Contents
Each individual’s metabolic rate, physical activity, genetic structure and daily calorie needs are different. Variables such as weight loss and weight gain programs, pregnancy and breastfeeding or bodybuilding programs are very effective in determining calorie needs.
A calorie is a unit of energy. In nutrition, calories measure how much energy food provides to your body.
The human body requires energy continuously to sustain life. Even when you are sleeping or resting, your body continues to burn calories to stay alive. In our previous article, we talked about calorie and energy balance. This energy is derived from food and used to support vital processes such as breathing, blood circulation, cellular repair, and temperature regulation, as well as voluntary activities like walking or exercising. The sum of these processes is referred to as metabolism.
Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) consists of three main components:
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) – energy used at complete rest
- Physical Activity Energy Expenditure (PAEE) – energy used during movement and exercise
- Thermic Effect of Food (TEF) – energy required to digest, absorb, and metabolize nutrients
Research shows that BMR accounts for approximately 60–70% of total daily energy expenditure in sedentary individuals, making it the most influential factor in calorie needs (McArdle et al., 2015).
One of the most common questions people ask when starting a fitness, weight loss, or healthy lifestyle journey is:
“How much calories do I need a daily?”
The answer is not a single number. Your daily calorie needs depend on many individual factors such as your age, sex, body weight, height, activity level, and overall health goals. Eating too many calories can lead to weight gain, while eating too few can slow your metabolism, reduce energy levels, and negatively impact hormonal balance. The factors affecting the metabolic rate and calorie requirement can be listed as follows:
Factors Determining Daily Calorie Needs
1. Gender and Body Composition
Men generally have higher calorie needs than women due to greater lean muscle mass. Muscle tissue is metabolically active and burns significantly more calories at rest compared to fat tissue. However, body composition is more important than gender alone; women with higher muscle mass may have higher calorie needs than sedentary men.
2. Physical Activity and Exercise
Physical activity is the most variable component of energy expenditure. Regular exercise not only increases daily calorie burn but also enhances muscle mass, which raises resting metabolic rate over time.
Strength training has been shown to improve metabolic health by increasing lean body mass and insulin sensitivity, while aerobic exercise contributes to cardiovascular health and fat oxidation (Willis et al., 2012).
3. Body Weight
Heavier individuals typically require more calories because maintaining a larger body mass demands more energy. However, weight alone is not a perfect indicator; two people of the same weight may have different calorie needs depending on muscle-to-fat ratio.
4. Height
Height influences energy needs through its effect on body surface area and lean mass. Taller individuals generally have more metabolically active tissue and therefore higher basal energy requirements, even when body weight is similar.
5. Age
Metabolic rate is highest during growth periods such as childhood and adolescence. It stabilizes in early adulthood and gradually declines with age, largely due to reductions in muscle mass and hormonal changes.
Recent research suggests that maintaining physical activity and adequate protein intake can significantly slow age-related metabolic decline (Pontzer et al., 2021).
6. Genetic Factors
Genetics influence metabolic rate, appetite regulation, fat distribution, and responsiveness to diet and exercise. While genetics may predispose individuals to obesity, lifestyle factors such as nutrition quality and physical activity remain the dominant determinants of body weight.
Certain inherited or acquired conditions—especially thyroid disorders—can significantly alter energy expenditure.
7. Environmental Factors and Climate
Exposure to cold environments increases energy expenditure as the body works to maintain core temperature. Although this effect is modest in modern living conditions, it may become significant in prolonged cold exposure or outdoor occupations.
8. Diseases and Hormonal Disorders
Acute and chronic diseases can substantially increase calorie and protein needs. Conditions such as burns, infections, cancer, trauma, and post-surgical recovery can elevate metabolic rate by 30–50% or more.
Hormonal disorders, including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, insulin resistance, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), directly affect metabolism and energy balance. Medical evaluation is essential in these cases.
What should my daily intake of calories be?
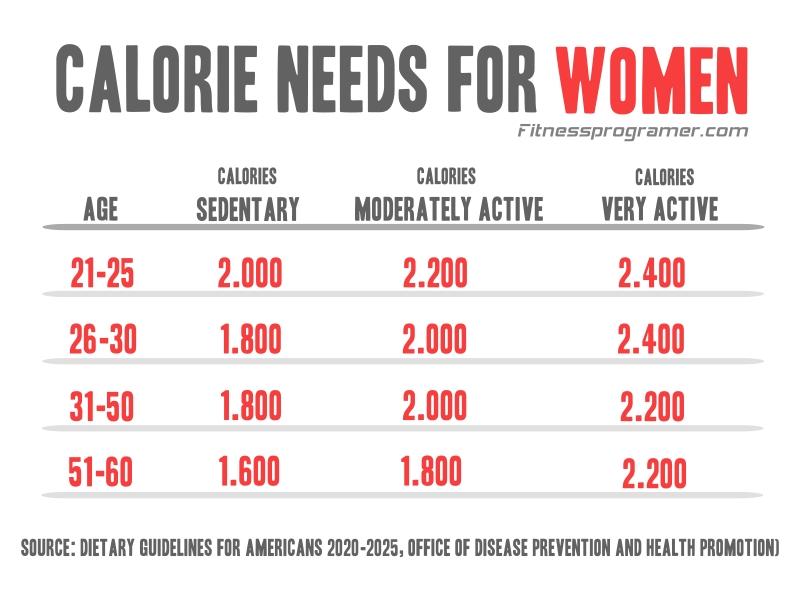
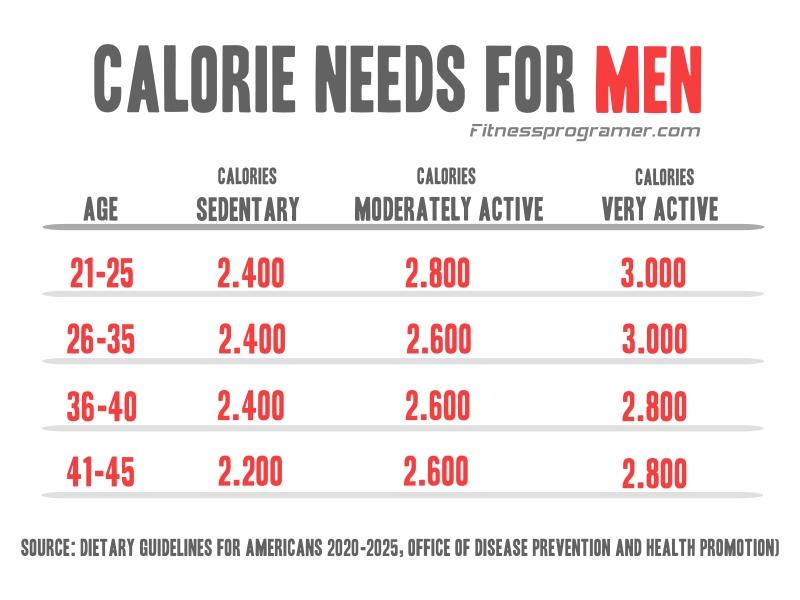
