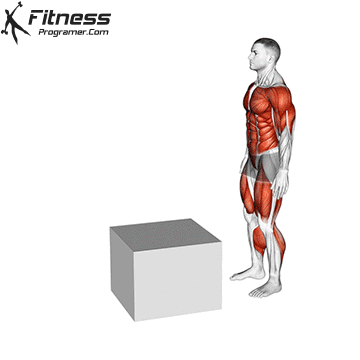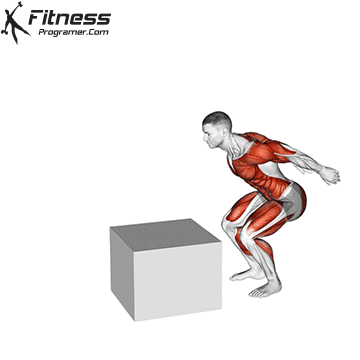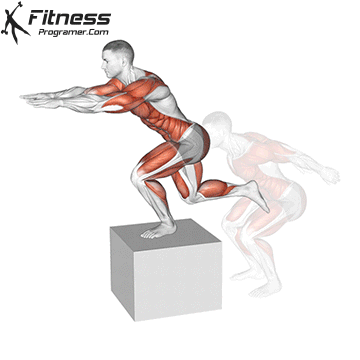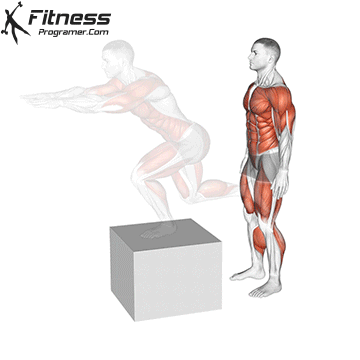
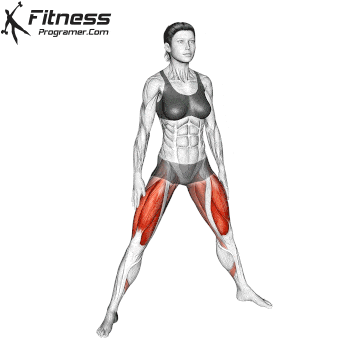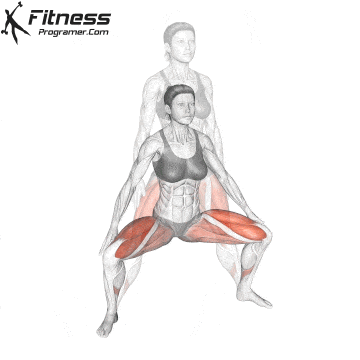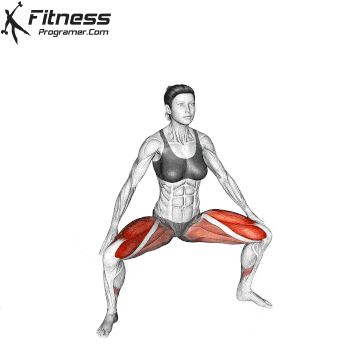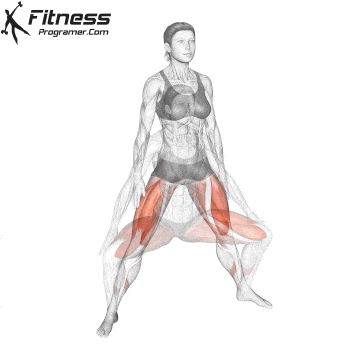
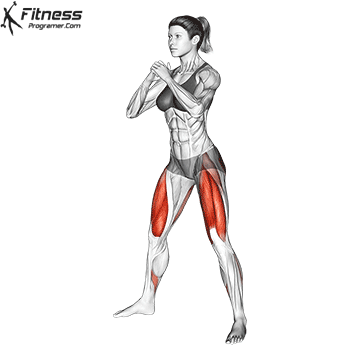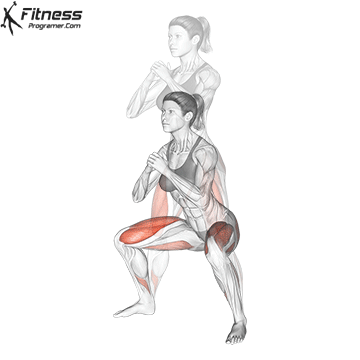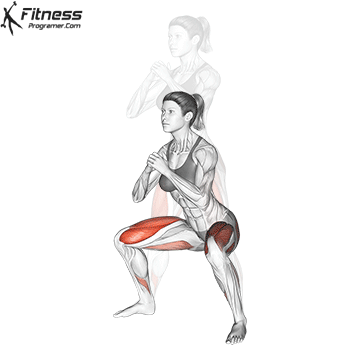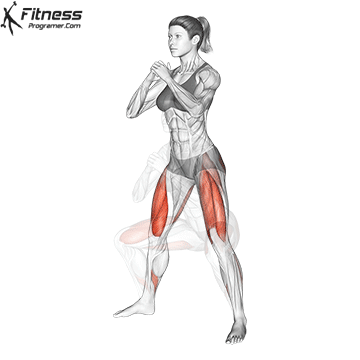
