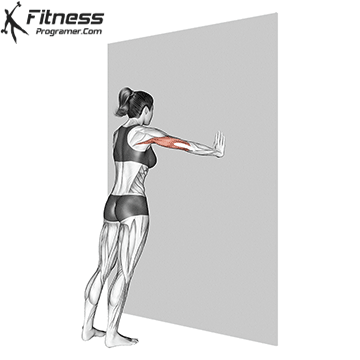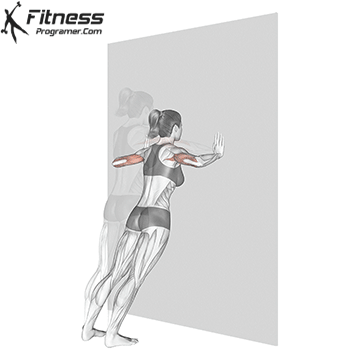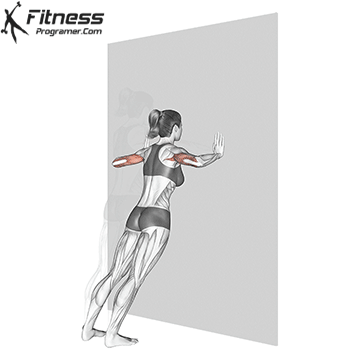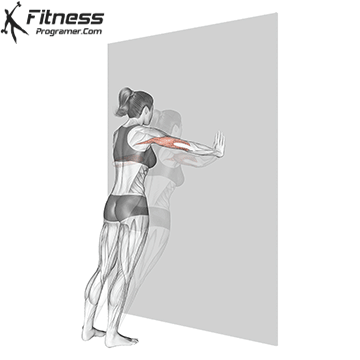
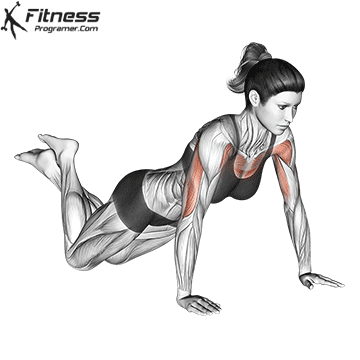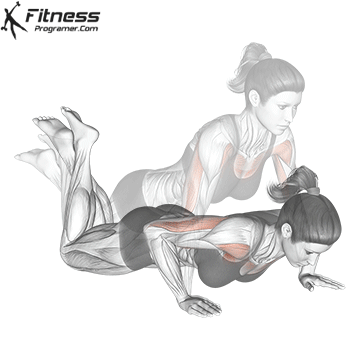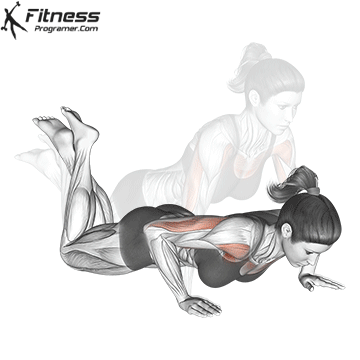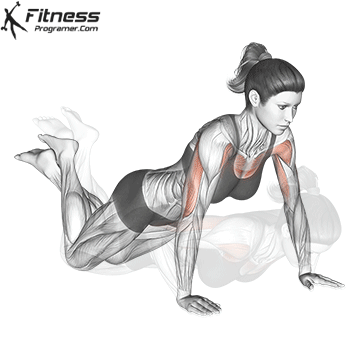
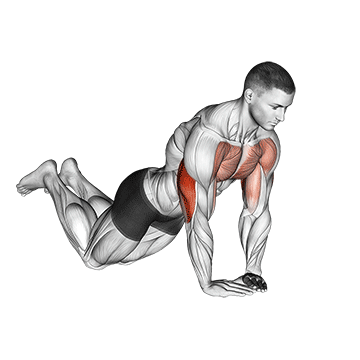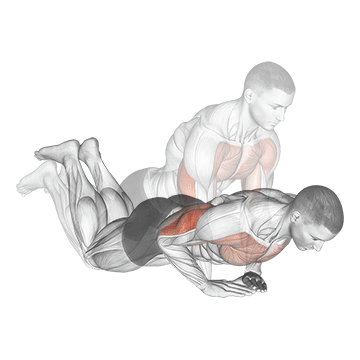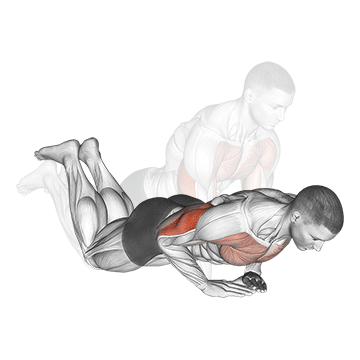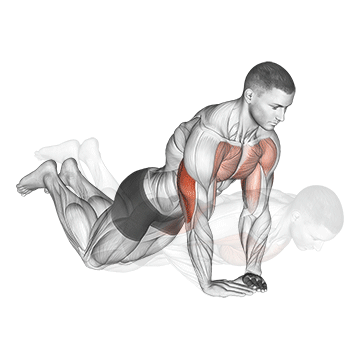
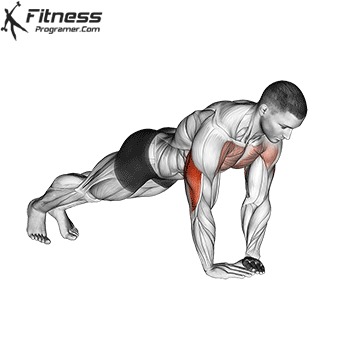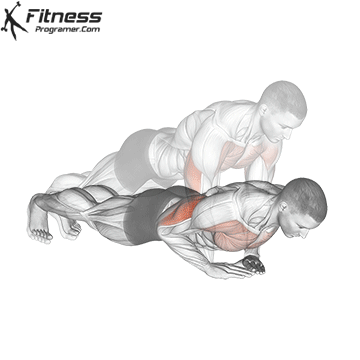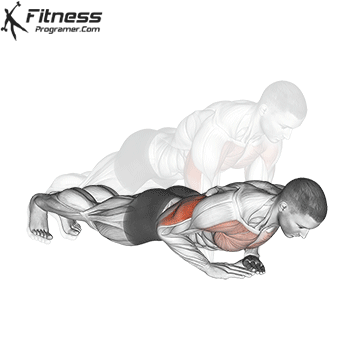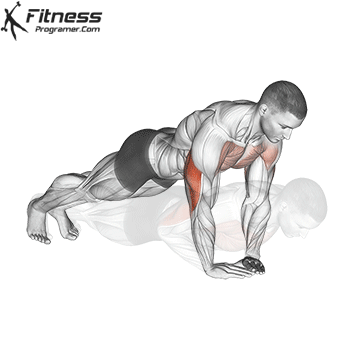
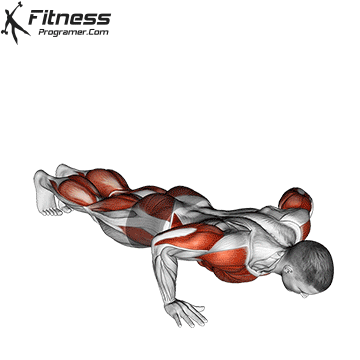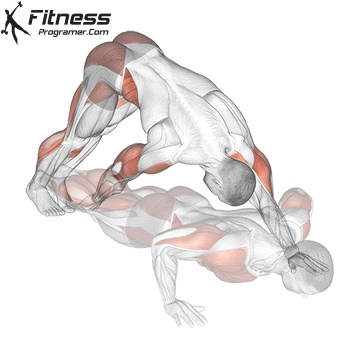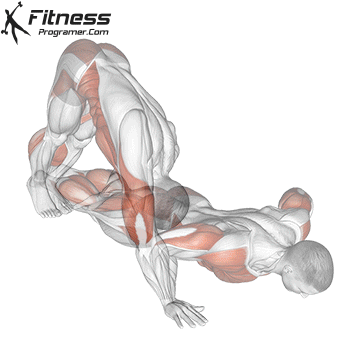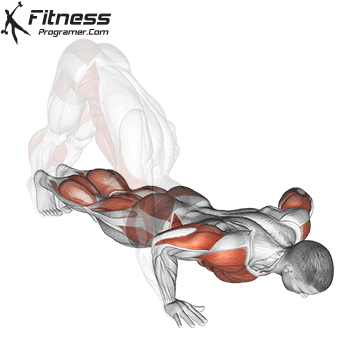
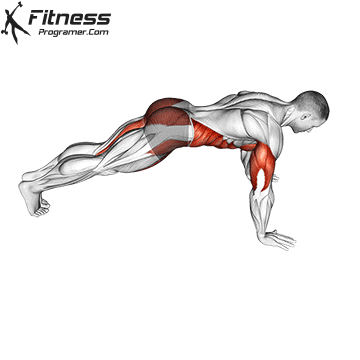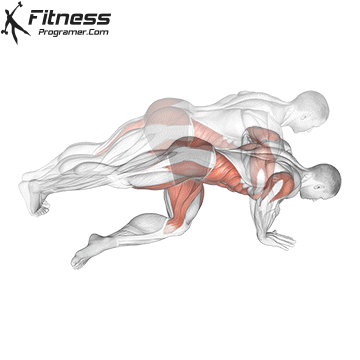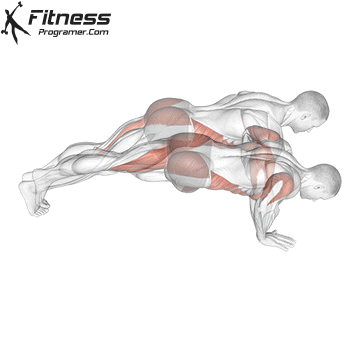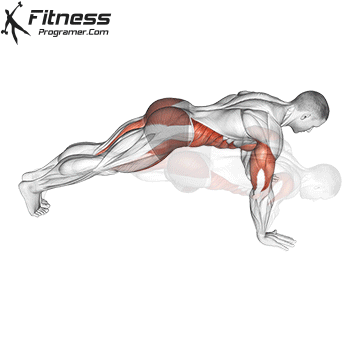
