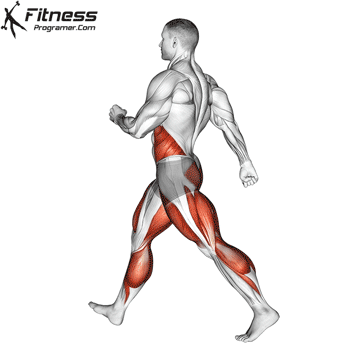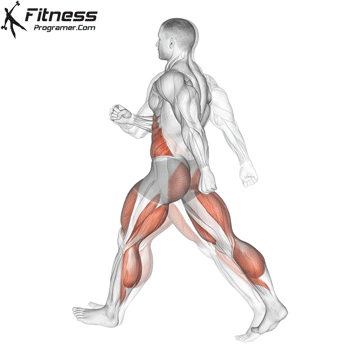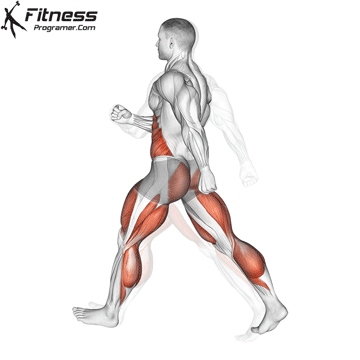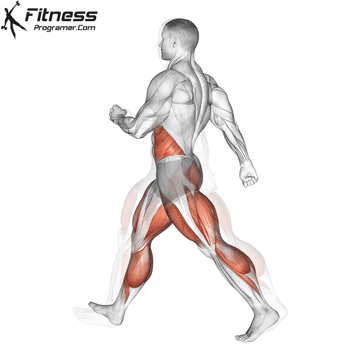
What is Cardio
Cardio is shorthand for cardiovascular exercises. We can express cardio training as exercises that accelerate breathing, increase heart rhythm, and intensely work and strengthen the heart and lungs. Cardio is also considered aerobic exercise, meaning it demands elevated oxygen flow, which causes you to breathe harder. eg; Cycling, jogging, jumping rope, rowing etc. activities such as
An effective cardio workout can take anywhere from 10 minutes to an hour or more depending on your goals and what kind of cardio you’re doing. If you want to design a cardio workout, our site has hundreds of exercises with or without equipment.
Benefits of Cardio
Cardio is a great exercise for those looking to slim down because it helps you burn body fat and lose calories. Performing cardio continually brings many benefits to our health. Aerobic exercises improve physical condition by increasing energy level and resistance capacity.
- Improves lung capacity
- Accelerates weight loss
- Strengthens your heart
- Aids sleep
- Strengthens immune system
- Increases your stamina, fitness and strength
Pairing a cardio workout with weight training could help you build muscle mass while you burn body fat. If your fitness goal is three to four days a week, you can split your workout into two, doing 30 minutes of cardio and 30 minutes of weight training.
Best Cardio Types
There are several types of cardiovascular training that can help you reach your fitness goals. Here are the 5 most common types of cardiovascular training.
1- LISS Cardio (Low Intensity, Long Duration)
Low-intensity steady-state (LISS) exercise refers to aerobic movement done at a low pace. LISS cardio is suitable for beginners as it is easier to do. Think brisk walking, light jogging, easy cycling, or hiking.
LISS cardio is typically performed for 30-60 minutes at a steady pace with limited changes in intensity. When doing LISS cardio, the goal is to keep your heart rate around 40 to 60 percent of your maximum heart rate.
If you’re a beginner, aim to do three LISS sessions per week.
If you’re at an intermediate or advanced level, try to include one or two sessions of LISS and one or two sessions of HIIT cardio per week.
Any movement is better than no movement.
LISS Cardio Exercise Selection
Any kind of physical activity that makes your heart rate go up is considered cardio. So, if an exercise gets your heart rate up for a while, it’s cardio exercise. If you can’t do any of these heart rate-boosting exercise, don’t worry. A few simple cardio exercises that can be done at home without any equipment are:
- Elbow to Knee Twist
- Dead Bug
- Montain Climber
- Run in Place
- Arm Circle
- Jumping Jack
- Bodyweight Sumo Squat
- Bcycle Crunch
Cardio training are essential for a healthy cardiovascular system. They are beneficial to the lungs, bones, muscles and even all organs as well as the heart. If you’re planning to do your cardio workout at home, don’t forget to start slowly to warm your body up.
2- Moderate-intensity Cardio (Medium Intensity, Medium Duration)
This involves aerobic activity done at around 50% to 70% of max HR. A moderate level of training noticeably increases your breathing rate and heart rate. You may sweat, but you are still able to carry on a conversation. You can talk, but you can’t sing. This type of training can be used for fat loss and for increasing aerobic capacity. This is also the next step up from the low intensity cardio.
