Contents
Looking to take your chest training to the next level? This advanced dumbbell chest workout routine is specifically crafted to push your muscles to their limits, stimulate growth, and assist you in reaching your desired chest gains. If you’ve already mastered the fundamentals of chest training and are ready for a fresh challenge, this routine is exactly what you need.
Benefits of Chest Workout with Dumbbells
1. Promoting Muscle Balance:
Dumbbell chest exercises require each side of your body to work independently. This means that your dominant side can’t compensate for your weaker side, helping you develop a more balanced chest. With barbell bench presses, for instance, the stronger side can often dominate the movement, leading to muscle imbalances over time.
2. Engaging Stabilizer Muscles:
Dumbbell workouts force your stabilizer muscles to work harder to maintain balance and control. This engagement not only enhances your chest development but also strengthens the surrounding muscles that support your shoulders and upper body.
3. Versatility in Range of Motion:
Unlike fixed barbells, dumbbells allow for a broader range of motion. This means you can achieve a deeper stretch at the bottom of your presses, promoting better muscle activation and flexibility.
Safety First
Before diving into your dumbbell chest workout routine, it’s crucial to prioritize safety. Here are some key safety considerations to keep in mind:
1. Proper Form: Always prioritize proper form over heavy weights. Using correct form ensures that you’re targeting the right muscles and reduces the risk of injury. It’s better to lift lighter weights with perfect form than to lift heavy weights with poor form.
2. Start with an Appropriate Weight: As a beginner, it’s essential to select a weight that challenges you without compromising your form. Start with a weight that allows you to perform the exercises with control and precision. Continuously challenge your muscles by increasing the weight or repetitions over time. Progressive overload is essential for muscle growth.
3. Know Your Limits: Listen to your body and know your limits. Pushing yourself to the point of failure is essential for muscle growth, but it should be done progressively and safely. Avoid overexertion, and if you’re uncertain about an exercise or experience pain beyond normal muscle fatigue, seek guidance from a fitness professional.
