Contents
What Is a Muscle Spasm?
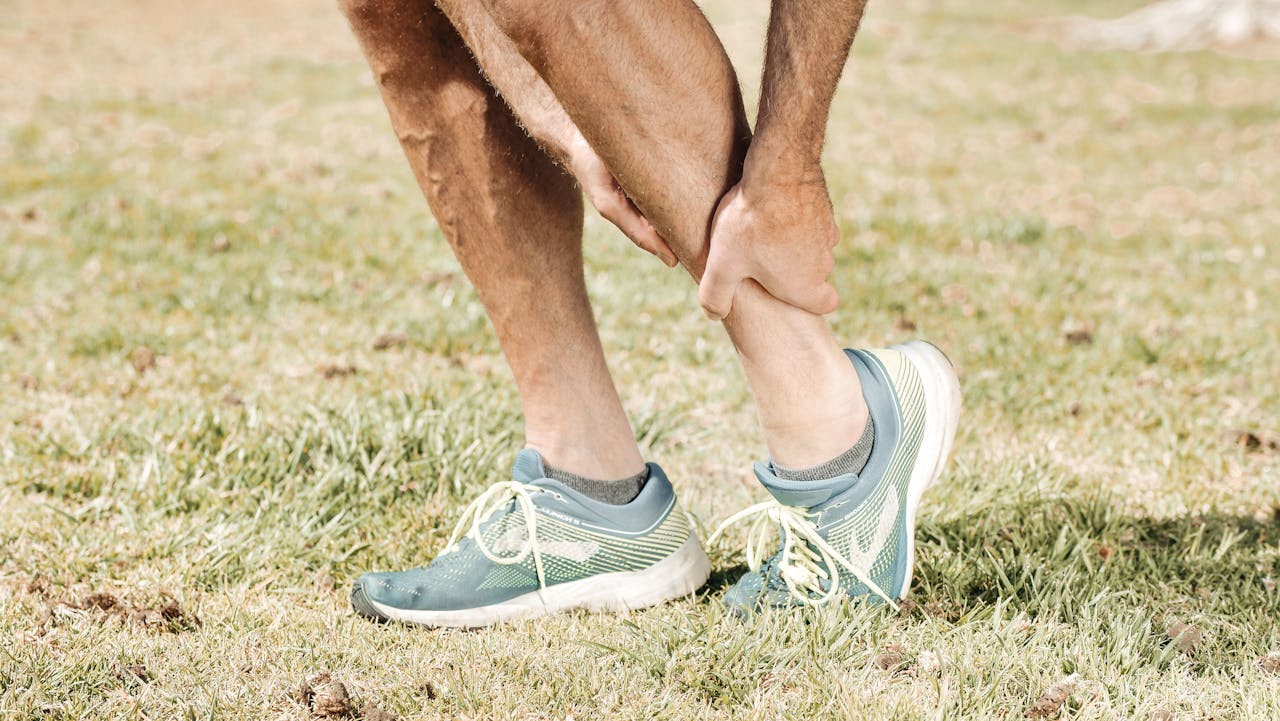
A muscle spasm, commonly referred to as a muscle cramp, is an involuntary and sudden contraction of one or more muscles. These spasms can be painful and may last from a few seconds to several minutes. They often occur in the legs, particularly the calf muscles(1), but can affect any muscle group in the body.
What Causes Muscle Spasms?
Several factors can contribute to the occurrence of muscle spasms:
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can lead to electrolyte imbalances, causing muscles to contract involuntarily .
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Low levels of minerals such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium are essential for muscle function. Deficiencies can trigger spasms .
- Overuse or Muscle Fatigue: Engaging in strenuous physical activity without proper conditioning can lead to muscle fatigue and subsequent spasms .
- Poor Blood Circulation: Restricted blood flow to muscles can cause cramps, especially during exercise.
- Nerve Compression: Conditions like spinal cord injuries or pinched nerves can lead to muscle spasms(2).
- Medical Conditions: Diseases such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, or neurological conditions can increase the risk of muscle cramps.
What Are the Symptoms of Muscle Spasms?
The primary symptom of a muscle spasm is a sudden, sharp pain in the affected muscle. Other signs include:
- Muscle Tightness: The muscle may feel hard or knotted to the touch.
- Visible Muscle Twitching: Involuntary movements or twitching can occur.
- Limited Mobility: Difficulty moving the affected muscle or joint.
- Residual Soreness: After the spasm subsides, the muscle may remain tender or sore for several hours.
What Is a Persistent Muscle Spasm?
While most muscle spasms are transient, some individuals experience persistent or recurrent spasms. These may be indicative of underlying health issues such as:
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions like multiple sclerosis or dystonia can cause chronic muscle spasms.
- Medication Side Effects: Certain drugs, including diuretics and statins, may lead to muscle cramps.
- Metabolic Imbalances: Chronic electrolyte disturbances can result in ongoing muscle spasms.
Persistent muscle spasms warrant medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
How Do Muscle Spasms Resolve?
Most muscle spasms resolve on their own without medical intervention. To alleviate discomfort:
- Stretching: Gently stretch the affected muscle to relieve tension .
- Massage: Massaging the muscle can improve blood flow and reduce tightness.
- Heat or Cold Therapy: Applying a warm towel or ice pack can soothe the muscle.
- Hydration: Drinking fluids replenishes electrolytes and aids muscle function.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce pain and inflammation.
Who Is at Risk for Muscle Spasms?
Certain populations are more susceptible to muscle spasms:
- Athletes: Intense physical activity increases the risk of muscle fatigue and cramps.
- Older Adults: Age-related muscle loss and decreased activity can lead to spasms.
- Pregnant Women: Hormonal changes and increased weight can strain muscles.
- Individuals with Medical Conditions: Those with diabetes, nerve disorders, or thyroid issues may experience more frequent spasms.
How to Prevent Muscle Spasms
Preventive measures include:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in consistent physical activity to strengthen muscles.
- Proper Hydration: Drink adequate fluids, especially during and after exercise.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure sufficient intake of electrolytes like potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
- Stretching: Incorporate stretching routines before and after workouts.
- Avoid Overexertion: Gradually increase exercise intensity to prevent muscle fatigue.
Frequently Asked Questions About Muscle Spasms
Q: Are muscle spasms dangerous?
A: While typically harmless, frequent or severe spasms may indicate underlying health issues and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Q: Can certain medications cause muscle spasms?
A: Yes, medications like diuretics and statins have been associated with muscle cramps.
Q: When should I see a doctor about muscle spasms?
A: Consult a healthcare professional if spasms are frequent, severe, or accompanied by other symptoms like muscle weakness or swelling.
Understanding the causes and management of muscle spasms can help in reducing their occurrence and improving quality of life. If you experience persistent or severe muscle cramps, it’s essential to seek medical advice to rule out any underlying conditions.