Daily calorie requirement is the amount of calories our body needs in a day to carry out its vital activities. The USDA’s 2020 “Dietary Guidelines for Americans” report states that adult women need 1,600 to 2,400 calories per day, and adult men 2,000 to 3,000 calories per day. However, this amount varies from person to person in line with the factors mentioned above.
Daily Calorie Calculator
This calorie calculator uses your age, weight, height, gender, and activity level to estimate the number of calories you should eat per day to maintain your weight. You can adjust this number based on your goals if you’re trying to lose weight or gain .
Daily calorie calculator expresses the calorie value required to meet the average energy consumed by the body in a day. If the calories consumed and the calories burned are equal every day, the body weight can remain at constant values. When the balance of the difference between these two is disturbed – regardless of man / woman – the process of gaining or losing weight begins.
Daily Calorie Calculator for Women
From puberty, the female body tends to store fat more as a fertility requirement than to build muscle. Therefore, the equations used to calculate women’s daily calorie needs differ from men’s according to their muscle and fat holding capacity. Women need to adopt a more intense daily pace so that their daily calorie consumption is equal to that of a man of the same age, height and weight.
Daily Calorie Calculator for Men
Although muscle weight develops depending on sports activity, men have more muscle mass than women due to their anatomical structure. Since muscle volume is a determining factor in energy consumption, men’s daily calorie needs may be higher than women’s. Moreover, this situation; It remains valid even if the age, weight, height values and activity intensity are the same.
How many calories do I need to gain muscle and gain weight?
The result you get from the calculation tool above shows the average energy value your body spends per day according to your goal.
To gain weight or build muscle, you need to meet the daily calorie needs in the results table and more. In addition, it is recommended that you exercise in order to build muscle mass with the nutrition program you apply to gain weight.
Example calorie increase for weight gain and muscle gain:
- Gender: male
- Age 30
- Weight: 80
- Height: 1.80
- Goal: Muscle Gain
- Activity: Lightly active
The daily requirement of the individual given in the example is 2458 calories. In order for this individual to increase muscle mass, he or she should increase the daily calorie amount by 300 to 500. However, this rate can be targeted between 700 to1000 calorie depending on the severity of physical activity.
How many calories do I need to lose weight?
To lose weight, you should eat according to the calorie needs in the results table and create a calorie deficit. Reducing your daily calories does not mean starving yourself. A few simple diet and lifestyle changes can help you lose weight, such as exercise to lose weight, drinking appropriate amounts of water, increasing your protein intake, and reduced carbohydrate intake.
Example calorie calculation for weight loss:
- Gender: Female
- Age: 27
- Weight: 80
- Height: 1.65
- Goal: Lose weight
- Activity: Moderately active
The daily requirement of the individual in the example to lose weight is 1796 calories. We do not know how many calories this individual consumes daily, but it seems that he needs an average of 1796 calories to lose weight. Assuming that this individual consumes 2500 calories per day, it is recommended to reduce the daily calorie amount by 200 to 500 and reduce it to 1750-1800 calories over time in order to lose weight in a healthy way.
Conclusion
Exercising is essential for a healthy life as well as creating a calorie deficit. When you support your diet with an exercise program, you can accelerate fat burning and increase your physical strength.
Daily calorie needs are influenced by a complex interaction of biological, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Understanding these variables allows individuals to make informed decisions about nutrition, exercise, and overall health.
For personalized guidance—especially in the presence of medical conditions—consulting a registered dietitian or healthcare professional is strongly recommended.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice.
References
- McArdle, W. D., Katch, F. I., & Katch, V. L. (2015). Exercise Physiology: Nutrition, Energy, and Human Performance. Wolters Kluwer.
- Pontzer, H. et al. (2021). Daily energy expenditure through the human life course. Science, 373(6556), 808–812.
- Willis, L. H. et al. (2012). Effects of aerobic and/or resistance training on body mass and fat mass in overweight adults. Journal of Applied Physiology, 113(12), 1831–1837.
- Morton, R. W. et al. (2018). Protein intake to maximize muscle mass. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 52(6), 376–384.
- USDA & HHS. (2020). Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020–2025.
- Hall, K. D. et al. (2012). Energy balance and its components. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 95(4), 989–994.