4. Warm-Up Thoroughly: Prior to your chest workout, spend 5-10 minutes on a warm-up routine that includes light cardio exercises, dynamic stretches, and mobility exercises to increase blood flow and prepare your muscles for action. (Learn how to warm up)
5. Cool Down and Stretch: After your workout, spend 5-10 minutes stretching your chest and shoulders. Static stretches can improve flexibility and reduce muscle tightness. (Learn how to cooldown)
Advanced Dumbbell Chest Workout Routine
This workout is designed for individuals who are already familiar with advanced chest exercises and can maintain proper form at an accelerated pace. In this advanced dumbbell chest workout, you’ll incorporate techniques like drop sets and supersets to challenge your muscles and promote growth.
If you’re a beginner, consider starting with a siple routine to establish a strong foundation. Building chest mass requires a structured and progressive workout routine. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do a chest workout for mass:
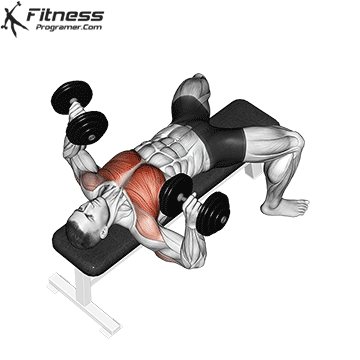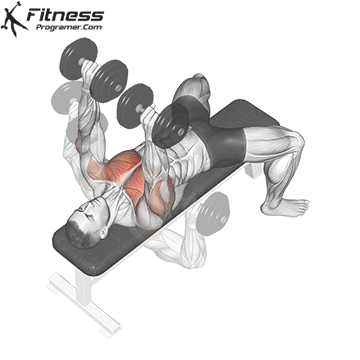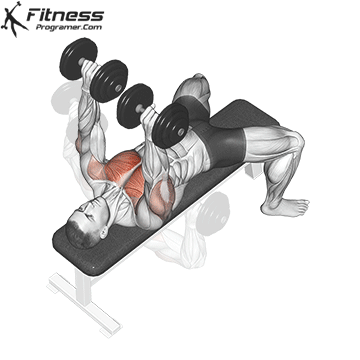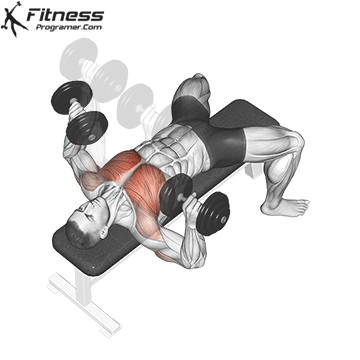
Exercise 1: Dumbbell Press (Incorporate Drop Sets)
- Sets: 4
- Repetitions: 8-10 (heavy), 12-15 (lighter)
- Rest Interval: 60-90 seconds
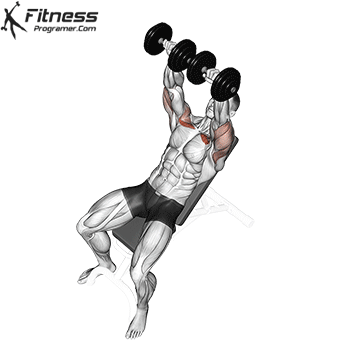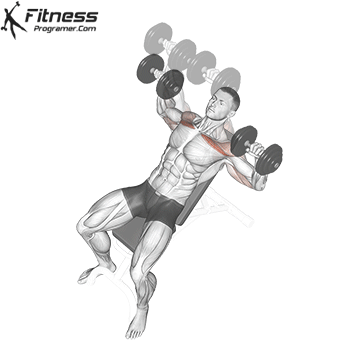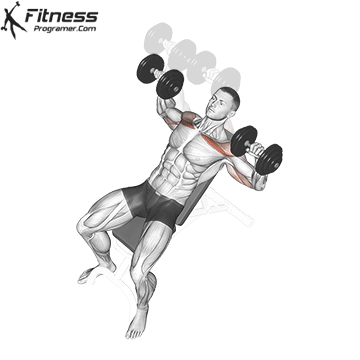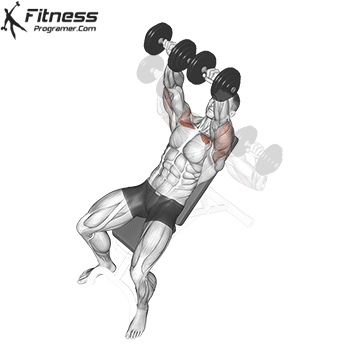
Exercise 2: Incline Dumbbell Press (Superset with Upward Fly)
- Sets: 3
- Repetitions: 8-10
- Rest Interval: Without resting, transition to the Upward Fly.
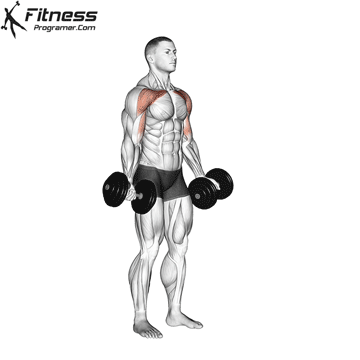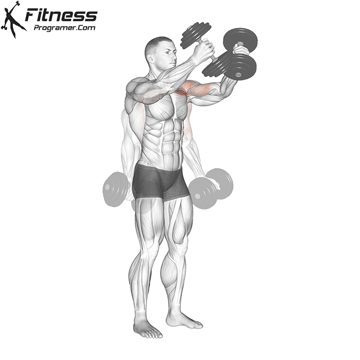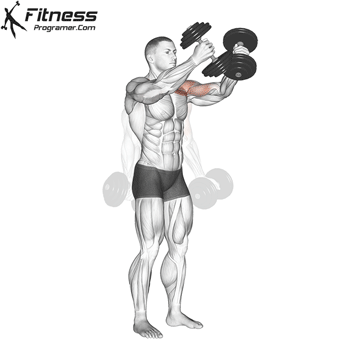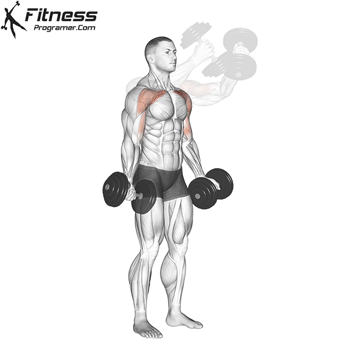
Exercise 3: Dumbbell Upward Fly (Superset with Incline Dumbbell Press)
- Sets: 3
- Repetitions: 10-12
- Superset Rest Interval: 60-120 seconds
Exercise 4: Decline Dumbbell Press (Superset with Dumbbell Fly)
- Sets: 3
- Repetitions: 8-10
- Rest Interval: Without resting, transition to the Dumbbell Fly.
