Contents
The push press is an explosive and effective compound exercise that targets multiple muscle groups while developing upper body strength and power. This exercise engages your shoulders, triceps, core, and even your legs, making it an excellent full-body movement. Whether you’re new to weightlifting or looking to add variety to your workout routine, mastering the push press can provide a range of benefits.
Benefits of the Push Press:
Before we delve into the details, let’s briefly touch on the benefits of incorporating the push press into your fitness routine:
The push press is a foundational exercise that builds strength, stability, and explosive power in the upper body. This exercise involves an explosive leg drive followed by an overhead press, uniting lower body strength with upper body power. The combination of these moves comes with a number of benefits.
1- Functional Fitness Enhancement:
The push press mirrors everyday movements that require pushing or lifting objects overhead. This functional aspect translates to improved performance in daily activities. The core muscles play a crucial role in stabilizing the body during the push press. This stability has a direct impact on your ability to maintain balance and posture during functional movements.
2- Explosive Power Generation:
The explosive leg drive and rapid extension of the hips and knees during the push press generate a significant amount of force. This explosive power transfer not only contributes to increased performance in the exercise itself but also carries over to various athletic activities and sports that require quick and powerful movements.
3- Strength and Stability:
The push press heavily engages the deltoids and triceps, contributing to improved shoulder strength and stability. Alongside the pressing muscles, the posterior chain (back, glutes, and hamstrings) plays a role in stabilizing your body during the movement. Regularly performing this exercise can enhance the stability and mobility of your shoulder complex, reducing the risk of injuries and promoting better posture.
4- Hypertrophy Potential
By adjusting the rep range and load, the push press can be tailored to promote muscle hypertrophy (growth). This makes it a valuable tool for bodybuilders and individuals aiming to increase muscle size and definition.
5- Coordination and Kinesthetic Awareness:
Executing the push press requires coordination and kinesthetic awareness to synchronize the movement of the lower body with the upper body press. Practicing this coordination can lead to improved overall body awareness and control.
The push press is a remarkable exercise that holds the potential to transform your strength training regimen. By seamlessly blending lower body power with upper body strength, it enhances your functional fitness, powers up your performance, and fosters a more well-rounded athletic prowess.
Mastering the Push Press
Step-by-Step Guide: Follow these steps to perform the push press correctly:
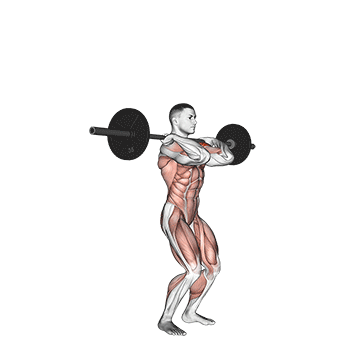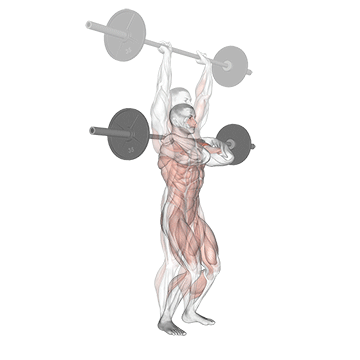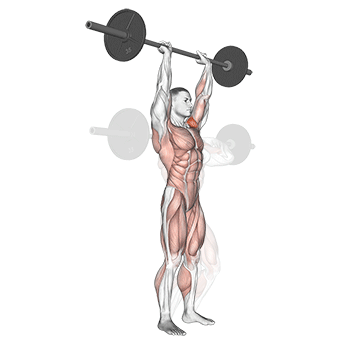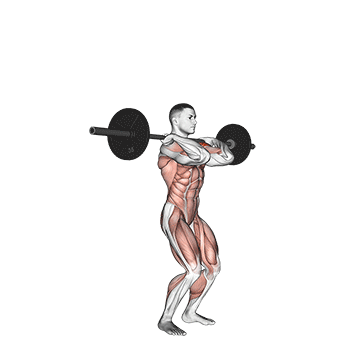
Step 1: Set Your Stance and Grip: Start by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart. Your toes can be slightly turned out for better stability. Grip the barbell or dumbbells with your palms facing forward and your hands just outside your shoulders.
