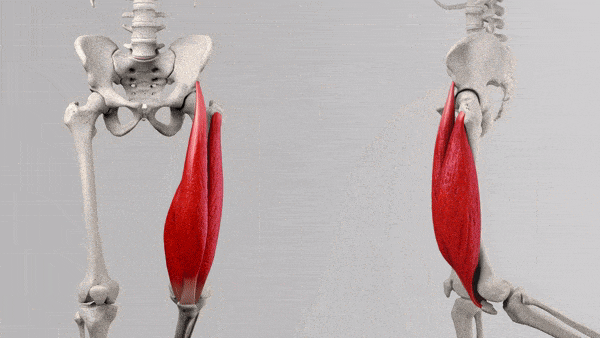
These four muscles work in harmony to control various leg movements, from everyday activities like walking and climbing stairs to more intense exercises like squats, lunges, and leg presses. Understanding the specific roles of each muscle within the quadriceps can help you tailor your training program to target different areas of your quads and achieve balanced, well-defined leg muscles.
Training Frequency and Volume for Quad Development
The right balance between training frequency and volume ensures that you stimulate muscle growth without overtraining. Here’s a guide to help you determine how often you should train your quads and the ideal training volume:
Training Frequency:
- Once a Week: Training your quads once a week can be effective, especially for beginners or individuals who are combining quad training with other leg muscle groups (hamstrings, glutes, etc.). This frequency allows you to create a foundation that will encourage growth and strength.
- Twice a Week: Training your quads twice a week is a common approach for intermediate to advanced lifters. Research consistently demonstrates that training muscle groups twice a week yields significantly greater gains in both muscle size and strength compared to training them only once a week. This approach allows for a higher training frequency, which can lead to more consistent muscle hypertrophy.
- More than Twice a Week: Some advanced bodybuilders or athletes may do quadriceps training three times a week. However, this approach requires careful planning, as it must include adequate recovery time between sessions to prevent overtraining.
Training Volume:
- Strength and Power (Low Volume): Low-volume quad workouts typically involve 3-4 sets per exercise with fewer repetitions (3-6) using heavier weights. This approach is suitable for building strength and power, as it allows for more significant recovery between sets.
- Muscle Size (Moderate Volume): A moderate-volume approach often consists of 3-5 sets per exercise with a moderate number of repetitions (8-12). This provides a balance between building strength and muscle size. This approach is effective for hypertrophy and can be suitable for individuals aiming to build massive quads.
- Muscular Endurance (High Volume): High-volume workouts include 6 or more sets per exercise with higher repetitions (15-20 or more). This approach is effective for muscular endurance and may be suitable for athletes aiming for long-term activity.
Frequency and Volume Selection:
- Beginners: Your training frequency and volume should align with your fitness level, recovery capacity, and goals. If you’re new to weight training or have limited experience, it’s a good idea to start with a moderate volume and gradually increase it as your strength and endurance improve.
- Intermediate/Advanced: More experienced individuals can experiment with different volume levels based on their specific goals and how their body responds to different training loads.
- Recovery: Pay attention to how your body responds to training frequency and volume. Ensure that you allow sufficient time for recovery between quad workouts, especially if you’re training frequently. Adequate sleep, nutrition, and active recovery techniques are essential.
The key is to find a balance that challenges your muscles, aligns with your goals, and allows for proper recovery. Experiment with different frequencies and volumes, and don’t be afraid to adjust your training regimen based on your progress and how your body responds.
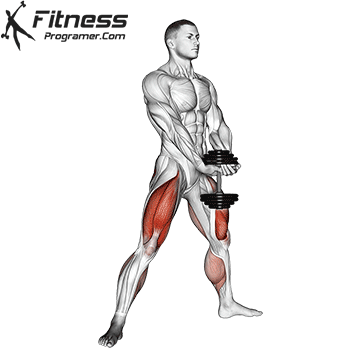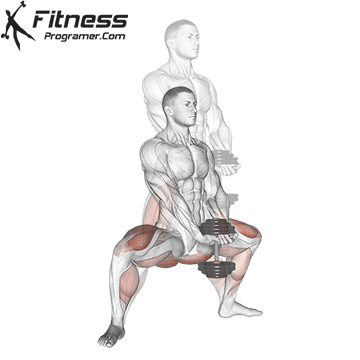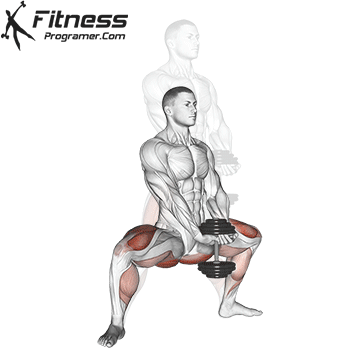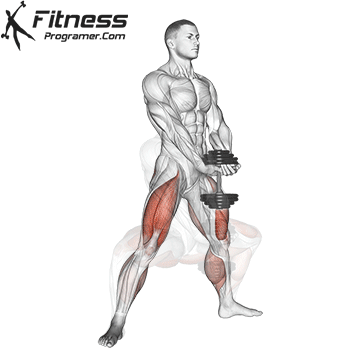
Compound Exercises for Quadriceps Mass
Building massive quads requires the incorporation of compound exercises into your leg workout routine. These multi-joint movements engage multiple muscle groups, including the quadriceps, and are highly effective for stimulating muscle growth and strength.