Moderate Intensity Cardio Exercises
3- HIIT Cardio (High Intensity, Short Duration)
High-intensity interval training (HIIT), is a form of cardio workout performed with short, intense bursts aimed at maximizing performance under conditions where the muscles are deprived of oxygen. While its health benefits are important, HIIT also improves performance in both anaerobic and aerobic activities. A classic and simple example of HIIT is 30 seconds of sprinting, 30 seconds of walking (rest) or 20 seconds of skipping 10 seconds of rest.
With HIIT, your heart rate is generally at 80 to 95 percent of your maximum heart rate for the high-intensity intervals and 40 to 50 percent for the low-intensity intervals.
HIIT cardio is done at a high intensity that helps increase fitness, but adding weight provides extra fat-burning and metabolism-boosting benefits. Pulse-increasing exercises, the concept of metabolic training, are compound exercises that aim to increase metabolic rate with less rest time between exercises to maximize calorie burning during and after training.
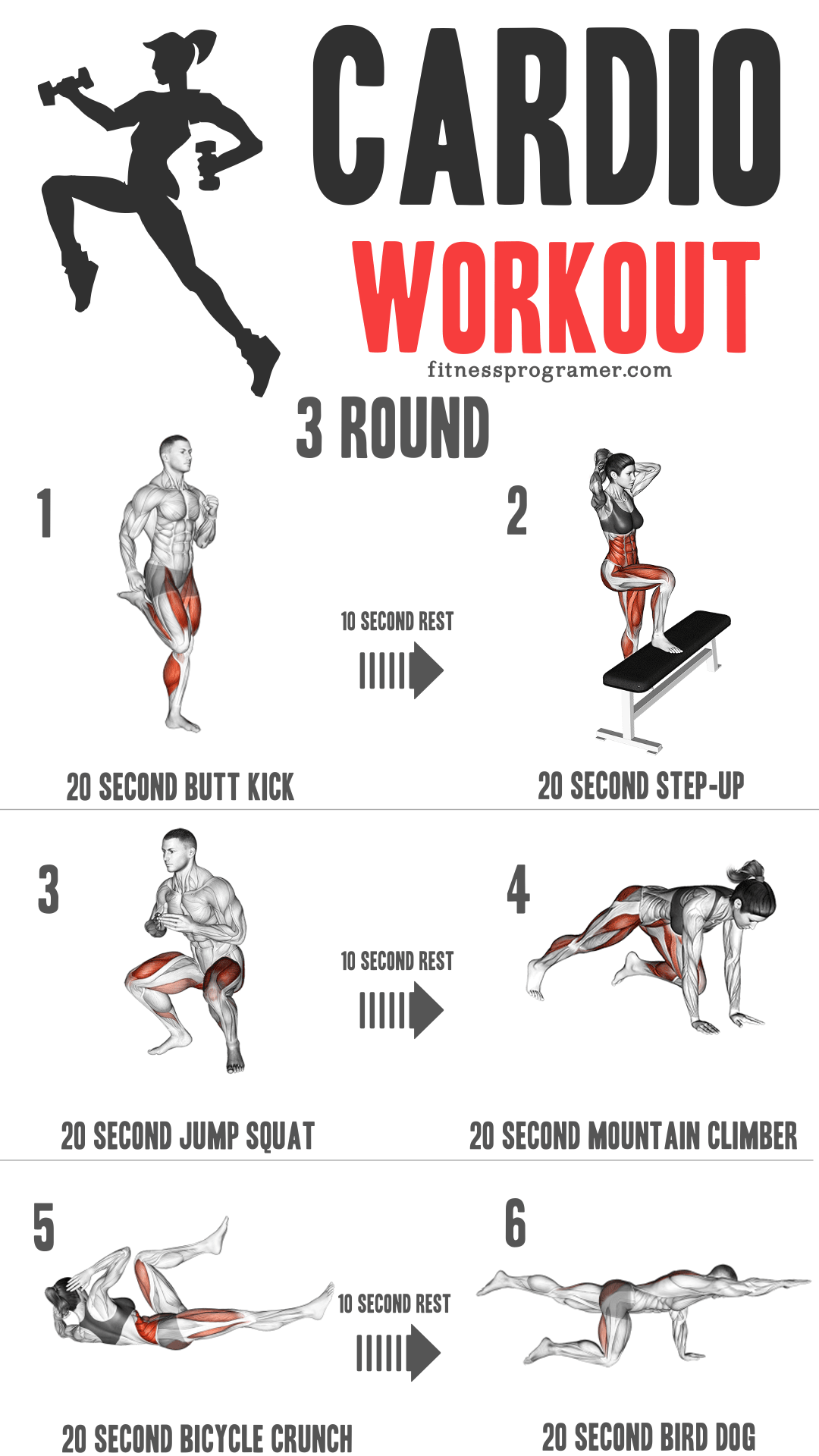
HIIT Workout
20 Sec High knee skips
10 Sec Rest
20 Sec Mountain Climber
10 Sec Res
20 Sec Hindu Push-ups
10 Sec Rest
20 Sec Jump Squat
10 Sec Rest
20 Sec Skater
60 Sec REST
Short of time? Try a hiit workout and enjoy a great workout with similar benefits as a standard aerobic workout in less time. In interval training, you alternate between short periods of intense activity and longer periods of less intense activity.