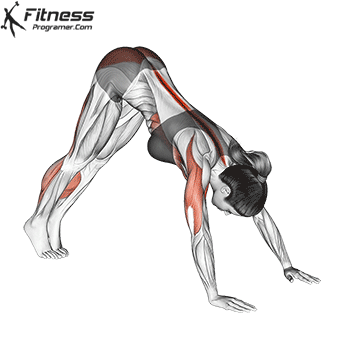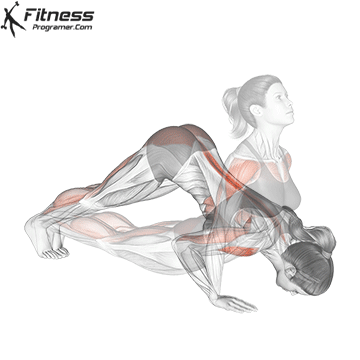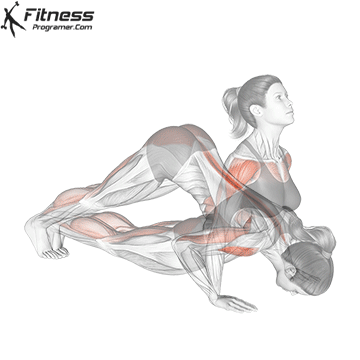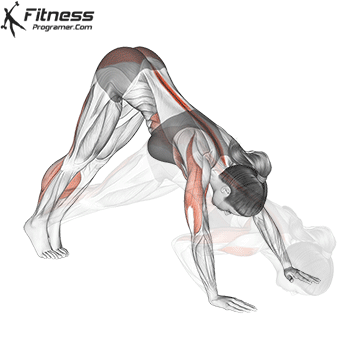
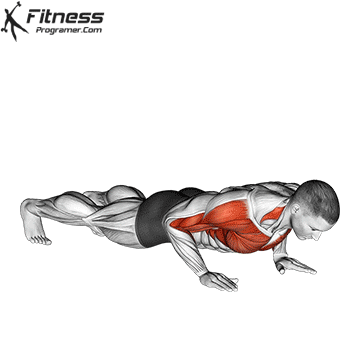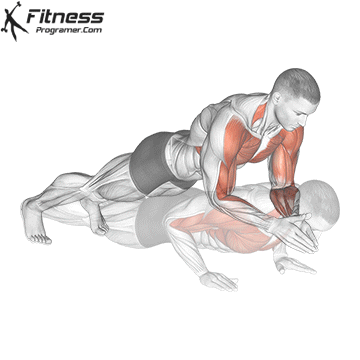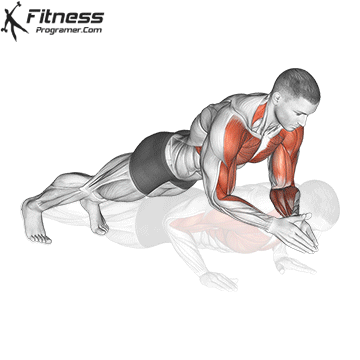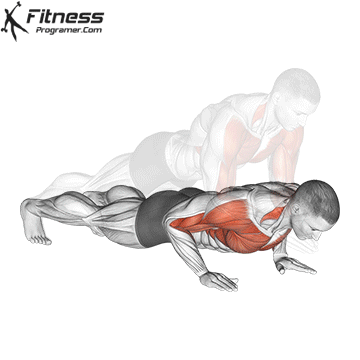
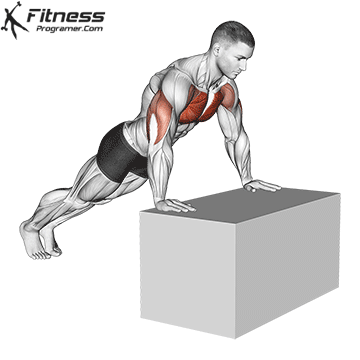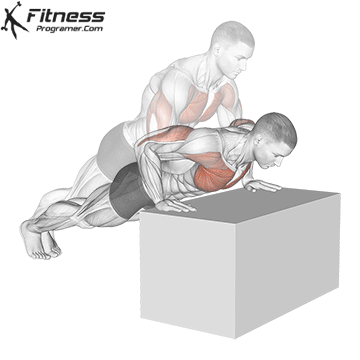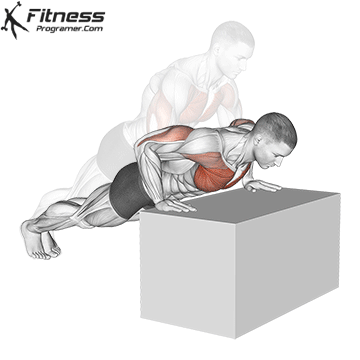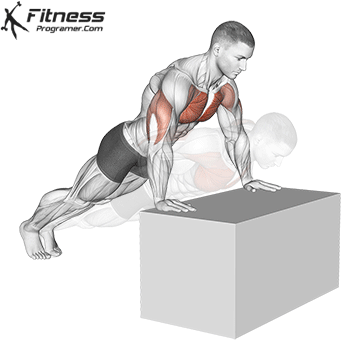
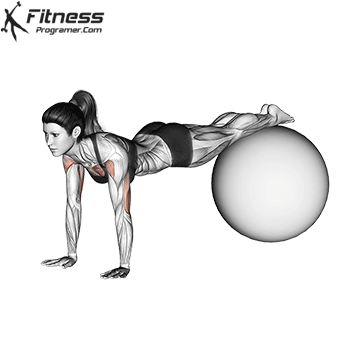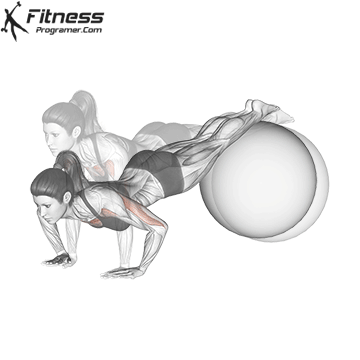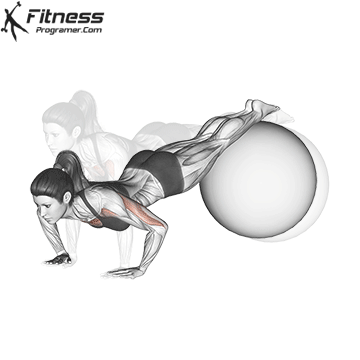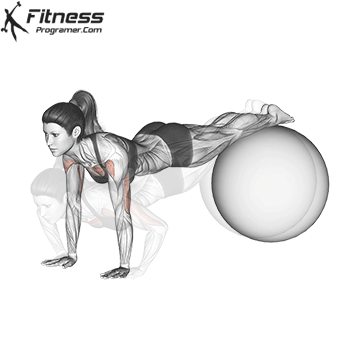
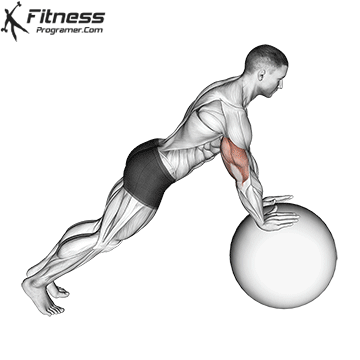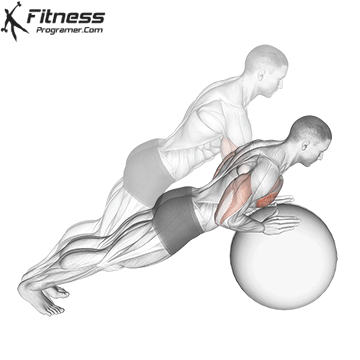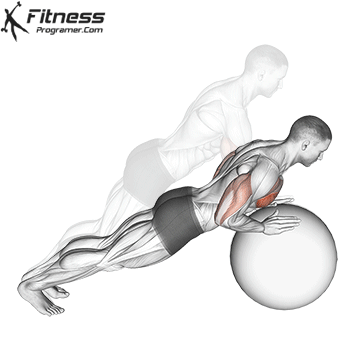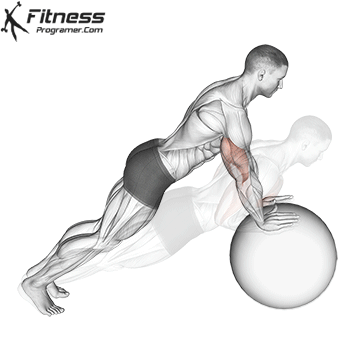
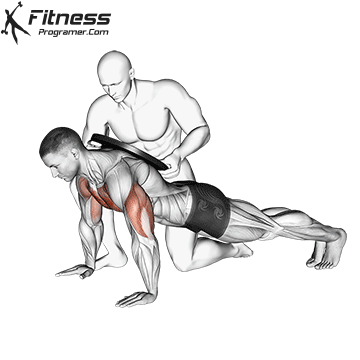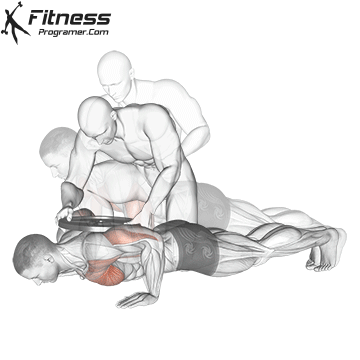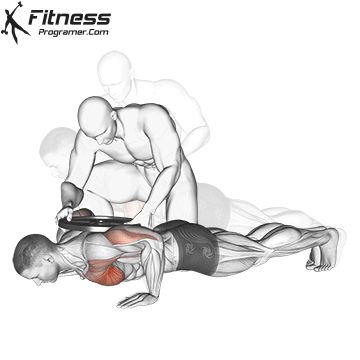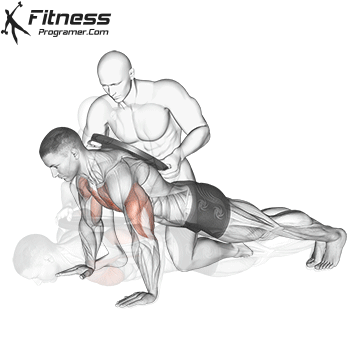
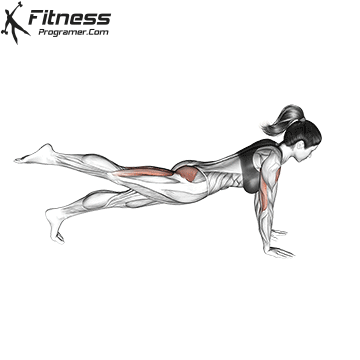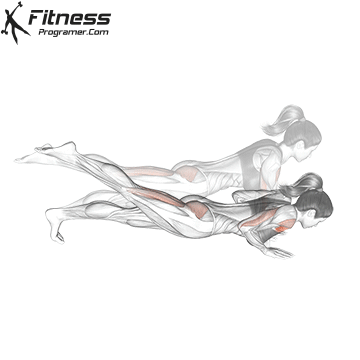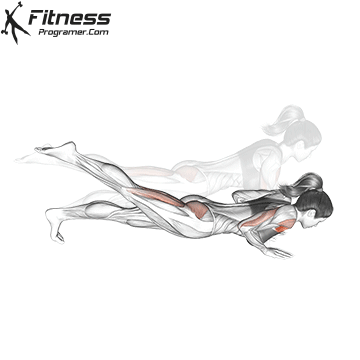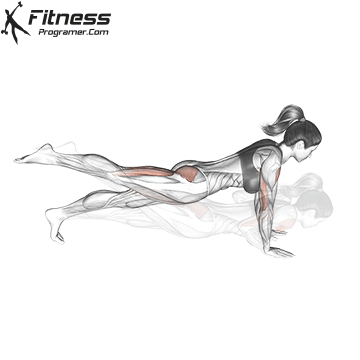