Exercise 5: Dumbbell Fly (Superset with Decline Dumbbell Press)
- Sets: 3
- Repetitions: 10-12
- Superset Rest Interval: 60-120 seconds
Exercise 6: Dumbbell Pullover
- Sets: 2
- Repetitions: 10-12
- Rest Interval: 60-90 seconds
The Key Exercises in Dumbbell Chest Workouts
Each exercise targets specific areas of your chest, and mastering them will be key to achieving the results you desire.
1. Dumbbell Bench Press:

When it comes to building a robust chest, the Dumbbell Press is a go-to exercise. The technique involves performing a set of Dumbbell Presses with heavy weights, followed immediately by reducing the weight (typically by 30% to 40%) and continuing with lighter reps. Drop sets push your muscles to near exhaustion, stimulating muscle fibers effectively for growth. By incorporating both heavy and lighter weights, you activate different muscle fibers, promoting overall chest muscle hypertrophy.
Muscles Targeted: The dumbbell press primarily targets the pectoralis major, the large chest muscle. It also engages the anterior deltoids (front shoulder muscles) and the triceps.
Execution:
- Begin by lying flat on a bench with your feet planted firmly on the ground.
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand, positioning them at chest level with your palms facing forward.
- Inhale and slowly lower the dumbbells towards your chest.
- Exhale and push the dumbbells upward until your arms are fully extended, nearly touching at the top.
- Lower the dumbbells back down to chest level while maintaining control throughout the movement.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Arching your back excessively.
- Using momentum to lift the weights.
- Allowing the dumbbells to drift too far apart at the top of the movement.
2. Incline Dumbbell Press

Supersets increase time under tension, a key factor for muscle hypertrophy and development. By combining the Incline Dumbbell Press with the Dumbbell Upward Fly in a superset, you’ll target your upper chest from different angles, creating a more balanced and impressive chest development.
Muscles Targeted: This move is one of the most effective upper chest exercises you can do in your workout; While it primarily targets the clavicle head of the pectoralis major muscle, it also exercises the anterior deltoid and triceps muscles.
Execution:
- Use an incline bench set at a 30-45 degree angle.
- Lie back on the bench with a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing forward.
- Inhale and lower the dumbbells towards your chest, ensuring a controlled descent.
- Exhale and push the dumbbells upward until your arms are fully extended.
- Lower the dumbbells back down, maintaining proper form.
Adjusting Bench Angle:
The incline bench press, performed at an angle of approximately 30-45 degrees, is a common exercise to target the upper chest. This angle places more emphasis on the clavicular head of the pectoralis major, which is the upper portion of the chest.
3. Dumbbell Upward Fly

Muscles Targeted: The dumbbell upward fly complements the incline press by further isolating the upper chest and also engages the anterior deltoids.
Execution:
- Lie on an incline bench, gripping a dumbbell in each hand.
- Start with your arms extended and palms facing each other.
- Inhale and open your arms wide in a hugging motion.
- Exhale and return your arms to the starting position.
- Focus on controlled movements to prevent excessive strain on the shoulder joints.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Maintain a slight bend in your elbows throughout the movement to avoid overextending and putting excess strain on your shoulder joints.
- Focus on control and avoid using momentum or swinging your arms.
- Start with a lighter weight to ensure proper form and gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable with the movement.