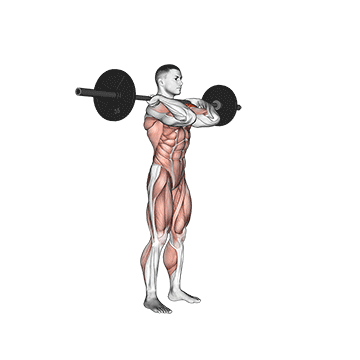
Step 2: Rack Position: Lift the barbell or dumbbells onto your shoulders, resting them across your collarbones. Your elbows should be slightly in front of the bar. Keep your chest up and engage your core muscles.
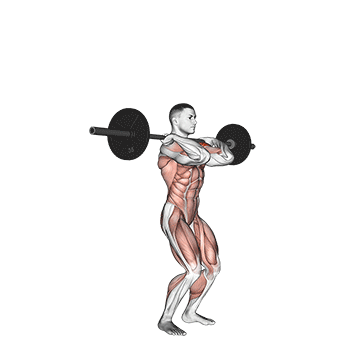
Step 3: Dip and Drive: Initiate the movement by slightly bending your knees and hips. This is called the “dip.” Maintain an upright torso and avoid leaning forward. As you begin to rise, explode upward using your legs’ power, driving the barbell or dumbbells overhead.
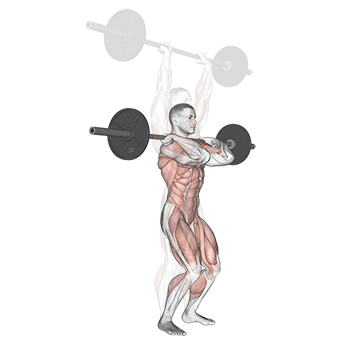
Step 4: Overhead Press: As you drive upward, fully extend your hips and knees. Simultaneously, press the weight overhead, fully extending your arms. Your head should move slightly forward as the weight passes your face.
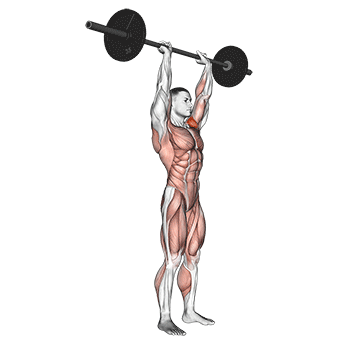
Step 5: Lockout and Return: At the top of the movement, lock your elbows and shoulders. Hold this position briefly before lowering the weight back down to the rack position by bending your knees and hips.
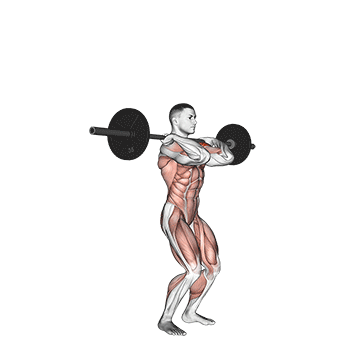
Step 6: Lowering: Lower the weight back to the starting position by bending your knees and hips. Repeat the movement for the desired number of reps.
Remember, mastering any exercise takes practice and patience. Start light, focus on form, and gradually increase the weight as you become more confident in your abilities.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Using Excessive Momentum: Remember, the push press should involve a controlled dip and drive, not a full-blown squat jump.
- Neglecting Core Engagement: Keep your core tight throughout the movement to support your spine and maintain stability.
- Leaning Back: Avoid leaning back excessively when pressing the bar overhead, as this can strain your lower back.
Tips for Success:
- Practice with Light Weights: Begin with a manageable weight to focus on proper technique before progressing to heavier loads.
- Maintain Balance: Distribute your weight evenly between both feet to prevent leaning to one side.
- Breathe: Inhale during the dip and exhale as you press the barbell overhead.
Incorporating Push Press into Your Workout Routine
The push press isn’t just an upper body exercise; it’s a compound movement that engages the lower body, core, and upper body muscles. By incorporating the push press, you’re tapping into a multi-dimensional exercise that maximizes muscle engagement and calorie burn.
Optimizing Push Press for Full-Body Strength Workout
Design full-body workouts that feature the push press as a central movement. Include other strength training exercises to engage various muscle groups and maximize overall power output.