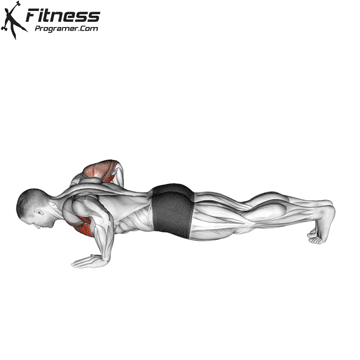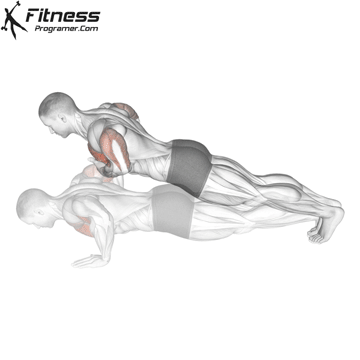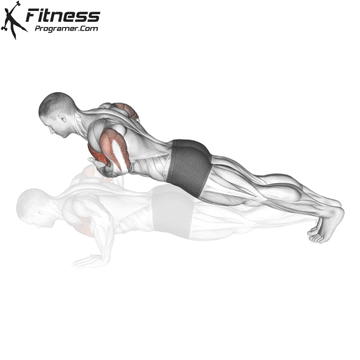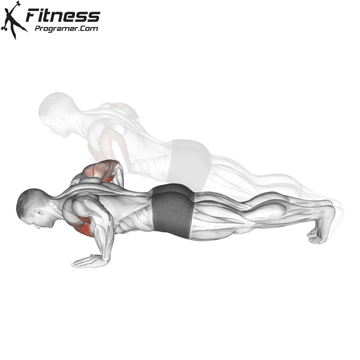
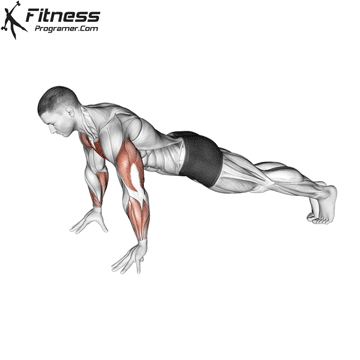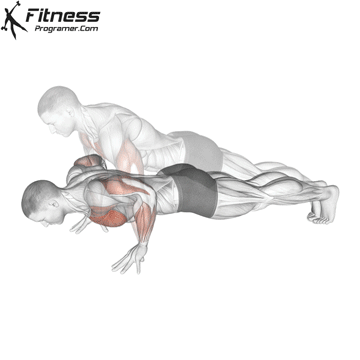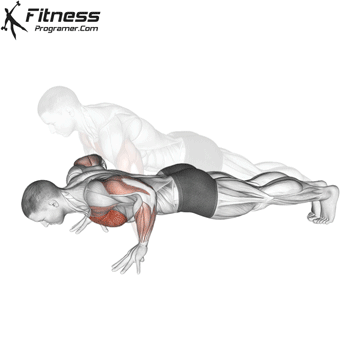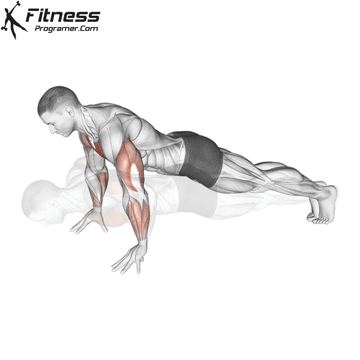
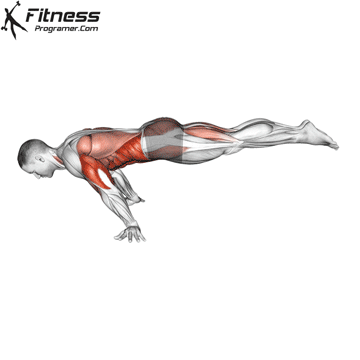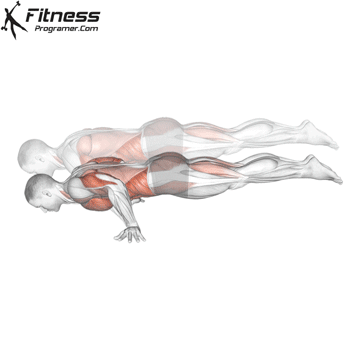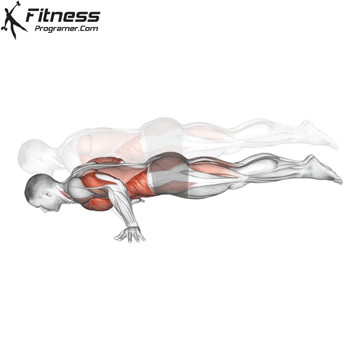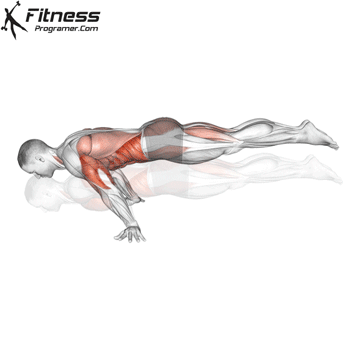
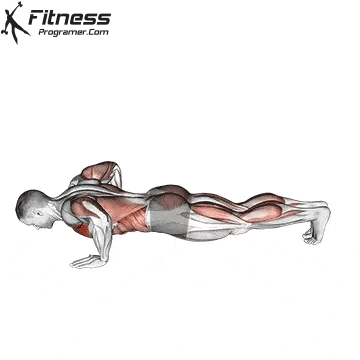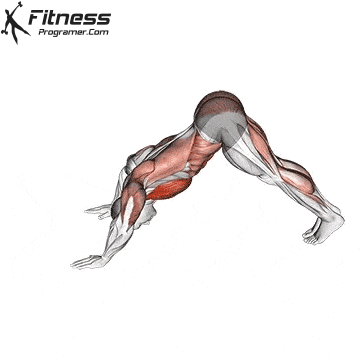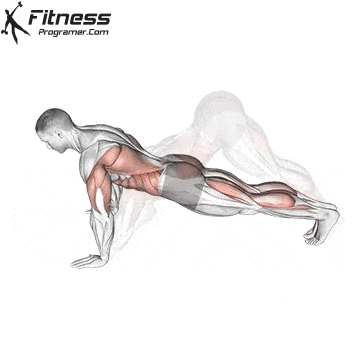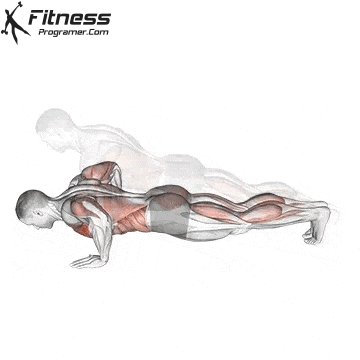
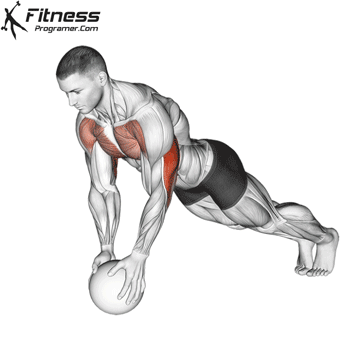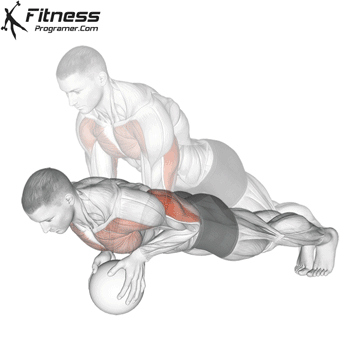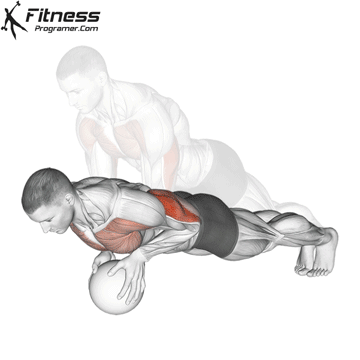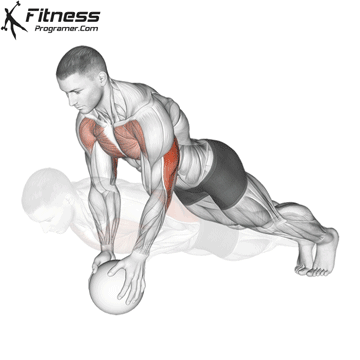
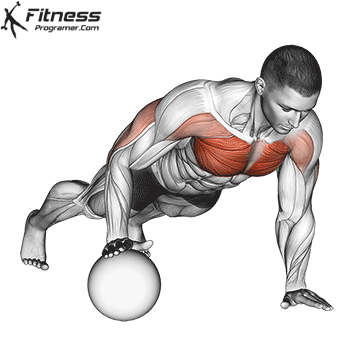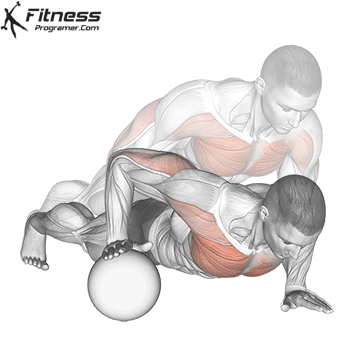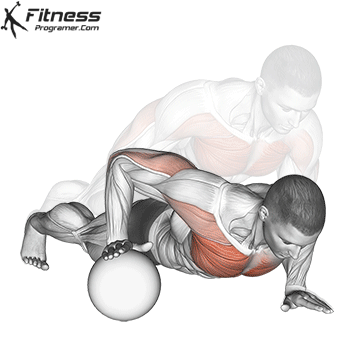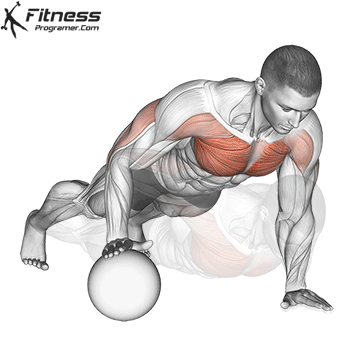