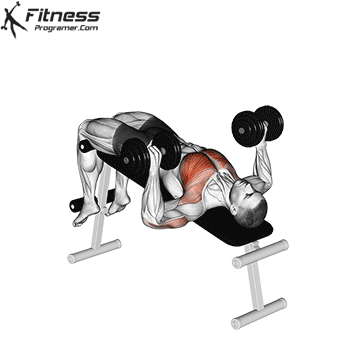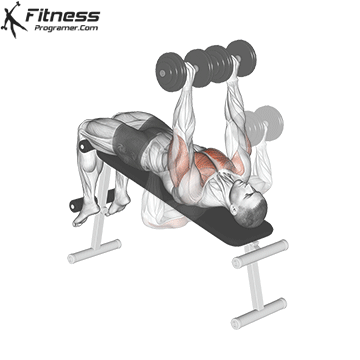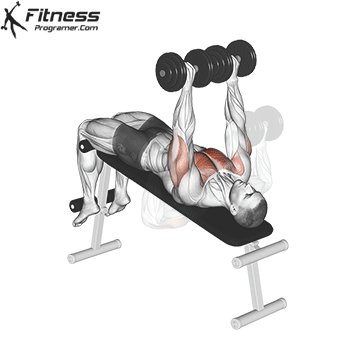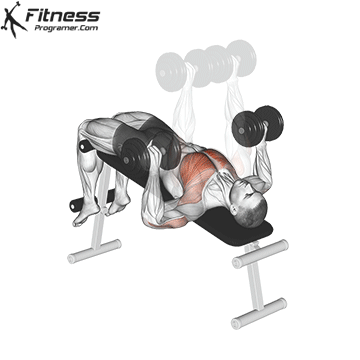
4. Decline Dumbbell Press

This superset targets various areas of the chest, including the lower and mid-chest, promoting a balanced chest development. By combining the Decline Dumbbell Press with the Dumbbell Fly in a superset, you’ll engage your chest muscles from different angles, fostering overall chest development.
Muscles Targeted: The decline dumbbell press effectively targets the lower chest (abdominal head of the pectoralis major) and also engages the anterior deltoids and triceps. It is an effective bench press variation, especially for lower chest activation and symmetry problems.
Execution:
- Use a decline bench set at a downward angle.
- Lie back on the bench with a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing forward.
- Inhale and lower the dumbbells towards your chest.
- Exhale and press the dumbbells upward until your arms are fully extended.
- Lower the dumbbells back down while maintaining control.
Adjusting Bench Angle: To target the lower chest, you can adjust the bench to create a decline angle. The specific angle may vary from -15 to -30 degrees, depending on your bench and your preference. This slight decline angle shifts the emphasis of the exercise towards the lower pectoral muscles (1).
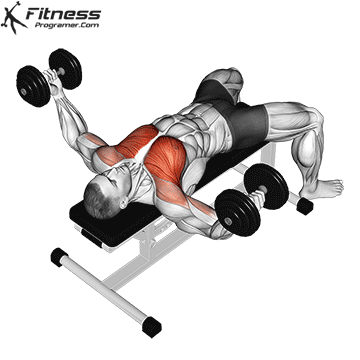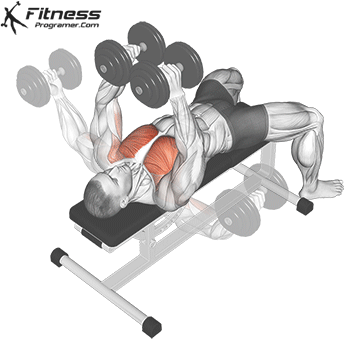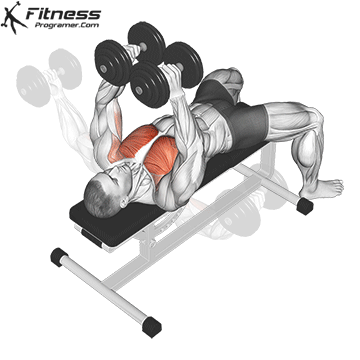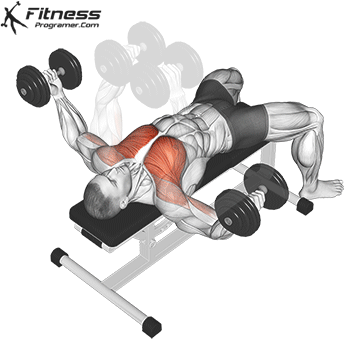
5. Dumbbell Fly
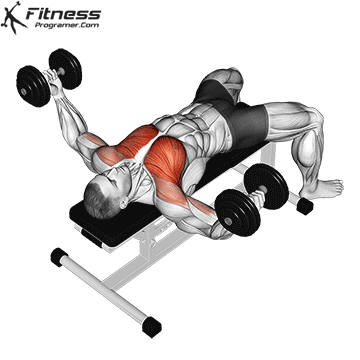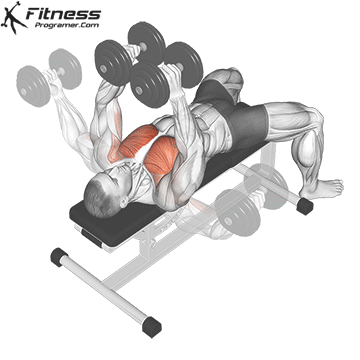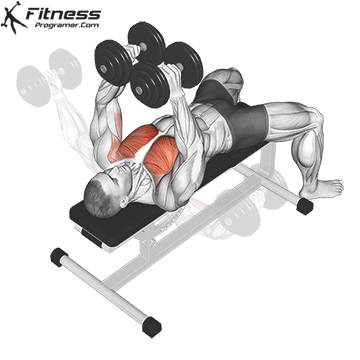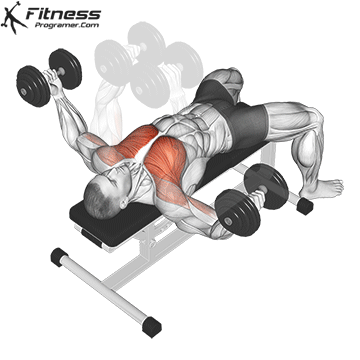
Muscles Targeted: The dumbbell fly is a classic isolation exercise that primarily targets the chest muscles, particularly the pectoralis major (sternal head). It’s a great exercise for developing chest strength, muscle definition, and achieving a well-rounded chest.