Isolation Exercises for Bigger Quads
While compound exercises are essential for overall quad development, isolation exercises play a crucial role in fine-tuning your quad muscles and achieving the chiseled “Quadzilla” look. These exercises specifically target the quadriceps and help enhance their definition and size. Here are some key isolation exercises you should consider incorporating into your leg routine:
Leg Presses:
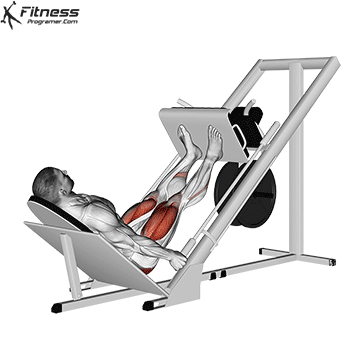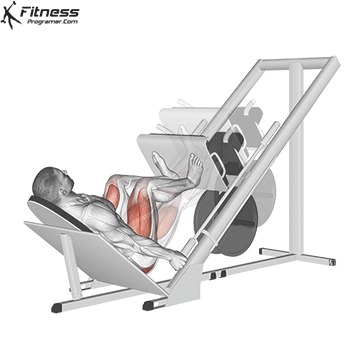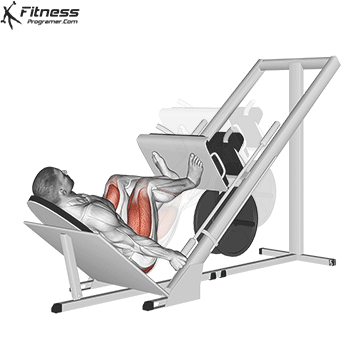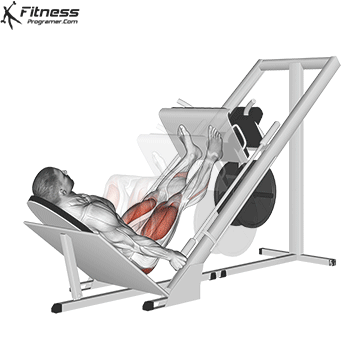
Exercise Description: Leg presses involve pushing a weighted platform with your legs while sitting on a machine. The movement primarily consists of extending your knees.
Leg presses mainly target the vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. They provide a great way to isolate and strengthen the quadriceps.
Leg Extensions:
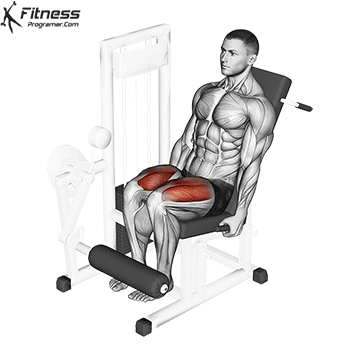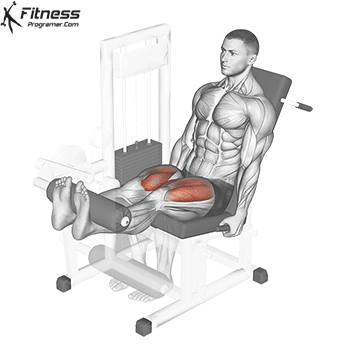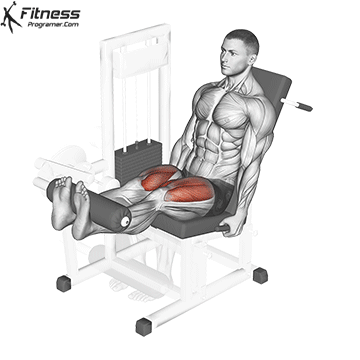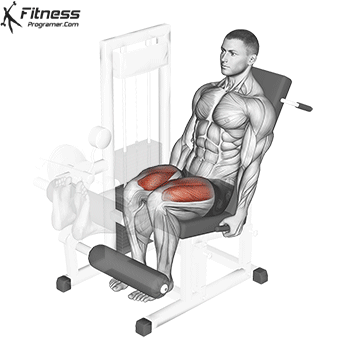
Exercise Description: Leg extensions are performed on a specialized machine that allows you to extend your legs against resistance. You sit on the machine with your knees bent at 90 degrees and extend your legs until they’re straight.
Leg extensions primarily isolate and target the quadriceps. This exercise provides a direct focus on the rectus femoris and the vastus muscles, helping to enhance quad definition and separation.
Single-Leg Extensions:
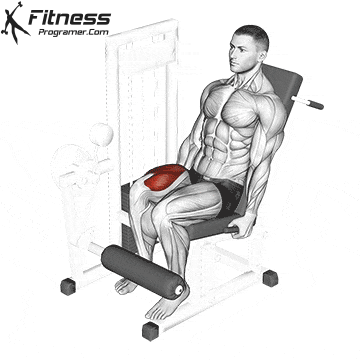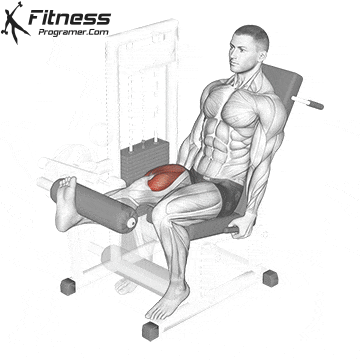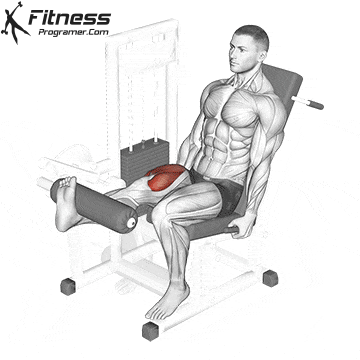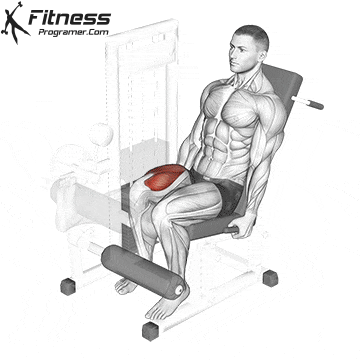
Exercise Description: This is a variation of leg extensions in which you work one leg at a time. Single-leg extensions provide a more concentrated focus on each quadriceps muscle, helping to correct imbalances and improve definition.