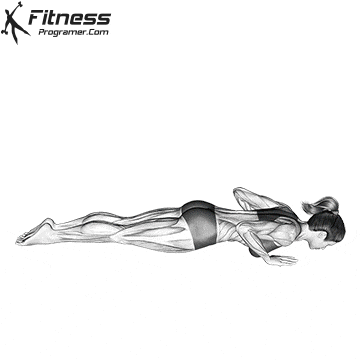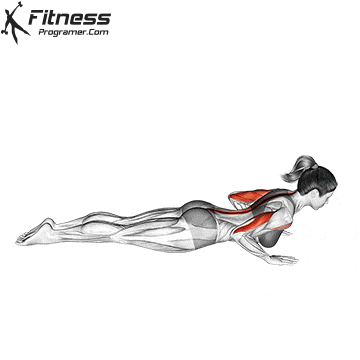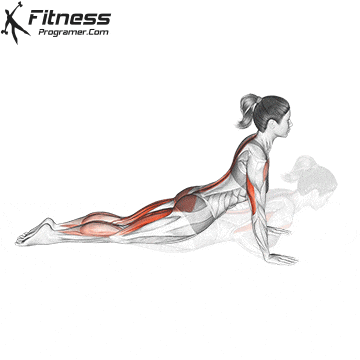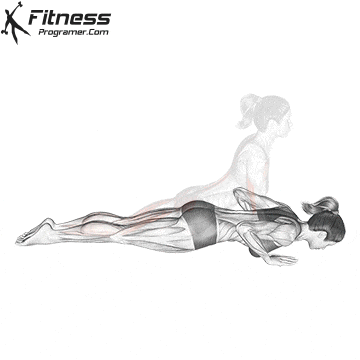
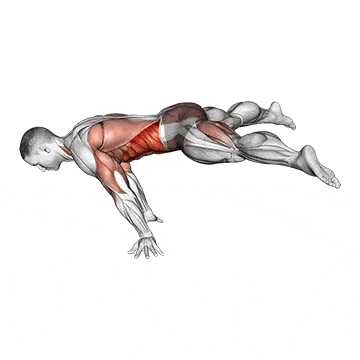
Push-up Overview
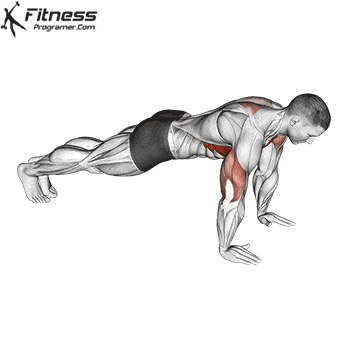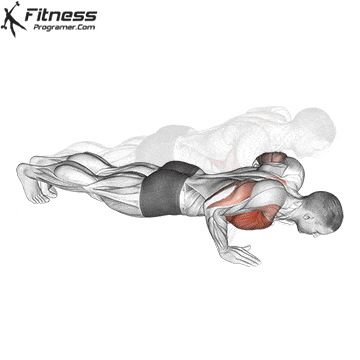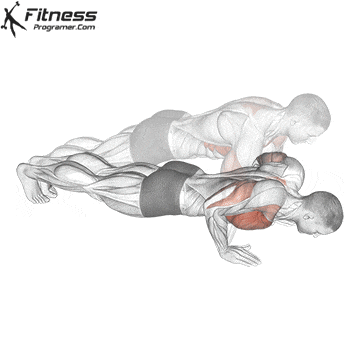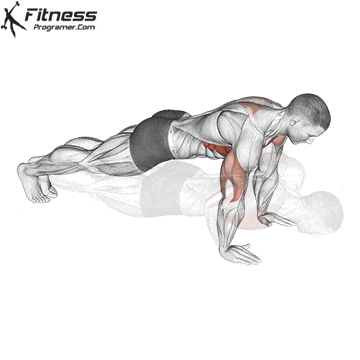
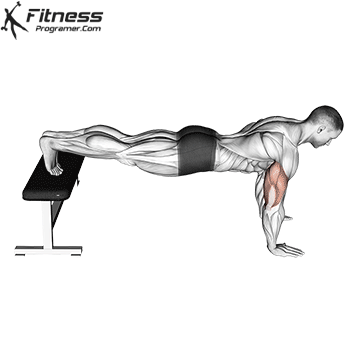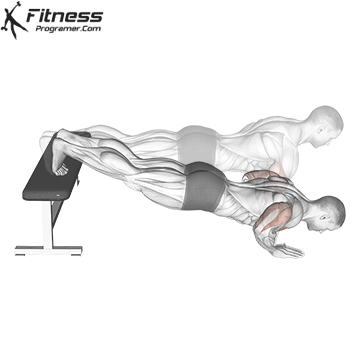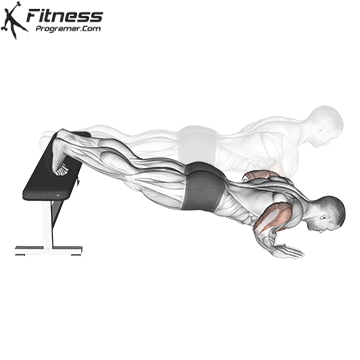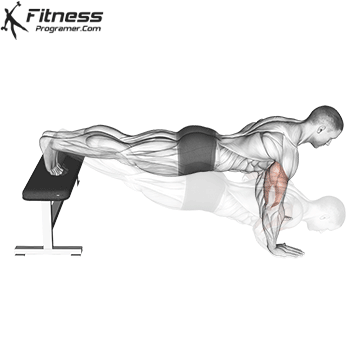
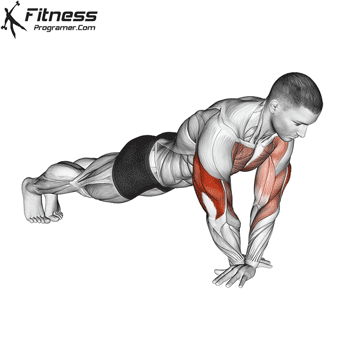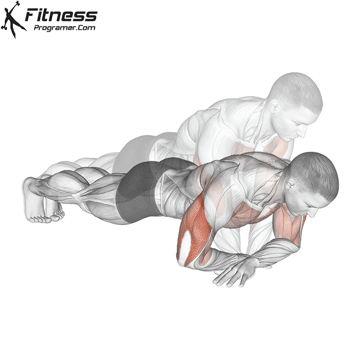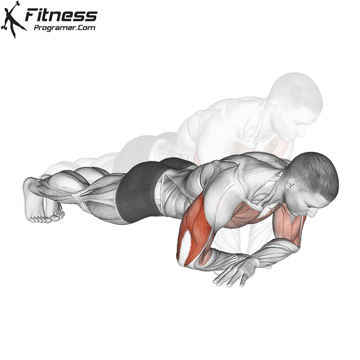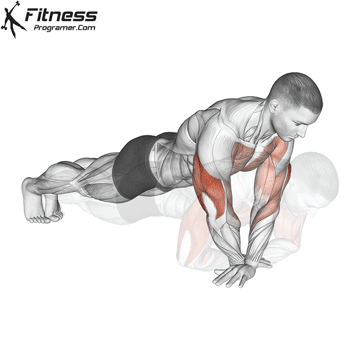
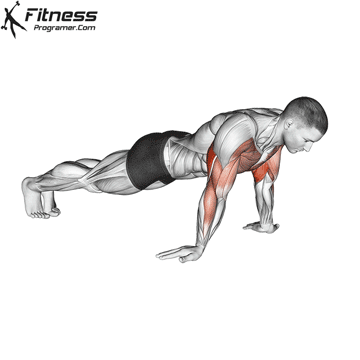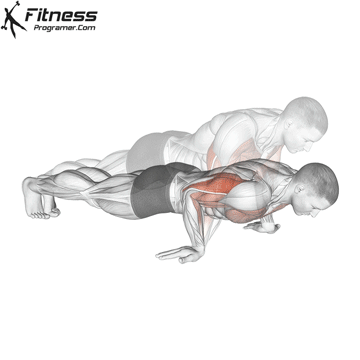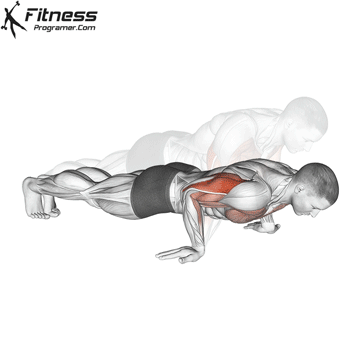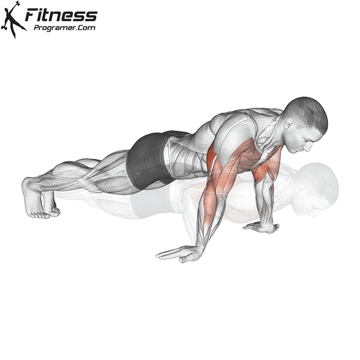
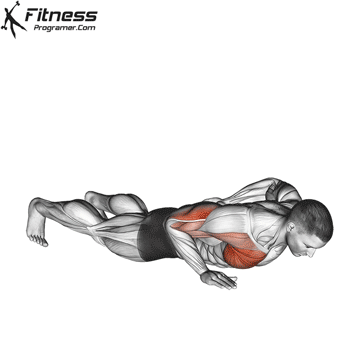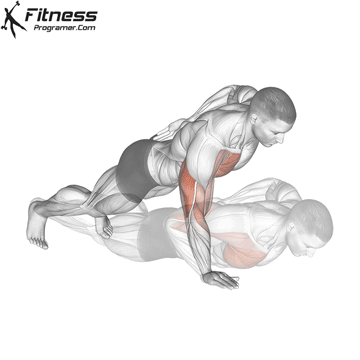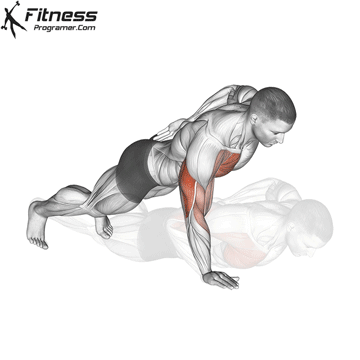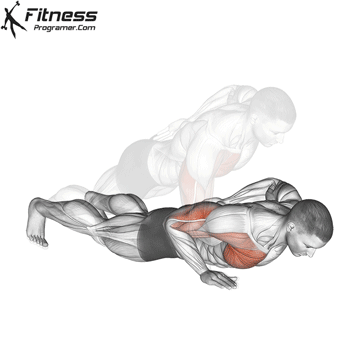