Execution:
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand with your palms facing each other, and extend your arms straight up over your chest.
- Keep a slight bend in your elbows.
- Lower the dumbbells out to the sides in a wide arc while keeping a slight bend in your elbows.
- Lower the weights until you feel a stretch in your chest muscles or when your upper arms are about parallel to the floor.
- Reverse the motion by bringing the dumbbells back together over your chest.
- Focus on squeezing your chest muscles as you bring the weights back up.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- One of the most common mistakes is using excessively heavy weights, which can lead to loss of control and improper form. Choose a weight that allows you to maintain proper form throughout the exercise.
- Avoid fully extending your elbows during the movement. Keep a slight bend in the elbows to prevent strain on the shoulder joints.
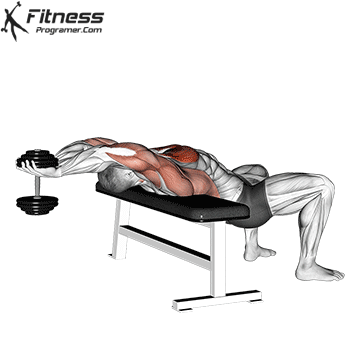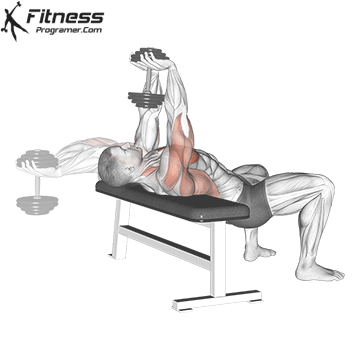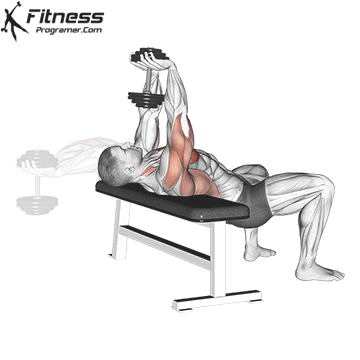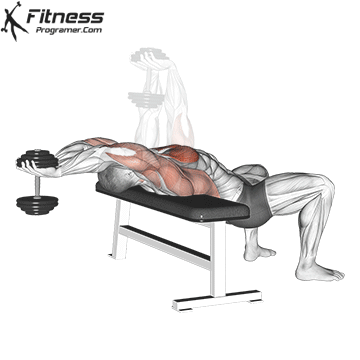
6. Dumbbell Pullover

Muscles Targeted: The dumbbell pullover primarily targets the pectoralis major, which is the large muscle of the chest. It allows you to isolate and engage the chest muscles effectively, helping to create a deep stretch and contraction.
Execution:
- Lie on your back on a bench with only your upper back and shoulders on the bench and your hips below it.
- Hold a single dumbbell with both hands above your chest, arms slightly bent.
- Inhale and lower the dumbbell backward over your head.
- Exhale and pull the dumbbell back up to the starting position.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Start with a manageable weight, as using excessively heavy dumbbells can lead to loss of control and poor form.
- Maintain a natural arch in your lower back throughout the exercise.