Sissy Squats:
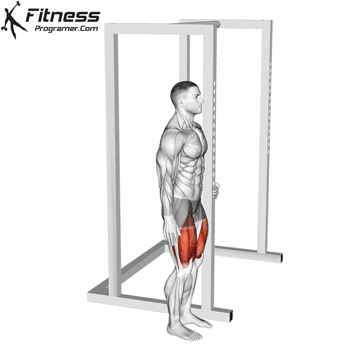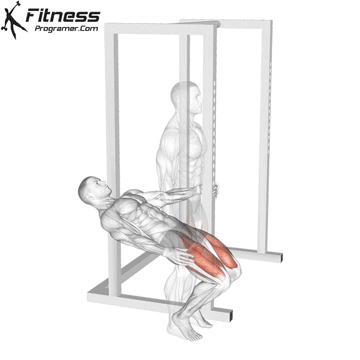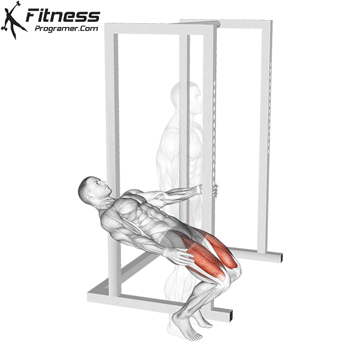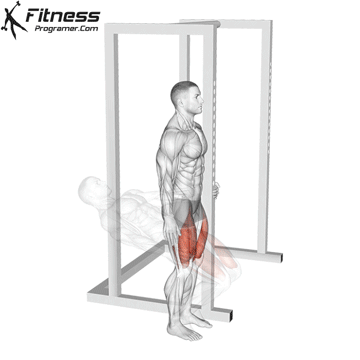
Exercise Description: They involve leaning back and then extending your knees to perform the exercise.
Sissy squats are a unique isolation exercise that targets the quads intensely, focusing on both the rectus femoris and vastus muscles. Pay attention to balance and stability during sissy squats, as they can be challenging. Perform them in a controlled manner to avoid excessive strain on the knee
Isometric Quad Contractions:

Exercise Description: This exercise involves static holds or isometric contractions of the quads. Isometric contractions are fantastic for building endurance and enhancing muscle definition in the quads. You can perform wall sits, leg extension machine holds, or any other static quad contraction.
Progressive Overload Techniques for Quad Training
Progressive overload is a fundamental principle in strength training that is essential for building massive quads. It involves consistently challenging your muscles with increased resistance or intensity over time to promote growth and strength. To apply this principle effectively to your quad training, consider the following techniques:
- Increase Weight:
- One of the most straightforward ways to apply progressive overload is to increase the weight you lift in your quad exercises. Gradually add more weight to the barbell, dumbbells, or machines you use for squats, leg presses, and other exercises.
- For example, if you were squatting 200 pounds for 3 sets of 10 reps, gradually work towards squatting 210, 220, and so on. The increased resistance will stimulate muscle growth.
- Add Repetitions:
- Increasing the number of repetitions (reps) is another way to progressively overload your quads. If you’ve been performing 3 sets of 10 reps, try increasing it to 12 or 15 reps per set.
- As you become more proficient at the exercises, adding extra reps can help you push your muscles to new limits.
- Include Additional Sets:
- Incorporating more sets into your workouts is a valid way to progressively overload your quads. For instance, if you’ve been doing 3 sets of squats, you can increase it to 4 or 5 sets.
- This extra volume can increase the overall training stimulus on your quads, encouraging growth.
- Shorten Rest Periods:
- Reducing the rest intervals between sets can elevate the intensity of your workouts, stimulating muscle growth. Shorter rest periods force your muscles to work harder and adapt to the increased demand.
- Try cutting your rest periods by 10-15 seconds between sets and gradually decrease them further as your conditioning improves.
- Use Forced Reps and Drop Sets:
- Forced reps involve having a training partner assist you in completing a few additional reps when you can’t lift the weight on your own. This is an advanced technique that can help push your muscles to failure and encourage growth.
- Drop sets involve reducing the weight after reaching failure and continuing the exercise. This intensifies the workout and challenges your muscles in a different way.
- Vary Exercises and Techniques:
- Regularly change your exercises and training techniques to keep your quads adapting. Variations like front squats, lunges, or single-leg exercises can target your muscles differently.
- Techniques like pause reps, partial reps, and slow negatives can add variety and challenge your quads in unique ways.
Quad Workout Routines
Here are sample quad-focused workout routines for various fitness levels, including beginners, intermediate, and advanced lifters. These routines include both compound and isolation exercises to help you build massive quads effectively. Remember to start each session with a warm-up.
Warm-Up Routine:
- Start your leg workouts with a dynamic warm-up that includes leg swings, hip circles, and bodyweight squats. These movements improve blood flow, increase core body temperature, and prepare your muscles for exercise.