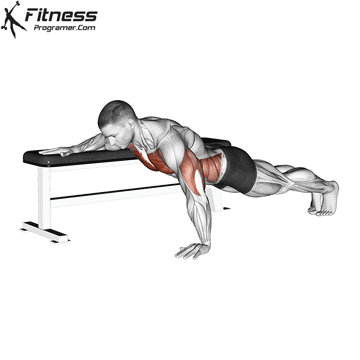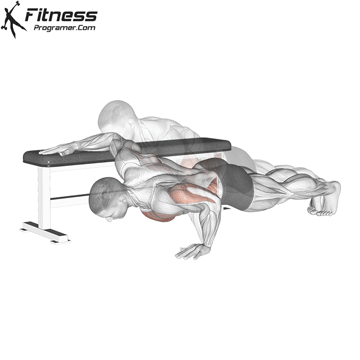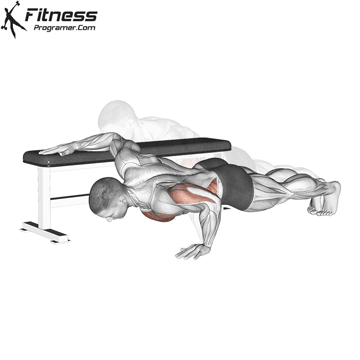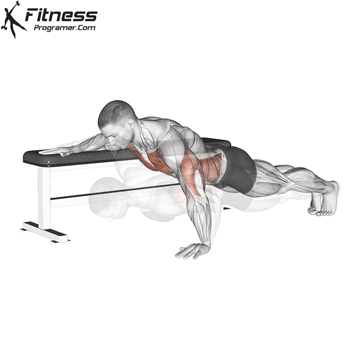
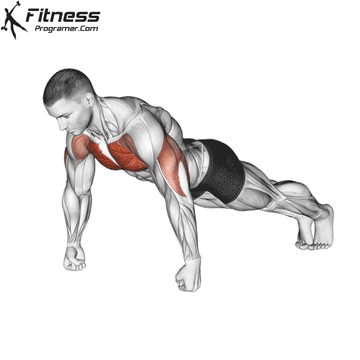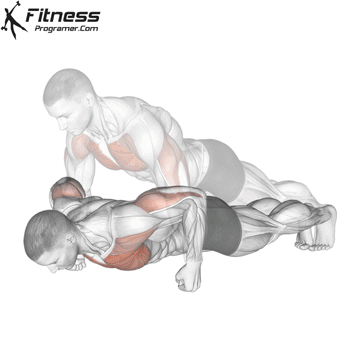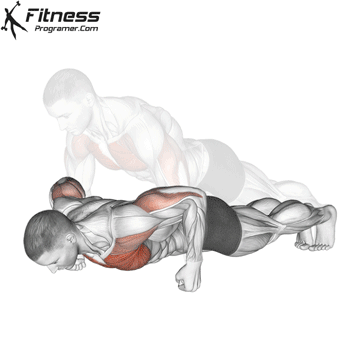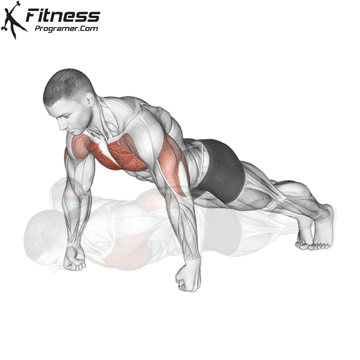
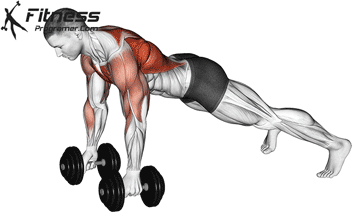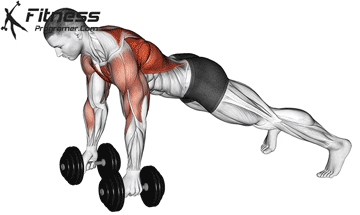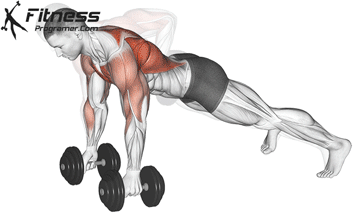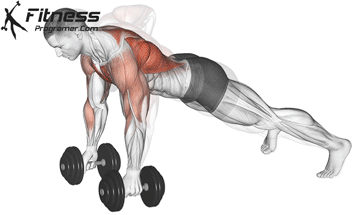
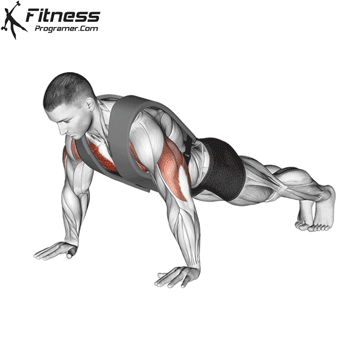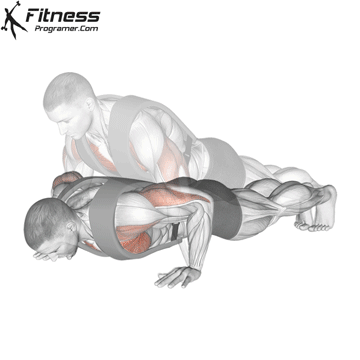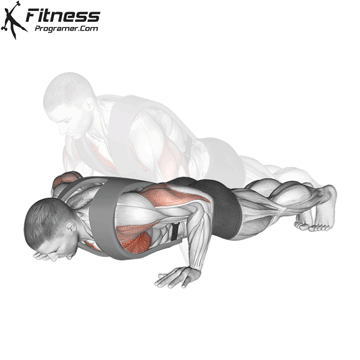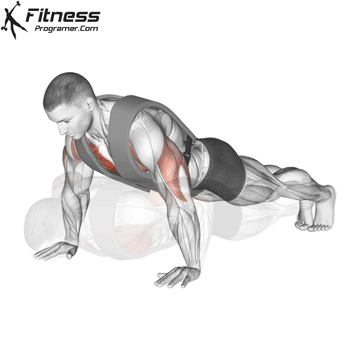
The push-up is one of the most effective bodyweight exercises for building upper body strength, endurance, and stability. It engages multiple muscle groups, including the chest, shoulders, triceps, and core. Suitable for all fitness levels, push-ups can be modified or progressed to match individual goals. It requires no equipment and is a fundamental movement used in calisthenic, strength training, sports conditioning, and rehabilitation programs.