- Perform the exercise in a smooth, controlled motion. Avoid jerking the weight or using momentum to lift it.
- Keep a slight bend in your elbows throughout the movement to avoid unnecessary strain on the elbow joints.
- Lower the dumbbell only as far as you can control it comfortably. Avoid allowing it to drift too far behind your head, which can strain the shoulders and neck.
3 Strategies to Get Fast Results from Chest Workout
By integrating these advanced workout strategies into your chest routine, you can expedite your progress and achieve rapid results.
1. Utilize Drop Sets for Intensity:
Drop sets involve performing an exercise to muscle failure and then immediately reducing the weight and continuing the set. Incorporate drop sets into your advanced dumbbell chest workout to exhaust your muscle fibers and stimulate growth. For example, after a set of heavy dumbbell presses, drop the weight by 30% to 40% and continue with lighter reps.
2. Supersets for Efficiency:
Supersets involve performing two exercises back-to-back with minimal rest in between. This approach keeps your chest muscles constantly engaged, leading to efficient gains.
3. Integrate Eccentric Training:
Eccentric training focuses on the lowering (eccentric) phase of an exercise. During the chest press, emphasize the controlled lowering of the dumbbells, which can lead to greater muscle damage and growth. Lower the dumbbells as slowly and under control as possible, taking at least 4 seconds for the descent.
Nutrition and Recovery Tips for Dumbbell Chest Workout
When it comes to achieving advanced gains in your chest workouts, it’s not just about lifting heavier weights or doing more reps. Proper nutrition and recovery play a pivotal role in maximizing muscle growth and optimizing performance. In this blog post, we’ll explore the essential aspects of nutrition and recovery tailored specifically for advanced dumbbell chest workouts.
1. Pre-Workout Nutrition
Before you hit the gym for your advanced dumbbell chest workout, it’s essential to fuel your body with the right nutrients to enhance your performance. Here’s what you need to know:
- Carbohydrates: Complex carbs provide a steady source of energy for your workout. Opt for sources like whole grains, sweet potatoes, and fruits about 1-2 hours before your workout.
- Protein: Protein is crucial for muscle repair and growth. Aim to consume a moderate amount of protein (about 20-30 grams) before your workout. Options like lean chicken, Greek yogurt, or a protein shake can work well.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated to maintain optimal muscle function and prevent fatigue. Sip on water throughout the day and consider a sports drink with electrolytes for intense workouts.
2. During the Workout
While you’re training, it’s crucial to stay hydrated. Sip on water between sets, especially during longer and more intense sessions. Consider branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) supplements to help reduce muscle fatigue and enhance endurance.
3. Post-Workout Nutrition: Maximizing Recovery
Your post-workout diet is more important for advanced chest workouts. Here’s what to focus on:
- Protein: Within 30 minutes to an hour after your workout, consume a protein-rich meal or shake. This helps kickstart the muscle recovery process. Opt for whey protein, which is quickly absorbed by the body.
- Carbohydrates: Pair your post-workout protein with carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores and aid in muscle recovery. Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and sweet potatoes are excellent choices.
- Fats: Include healthy fats like avocados, nuts, or olive oil in your post-workout meal to support overall recovery and hormone regulation.
4. Supplementation for Enhanced Recovery
Supplements can complement your advanced chest workout routine:
- Creatine: Creatine monohydrate can enhance muscle recovery and strength. Consider taking 3-5 grams daily.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 supplements can help reduce inflammation and promote recovery. Aim for 1-2 grams of EPA and DHA per day.
5. Sleep and Recovery
Nutrition is just one piece of the puzzle. Adequate sleep and effective recovery strategies are equally vital:
- Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. During deep sleep, your body repairs and grows muscle tissue.
- Active Recovery: Incorporate light activities like walking, yoga, or swimming on your rest days to promote blood flow and reduce muscle soreness.
- Foam Rolling: Use foam rollers to release muscle tension and improve flexibility.
- Hydration: Continue to hydrate post-workout to aid in the removal of metabolic waste and toxins from your muscles.
In conclusion, nutrition and recovery are the unsung heroes of advanced dumbbell chest workouts. By optimizing your pre-workout and post-workout nutrition, supplementing strategically, and prioritizing recovery, you’ll create the ideal environment for muscle growth and peak performance. Remember that consistency in these practices is key to sustaining your gains and achieving your fitness goals.