Choose a rep and set scheme based on your goals. For strength, go for lower reps (3-6 reps) with heavier weights. Aim for lower weights (40-60%) and higher reps (12-15 reps) for muscular endurance.
Get ready to sweat and challenge your body with this full-body workout that seamlessly integrates the push press:
- Begin with 5-10 minutes of dynamic stretching to prepare your muscles for the workout ahead.
- Incorporate light cardio, such as jogging or jumping jacks, to elevate your heart rate.
Workout Circuit: Perform 3 rounds of the following circuit. Rest for 1-2 minutes between each round. Use a weight between 50-70% of max 1 rep.
- Push Press:
- Reps: 8-10
- Technique: Follow the proper push press form, generating power from your legs and pressing the weight overhead.
- Goblet Squats:
- Reps: 12-15
- Technique: Hold a kettlebell or dumbbell close to your chest and perform squats, maintaining an upright posture.
- Bench Press:
- Reps: 8-10
- Technique: Focus on maintaining a controlled and steady motion throughout the press. Avoid bouncing the bar off your chest; control the movement at all times.
- Bent-Over Row
- Reps: 8-10
- Technique: Holding dumbbells, bend at the hips while keeping your back straight, and perform rows to engage your back muscles.
- Kettlebell Swings:
- Reps: 15-20
- Technique: Swing the kettlebell between your legs and explosively drive your hips forward to bring it to shoulder height.
- Dedicate 5-10 minutes to static stretching to relax your muscles and enhance flexibility.
- Focus on stretching the major muscle groups targeted in the workout.
Safety Precautions:
- Use proper form throughout each exercise to prevent injury.
- Choose weights that challenge you but allow you to maintain proper technique.
- If you’re new to these exercises, consider working with a fitness professional to ensure correct form.
Optimizing Push Press for Hypertrophy Workouts
While the push press is known for its power and explosive capabilities, it can also be harnessed to promote muscle growth and hypertrophy. When optimized for hypertrophy, it becomes a versatile tool to stimulate muscle growth in various upper body muscles, including the shoulders, triceps, and upper chest.
Guidelines for hypertrophy: 3-6 sets of 6-12 reps 30 to 90 seconds rest -60 to 85% of 1RM-
These guidelines allow you to achieve the best results when designing a training program for the development of hypertrophy.
Example: Hypertrophy Shoulder Workout including Push Press
This workout is designed to target your shoulder muscles using the push press exercise as the primary compound movement. By focusing on moderate reps, controlled tempo, and progressive overload, you’ll stimulate muscle growth and develop well-rounded shoulders.
Warm-Up:
- 5-10 minutes of light cardio to increase blood flow to your muscles.
- Dynamic shoulder stretches to improve mobility.
Workout:
- Push Press:
- Reps: 4 sets of 10-12 reps
- Technique: Focus on explosive leg drive and controlled overhead press. Use a weight that challenges you within the rep range.
- Dumbbell Lateral Raises:
- Reps: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Technique: Hold a dumbbell in each hand and lift them laterally, targeting your side deltoids.
- Arnold Press:
- Reps: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Technique: Sit on a bench with back support. Start with palms facing you, then rotate them outward as you press the dumbbells overhead.
- Front Dumbbell Raises:
- Reps: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Technique: Hold a dumbbell in each hand and lift them forward, targeting your front deltoids.
- Bent-Over Dumbbell Rear Delt Raises:
- Reps: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Technique: Bend at the hips and lean forward slightly. Lift the dumbbells laterally, targeting your rear deltoids.
This sample push press hypertrophy shoulder workout provides a comprehensive routine to target your shoulder muscles for growth and strength. By combining the power-building nature of the push press with targeted isolation exercises, you’re creating a well-rounded approach to shoulder development. Remember to prioritize proper form, gradual progression, and recovery for optimal results.
References
- Weightlifting Overhead Pressing Derivatives: A Review of the Literature Marcos A. Soriano, Timothy J. Suchomel, Paul Comfort Sports Med. Published 2019 Mar 28. doi: 10.1007/s40279-019-01096-8 PMCID: PMC6548056
- Waller M, Piper T, Miller J. Overhead pressing power/strength movements. Strength Cond J. 2009;31(5):39–49 [Google Scholar]