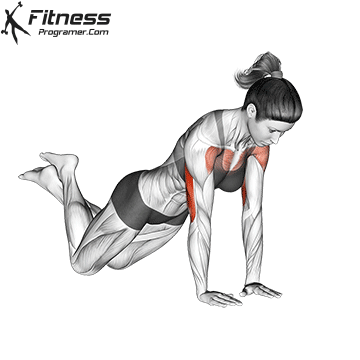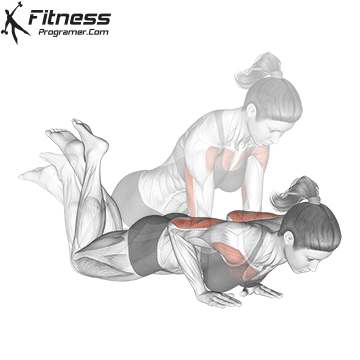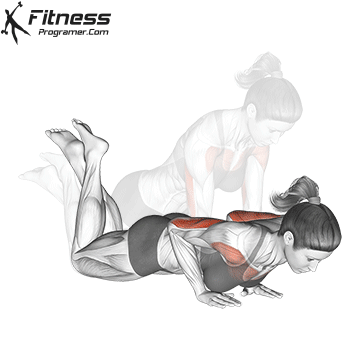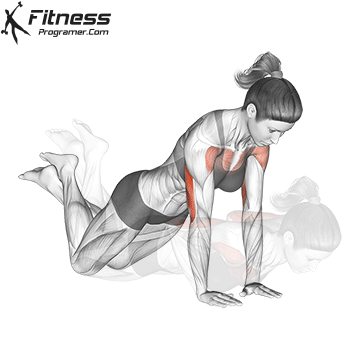
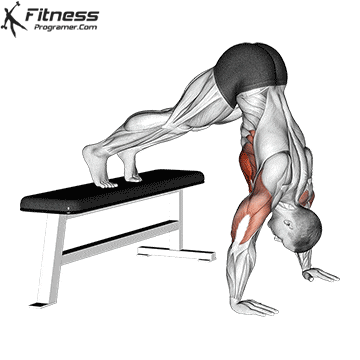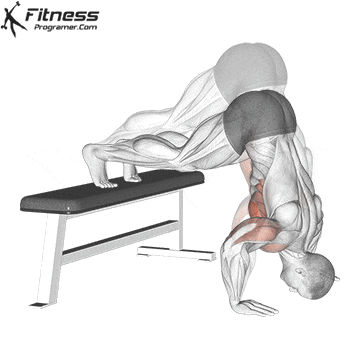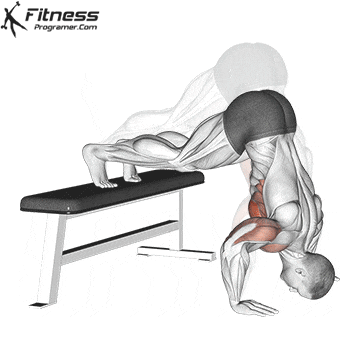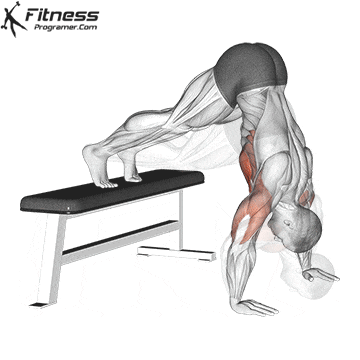
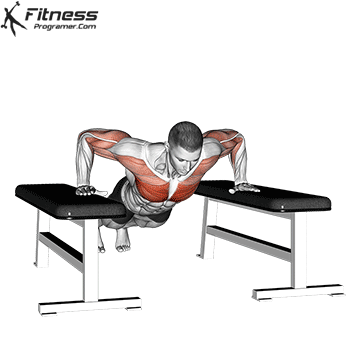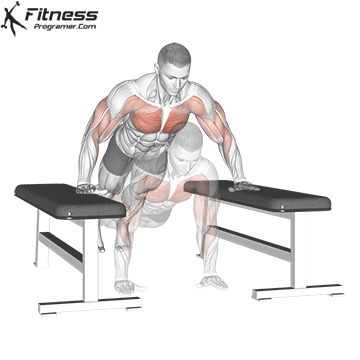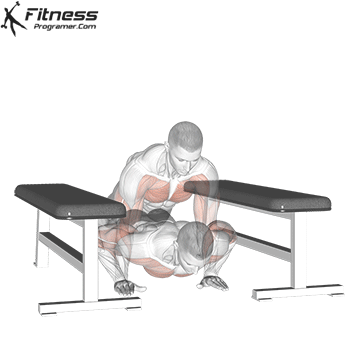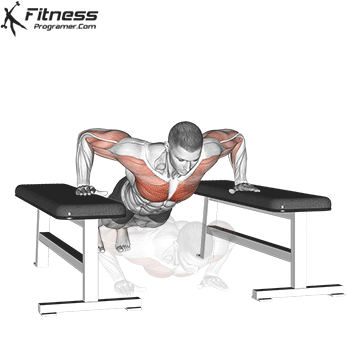
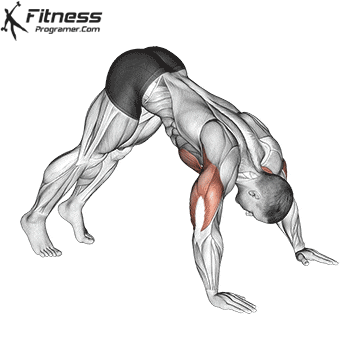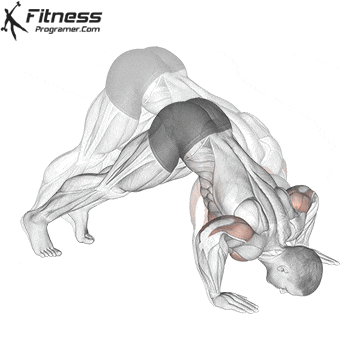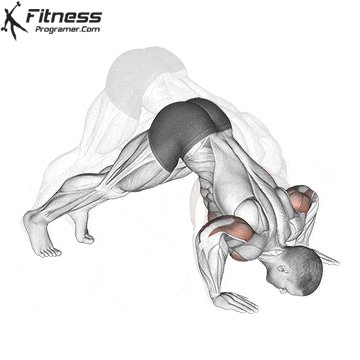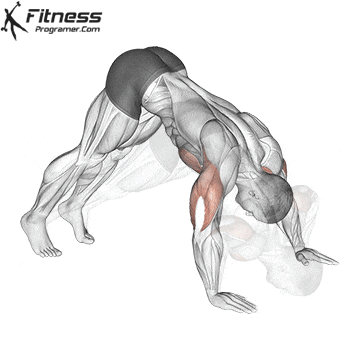
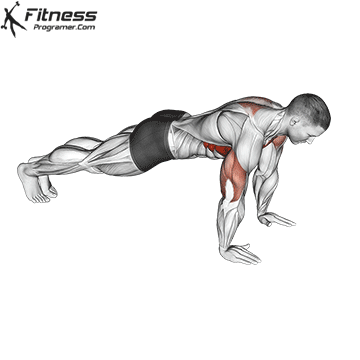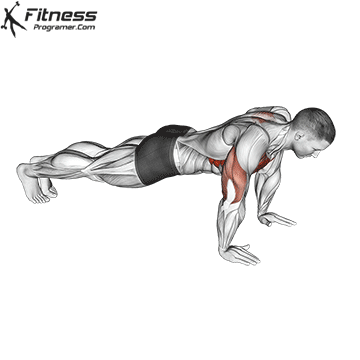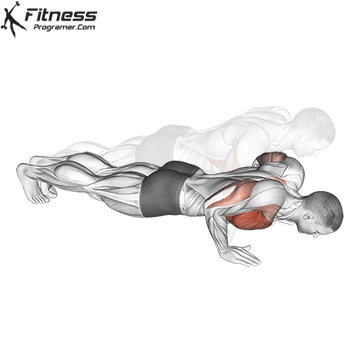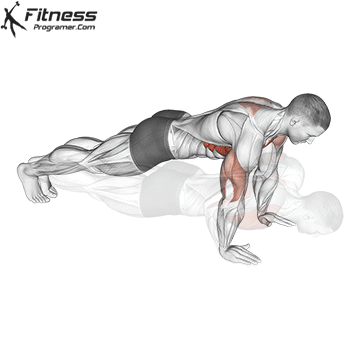
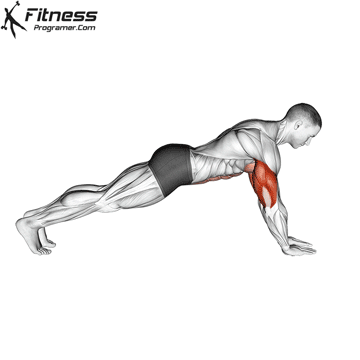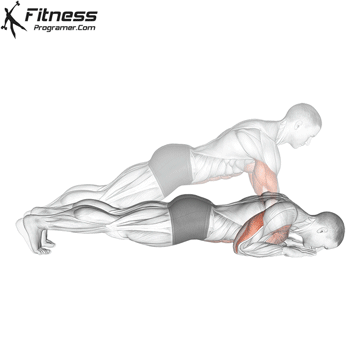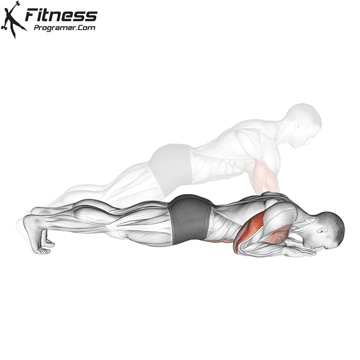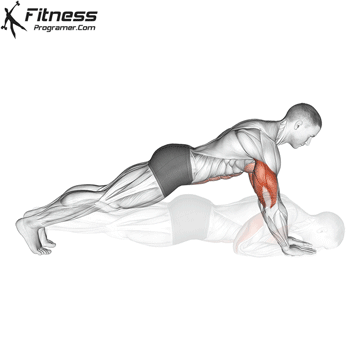
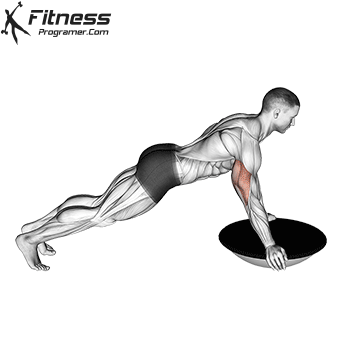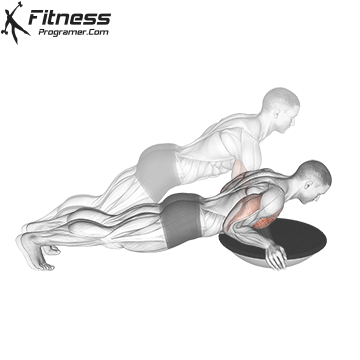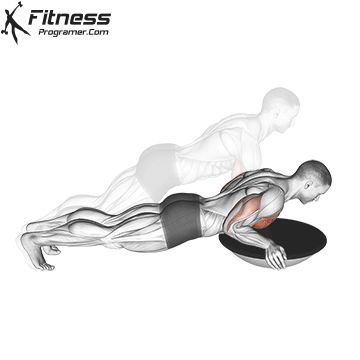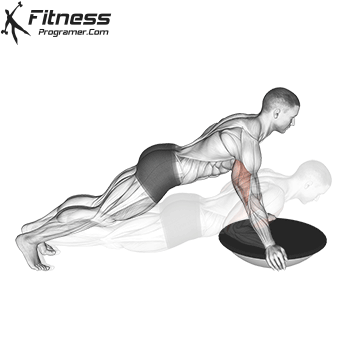
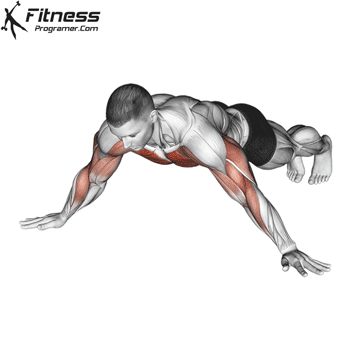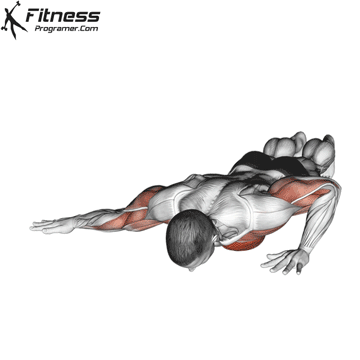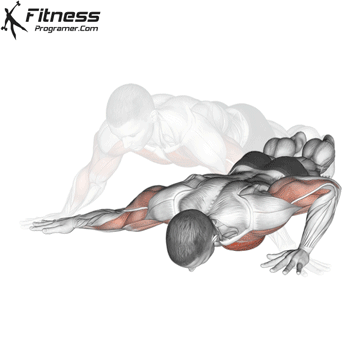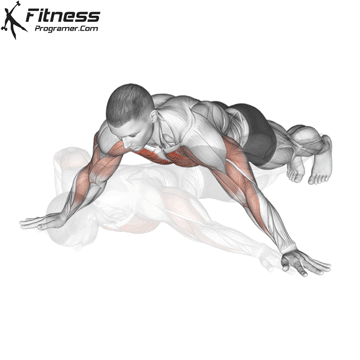
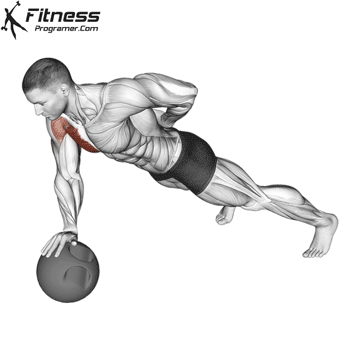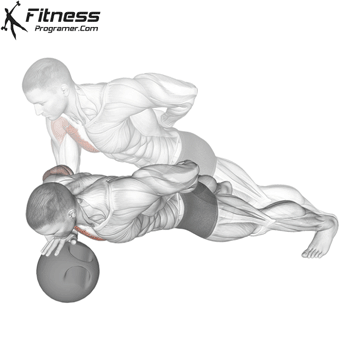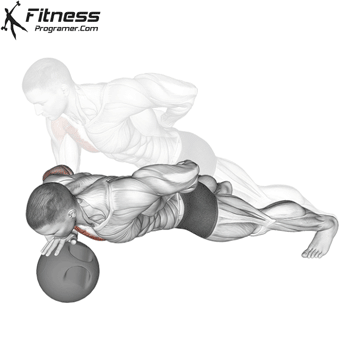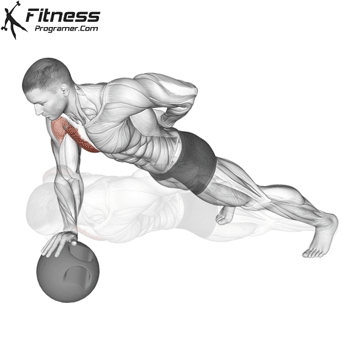
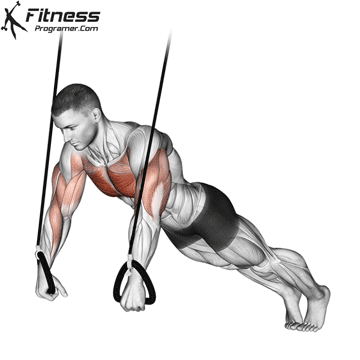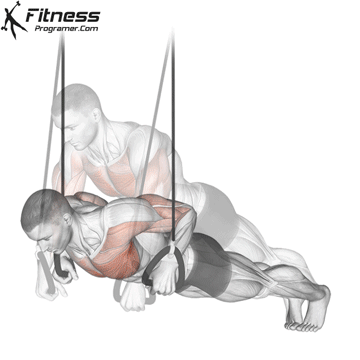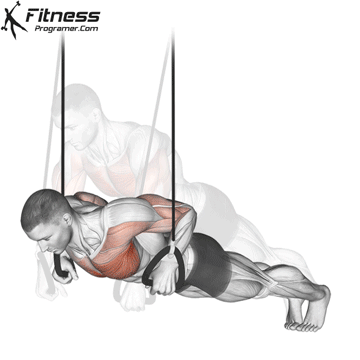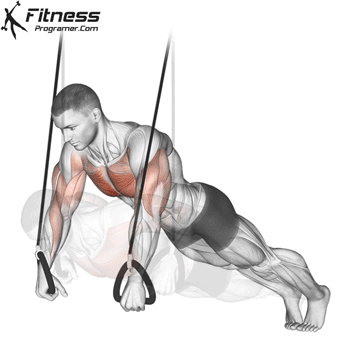
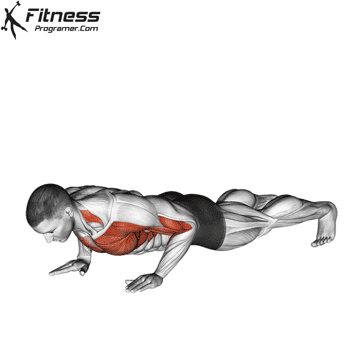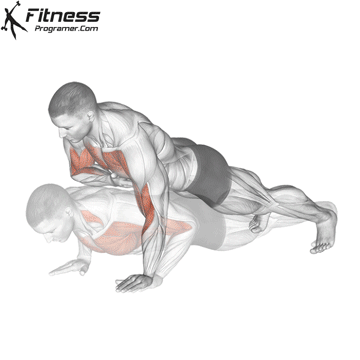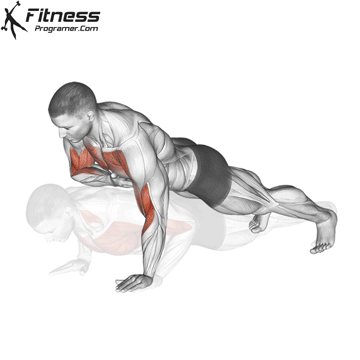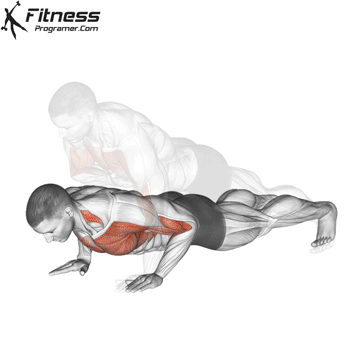
How to Perform a Push-Up:
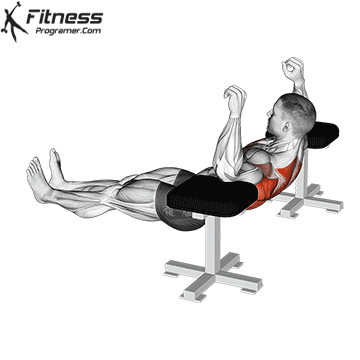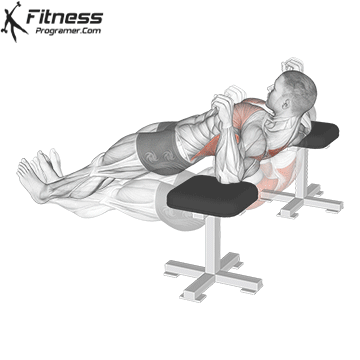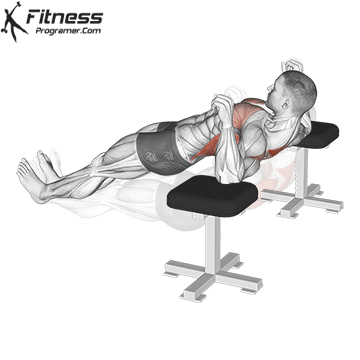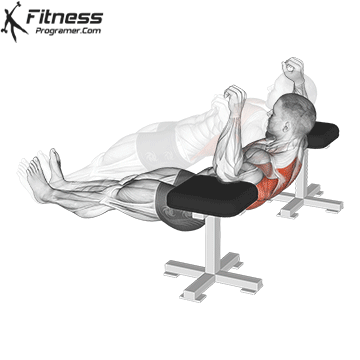
Starting Position:
- Begin in a high plank position with hands placed slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Keep your body in a straight line from head to heels.
- Engage your core and keep your neck neutral.
Lowering Phase:
- Inhale as you bend your elbows and lower your chest toward the ground.
- Keep your elbows at a 45-degree angle to your torso.
- Lower until your chest is just above the floor or as far as mobility allows.
Pressing Phase:
- Exhale as you push through your palms to return to the starting position.
- Fully extend your arms while maintaining core engagement.
Repetition and Breathing:
- Perform controlled reps at a steady pace to maximize muscle engagement.
Tips for Proper Form:
- Keep your core tight to prevent your lower back from sagging.
- Maintain a straight body line from head to heels.
- Avoid locking out your elbows at the top of the movement.
- Place your hands firmly on the ground for better stability.
Common Mistakes:
- Allowing the Hips to Sag: This reduces core engagement and may strain the lower back.
- Flaring the Elbows: Keeping elbows too wide places stress on the shoulders.
- Incomplete Range of Motion: Performing half-reps limits muscle activation and strength gains.
- Holding the Breath: Breathing properly ensures oxygen flow and better endurance.
Benefits of Push-Ups:
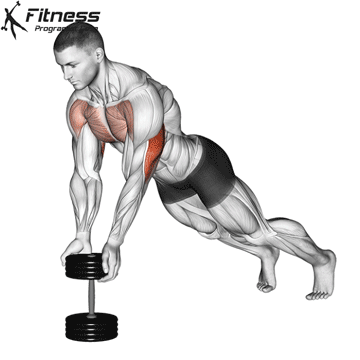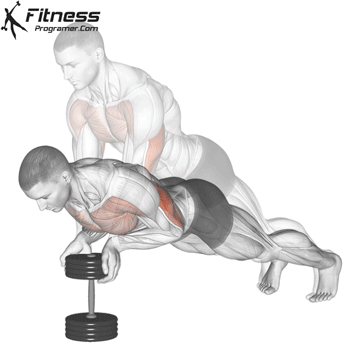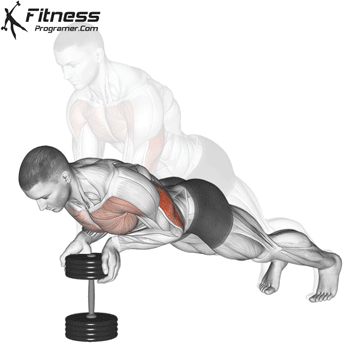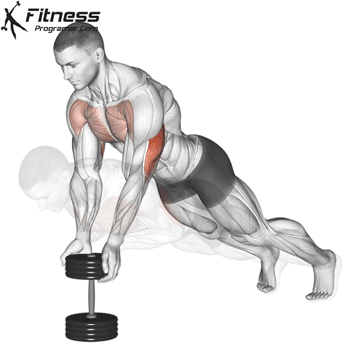
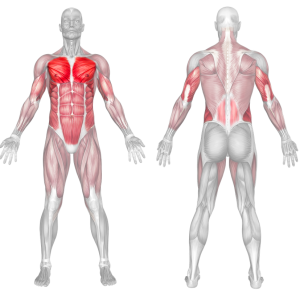
- Strengthens Chest Muscles: Push-ups primarily target the pectoral muscles (chest), helping to build and tone the chest muscles, which can improve your upper body strength and appearance.
- Strengthens Triceps: Push-ups also engage the triceps, the muscles at the back of your upper arm. This helps to strengthen and tone these muscles.
- Strengthens Shoulders: The anterior deltoids in your shoulders are engaged during push-ups, contributing to shoulder strength and stability.
- Core Stability: Push-ups require you to engage your core muscles to maintain a straight body position. This helps improve core strength and stability.