Beginner Quad Workout:
Goblet Squats:
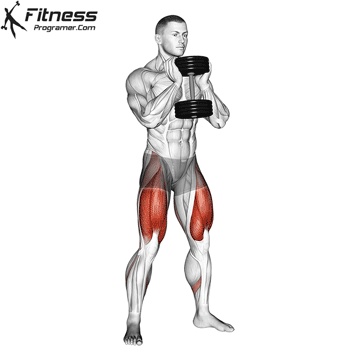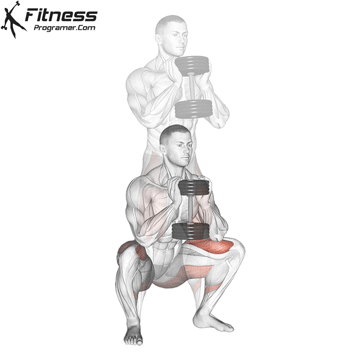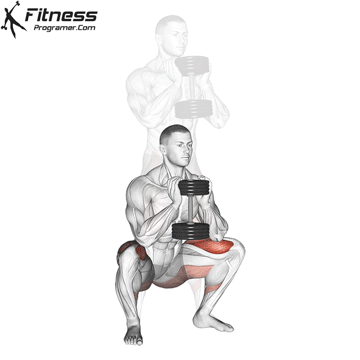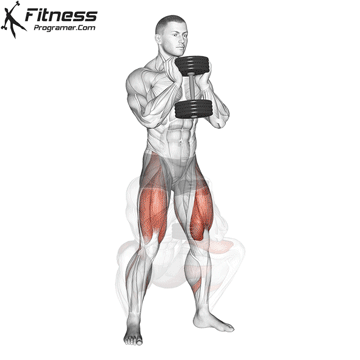
- 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Rest: 1 minutes
Leg Press:

- 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Rest: 1 minutes
Leg Extensions:

- 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Rest: 1 minutes
Wall Sits:

- 2 sets for 30 seconds
- Rest: 1 minute between sets
Intermediate Quad Workout:
Barbell Hack Squats:
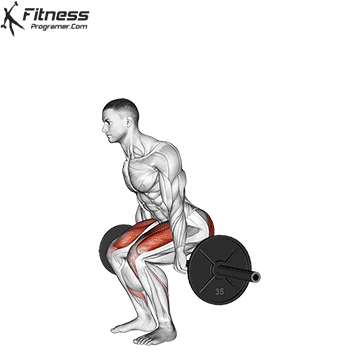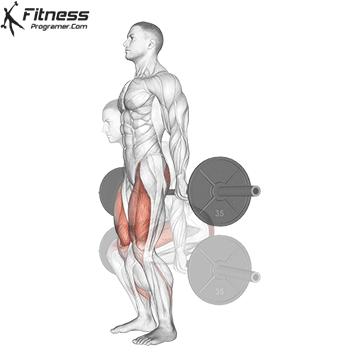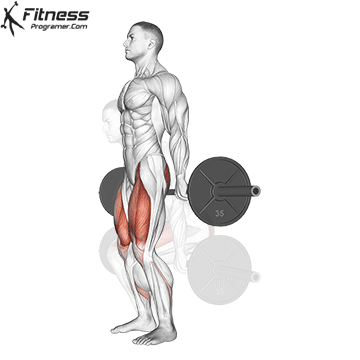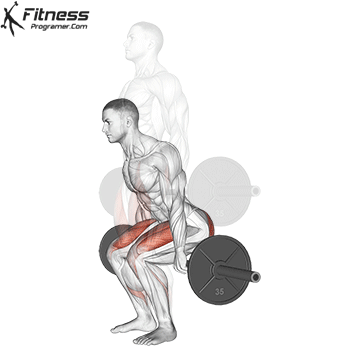
- 4 sets of 8-10 reps
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
Dumbbell Walking Lunges:
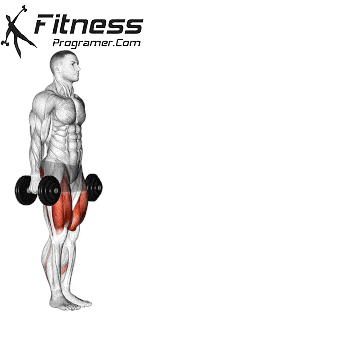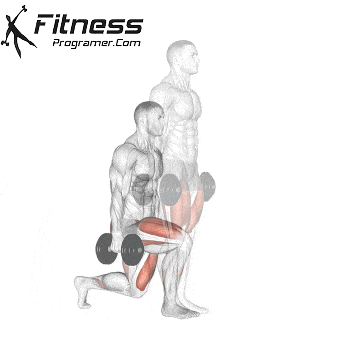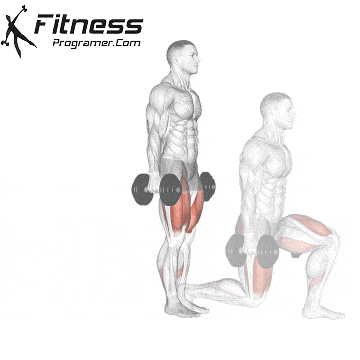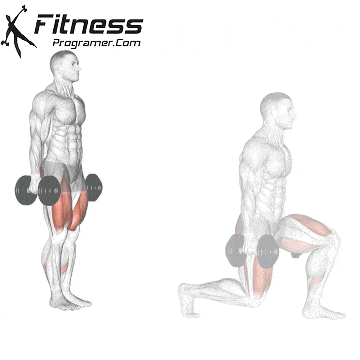
- 3 sets of 12 steps per leg
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
Leg Press:

- 4 sets of 10-12 reps
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
Leg Extensions:

- 3 sets of 12 reps per leg
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
Advanced Quad Workout:
1. Barbell Squats:
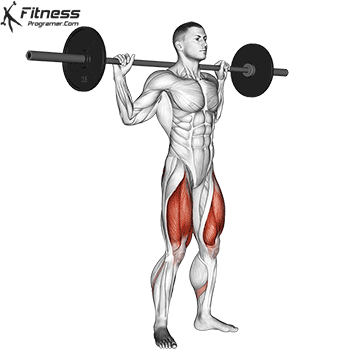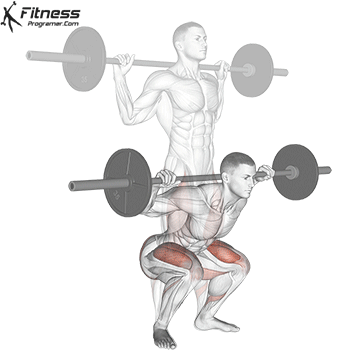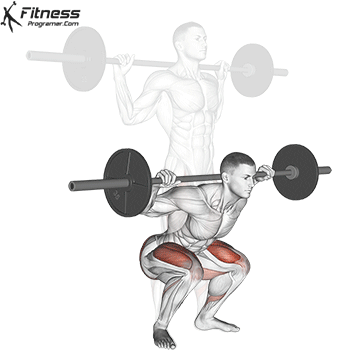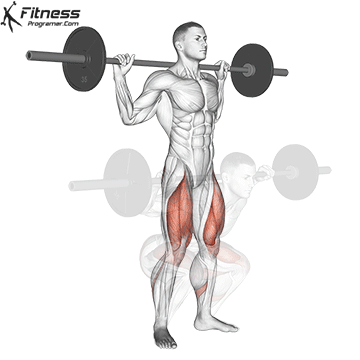