HIIT Cardio Exercise Selection
4- Aerobic Interval Training
The first way of doing aerobic interval training involves doing a period of moderate to high intensity aerobic activity, alternating with a period of rest of low intensity work.
For example. 3 minutes of fast running or 30 second sprint then 1 minute of briskly walking or slow walking, repeated 3-4 times. You can vary the intervals and intensities to your fitness level, e.g. 5 minutes of moderate activity, 2 minutes easy, 1 minute hard, or perhaps 5 minutes hard, 5 minutes easy.
Interval training is good for developing both the aerobic (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without oxygen) energy systems and is very effective at improving your VO2 Max and anaerobic threshold. What this means is that you can work harder (run or swim faster) and then maintain that intensity for longer (run harder at your higher pace).
Interval training is highly effective for improving performance in endurance sports. It can be used to increase performance and recovery rate, especially in sports that require repetitive bursts of high-intensity exercise such as football, running, basketball, cycling or swimming.
5- Anaerobic Interval Training
Anaerobic means “without oxygen” and aerobic means “with oxygen”. Anaerobic training involves short, fast, high-intensity exercises that don’t make your body use oxygen like it does for cardio activities. It is done at intensities of 85 to 100% of your HR max. This type of activity involves going hard for short periods of time then resting for equal or longer periods of time.
Sprint 20 seconds
Walk 20 seconds
Sprint 30 seconds
Walk 30 seconds
Repeat 3 to 5 times depending on fitness level.
Examples of anaerobic training include:
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT)
- Weight lifting and strength training
- Tabata, crossfit and plyometrics
How often should I do cardio workout?
Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommend that adults perform at least 150–300 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75–150 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity, or some combination of the two, each week. Aerobic training 3 to 5 days per week will improve your cardiovascular fitness. Training just 2 days a week will help you maintain the aerobic fitness you already have. Beginners should not do high-intensity interval training more than once or twice a week. You should only do this after you’ve established a good base of cardiovascular fitness.
Cardio exercise doesn’t have to take place in a gym. Many activities in our daily lives can provide cardio exercise, like taking the stairs, raking leaves or shoveling snow. Aim for at least 2-3 cardio workouts per week—a 10-15-minute high-intensity workout or an hourlong low-intensity activity.
- The American College of Sports Medicine states that moderate-intensity physical activity between 150-250 minutes per week is effective in preventing weight gain, but will provide only modest weight loss. Physical activity greater than 250 minutes per week is recommended for weight loss and the prevention of weight gain.
How Long Should my Cardio Workout Be?
If you’re into resistance or weight training, doing cardio two to three days a week is ideal for your overall health. However, if you are not doing any activity, your daily cardio time for your health is as follows.
- If you’re just starting out, 30-60 minutes of LISS cardio per day
- 30 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio activity at least five days per week (150 minutes per week)
- at least 25 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity three days per week (75 minutes per week)
Creating a Cardio Plan
If you want to customize your own cardio routine, just follow a few simple principles. First of all, to achieve a full body workout, exercise each muscle group during your routine.
In order to create a high-intensity or low-intensity cardio program, select the “cardio” category from the exercises section.
If you’ve never had training experience before, it’s best to start by choosing low-intensity (walking, jogging, cycling, stair) exercises. Beginners should aim for three to four cardio workouts a week for 30 to 60 minutes each session.
High-intensity training methods performed in a row with short rest intervals require much more effort on the body. (Air squat, jump rope, mountain climber, sprint, power skips, burpee). For example, Tabata training: It calls for 20 seconds of work followed by 10 seconds of recovery, repeated eight times in a row for a total of 4 minutes. If you want to design a cardio program that suits your level, choose your favorite exercises, start slow and work your way up gradually.
All information provided on this website is for information purposes only. Please see a healthcare professional for medical advice.