- Improves Posture: Strengthening the chest, shoulders, and core can lead to improved posture, as these muscles play a key role in maintaining an upright position.
- Enhances Upper Body Endurance: Regular push-up practice can increase your upper body endurance, allowing you to perform other exercises and activities more effectively.
- Boosts Metabolism: Like other strength-training exercises, push-ups can help increase your metabolism, which may assist with weight management and fat loss.
- Increases Bone Health: Weight-bearing exercises like push-ups can help improve bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis as you age.
- Low Impact: Push-ups are generally low-impact, making them suitable for individuals with joint issues or those who want to avoid high-impact exercises.
- Functional Strength: Push-ups mimic functional movements, such as pushing a heavy object or getting up from the ground. This can improve your ability to perform everyday activities.
- Improved Mental Health: Exercise, including push-ups, can release endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. Regular physical activity is associated with improved mental well-being and reduced stress.
- Heart Health: Engaging in regular exercise like push-ups can contribute to better cardiovascular health by lowering the risk of heart disease and improving blood circulation.
How to Incorporate Push-Ups Into Your Routine:
- Beginner Routine: Perform 3 sets of 10–15 reps with proper form.
- Strength Progression: Add weighted push-ups or resistance bands for added difficulty.
- Endurance Training: Perform high-rep push-up sets with minimal rest.
- Full-Body Workouts: Combine with squats, lunges, and planks for a complete session.
Push-up Muscles Worked
Push-up Variations
Push-ups can be modified and progressed to suit your fitness level. You can start with knee push-ups and work your way up to more challenging variations like diamond push-ups or one-arm push-ups.