- 4 sets of 10-12 reps
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
2. Dumbbell Bulgarian Split Squats:
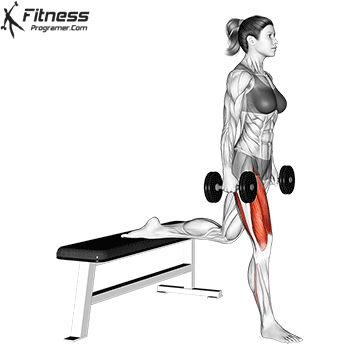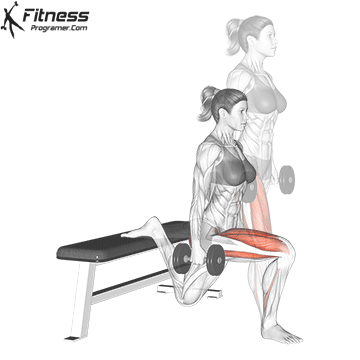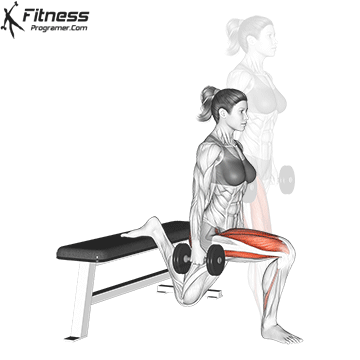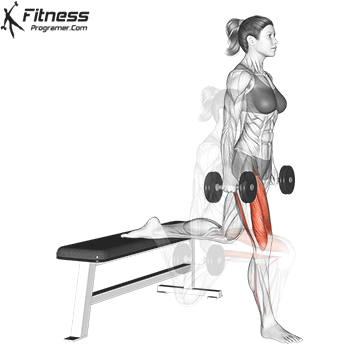
- 3 sets of 8-10 reps per leg
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
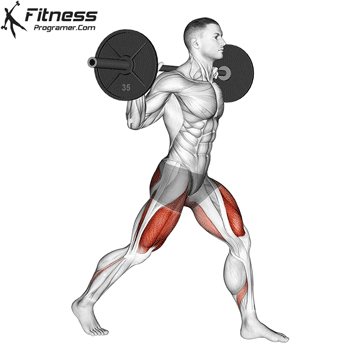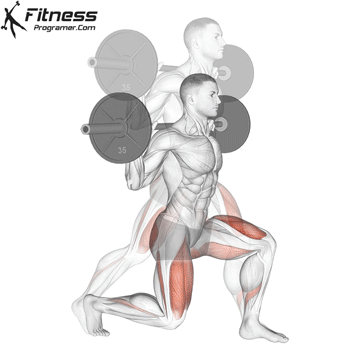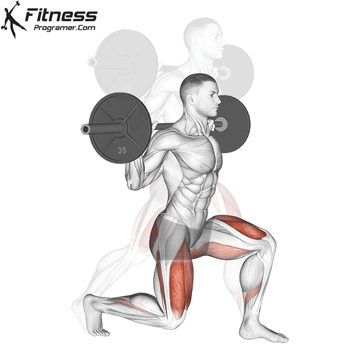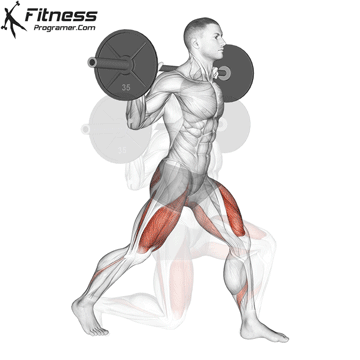
3. Barbell Side Lunge:
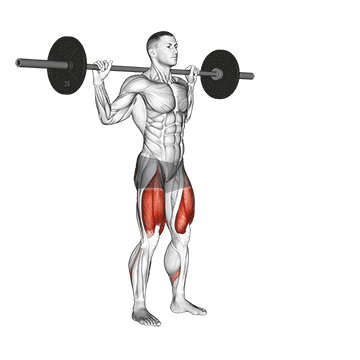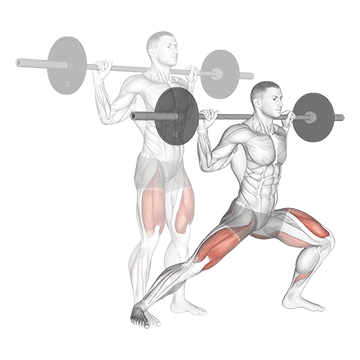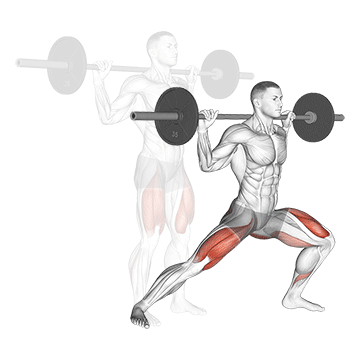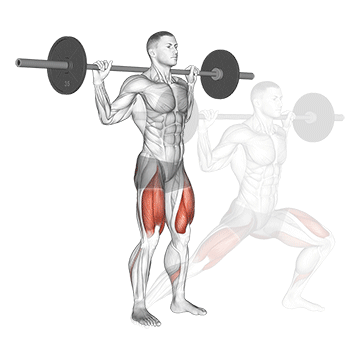
- 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
4. Leg Extensions (with drop sets):

- 4 sets of 12 reps, followed by a drop set (reduce the weight and continue)
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
These quad-focused workout routines are designed to help you develop massive quads, but it’s important to balance your leg training with exercises for other lower body muscle groups to achieve overall leg development and avoid muscle imbalances. Adjust the routines to your fitness level and specific goals, and remember that consistency is key to seeing progress.
A comprehensive leg workout
1. Barbell Squats:

- 4 sets of 10-12 reps
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
2. Dumbbell Bulgarian Split Squats:

- 3 sets of 8-10 reps per leg
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
3. Romanian Deadlift:
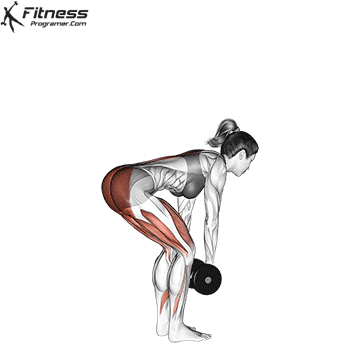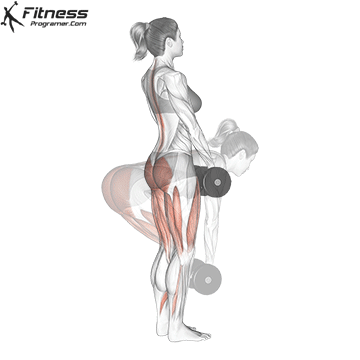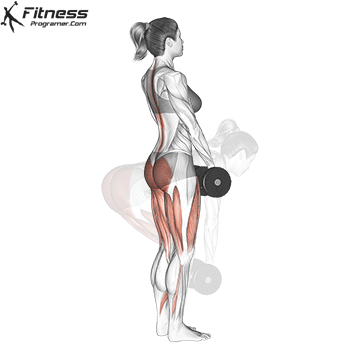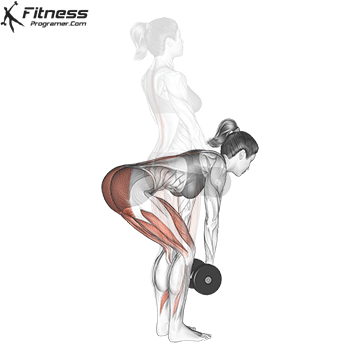
- 4 sets of 10-12 reps
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
4. Leg Curl
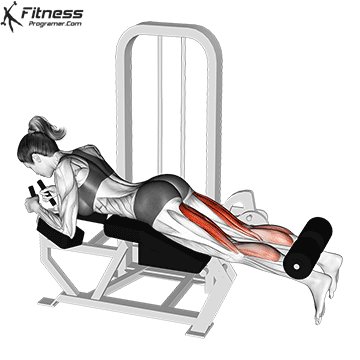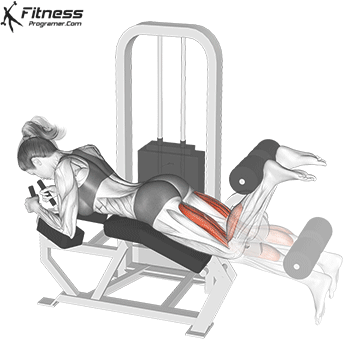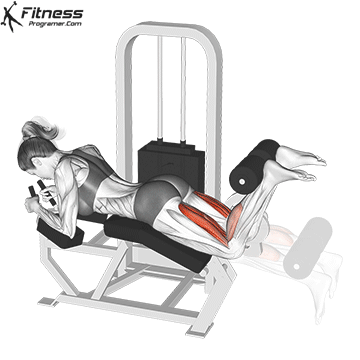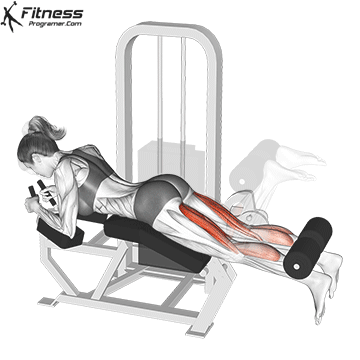
- 3 sets of 12 reps
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
5. Hip Thrust:
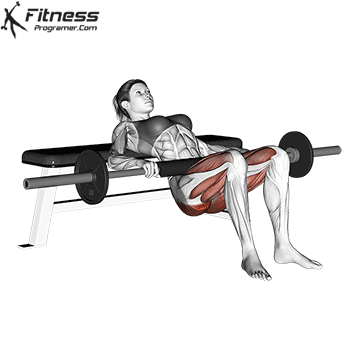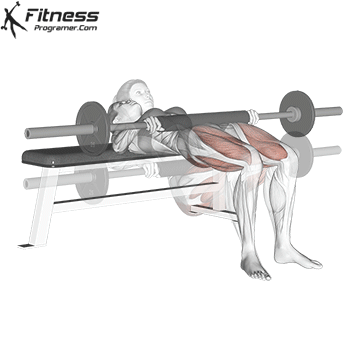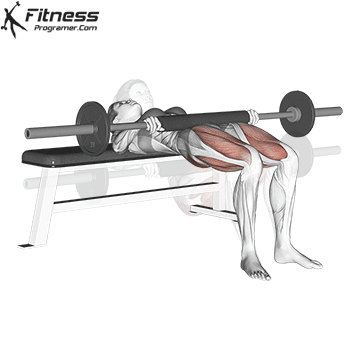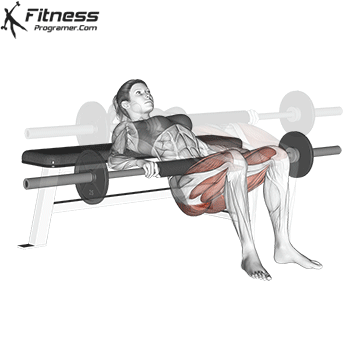
- 4 sets of 12 reps
- Rest: 1-2 minutes
6. Calf Raise:
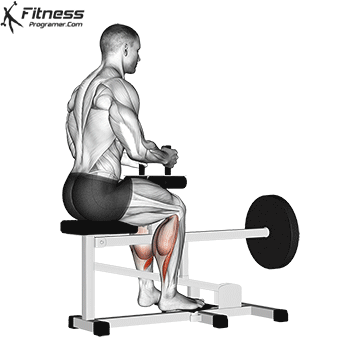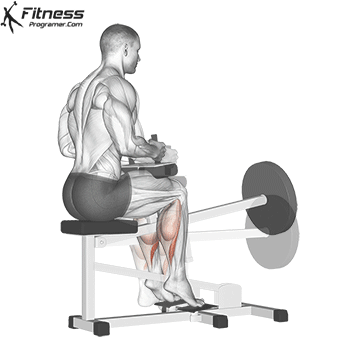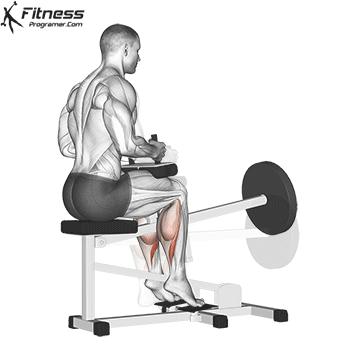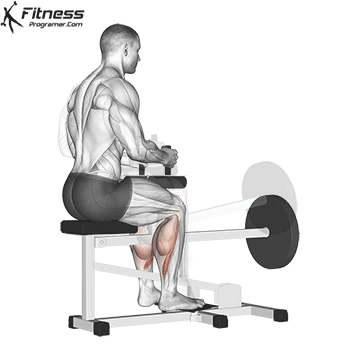
- 4 sets of 10-12 reps
- Rest: 1 minute between sets
Notes:
- Ensure proper warm-up with light cardio and dynamic stretches.
- Use a weight that allows you to complete the desired number of reps with proper form.
- Gradually increase the weight as you progress and your strength improves.
- Maintain good form throughout each exercise to prevent injury.
- Listen to your body and allow sufficient time for recovery between workouts.
Incorporating Mobility and Flexibility for Quad Workouts
Neglecting mobility and flexibility can lead to muscle imbalances, limited mobility, and decreased workout efficiency. After your workout, perform static stretching exercises to improve flexibility. Focus on the quadriceps, hamstrings, calves, and hip flexors. Hold each stretch for 20-30 seconds, breathing deeply and gently easing into the stretch.
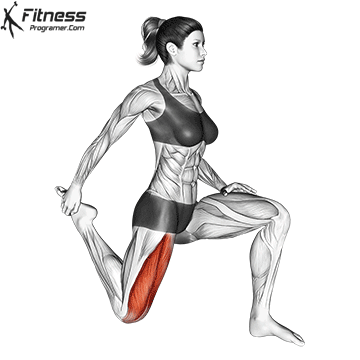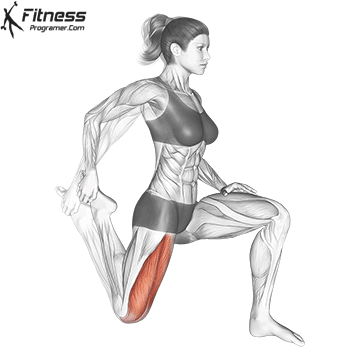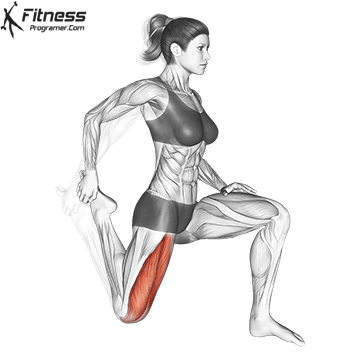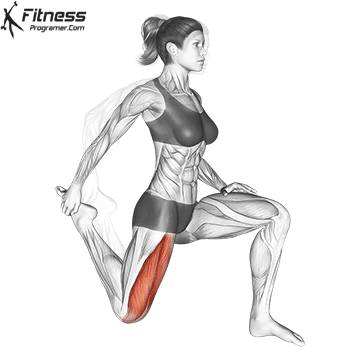
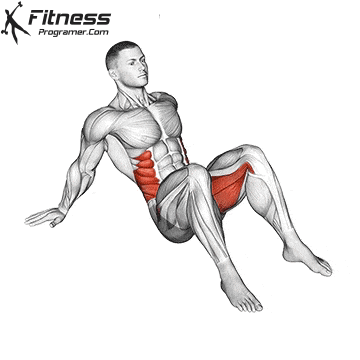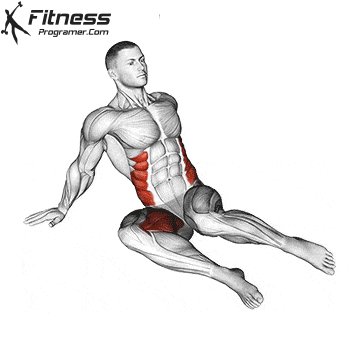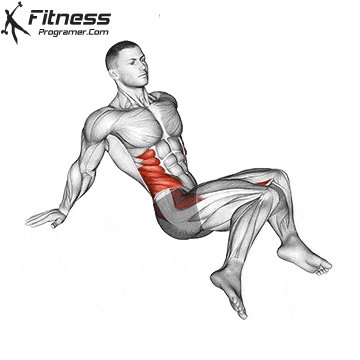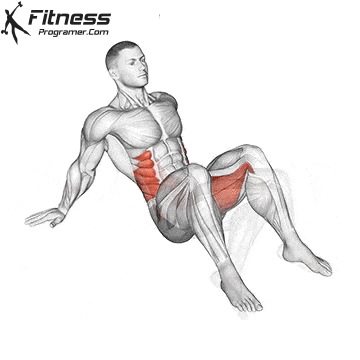
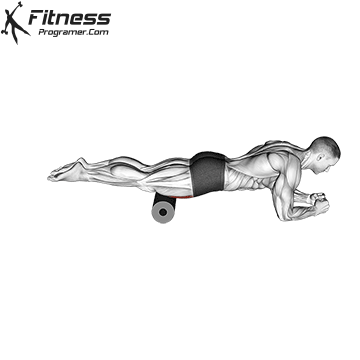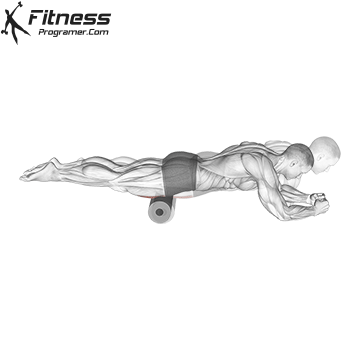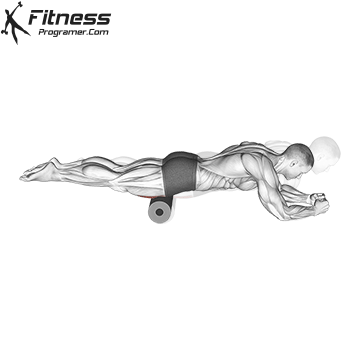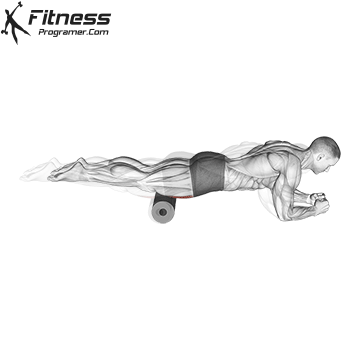
- Mobility Drills: Integrate mobility exercises like leg circles, hip openers, and ankle mobility drills into your warm-up and cool-down routines. These movements can help improve joint mobility and flexibility.
- Foam Rolling and Self-Myofascial Release (SMR): Use a foam roller or lacrosse ball to release tension in your muscles and fascia. This can help alleviate knots, improve circulation, and enhance flexibility.
The Importance of Nutrition in Building Massive Quads
Calorie Surplus:
Building muscle, including your quadriceps, requires a surplus of calories. You need to consume more calories than your body burns to provide the energy necessary for muscle growth.
The daily calorie intake calculator is a powerful tool designed to assist you in making informed decisions about your dietary needs. By taking into account various factors such as your age, weight, activity level, and fitness goals, this calculator provides a detailed and personalized estimation of the number of calories you should aim to consume on a daily basis.
Whether you’re striving to maintain your current weight, lose a few pounds, or build muscle, this calculator offers tailored recommendations to align with your unique objectives and ensure that your nutritional intake supports your desired outcomes.
Protein for Muscle Building:
Protein is the primary macronutrient responsible for muscle repair and growth. To maximize quad development, consume an adequate amount of protein.
Aim for 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram (0.73 to 1.0 grams per pound) of your body weight each day. High-quality protein sources include lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy, and plant-based options like tofu and legumes.
Carbohydrates for Energy:
Carbohydrates provide the energy needed for intense leg workouts. They replenish muscle glycogen stores, supporting your quad training performance.
Focus on complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, vegetables, and fruits to maintain energy levels throughout the day and during your workouts.
Healthy Fats and Micronutrients:
Healthy fats and micronutrients are essential for overall health and function. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in sources like fatty fish and flaxseeds, are particularly valuable.
Ensure your diet is rich in vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D, calcium, magnesium, and iron, which contribute to muscle function and overall well-being.
Hydration:
Staying hydrated is crucial for muscle function and recovery. Dehydration can lead to reduced muscle performance and hinder your quad training progress.
Aim to drink enough water daily, and consider sports drinks or electrolyte replacements during intense workouts to replenish lost electrolytes.
Nutrient Timing:
Timing your meals and nutrient intake around your workouts can optimize muscle growth. Consuming a balanced meal with carbohydrates and protein before and after training can enhance recovery and muscle protein synthesis.
Eating a combination of fast-digesting and slow-digesting carbohydrates can provide immediate energy and sustained recovery.
Supplements:
While it’s best to obtain nutrients from whole foods, supplements can help fill in nutritional gaps. Creatine, branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), and protein shakes are supplements that some individuals find beneficial for muscle growth.
In Summary:
Building massive quadriceps is a multifaceted journey that involves understanding the anatomy, training methodologies, nutrition, and recovery strategies.
Remember, progress takes time and consistency, so be patient, stay committed, and enjoy the process of building powerful and quadriceps. Your success lies in the dedication to your workout goals and the ongoing pursuit of a healthier, more active lifestyle.