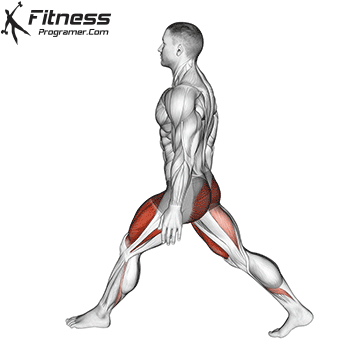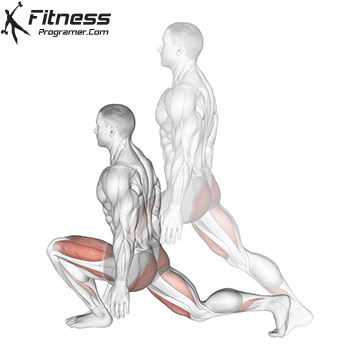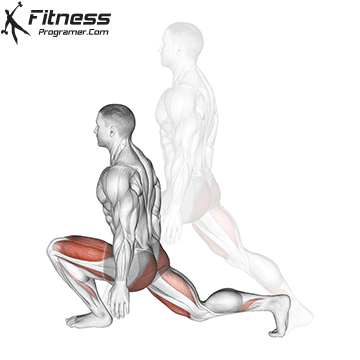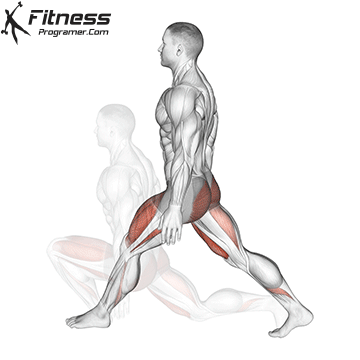
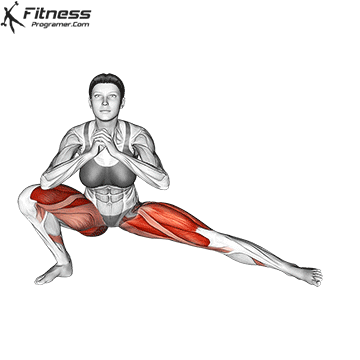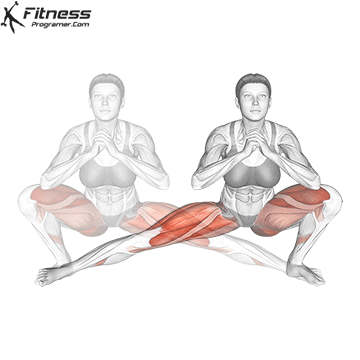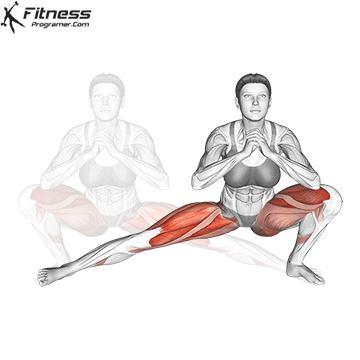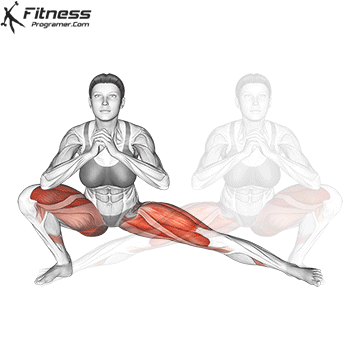
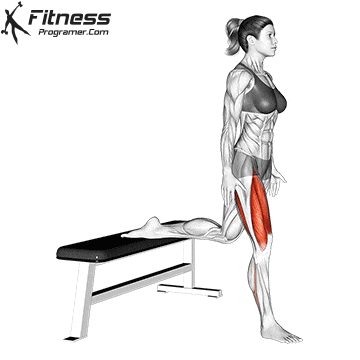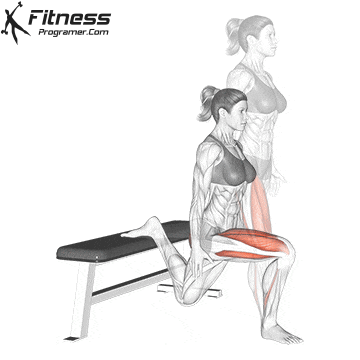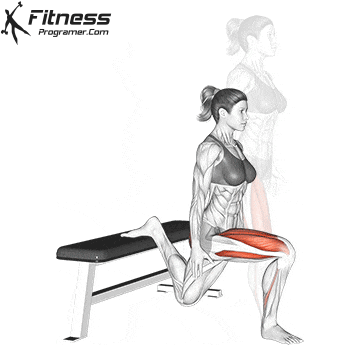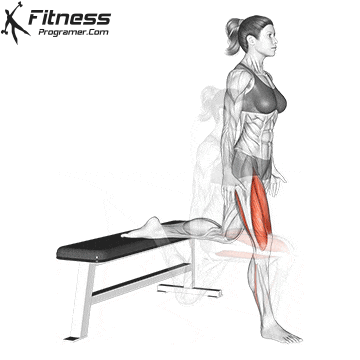
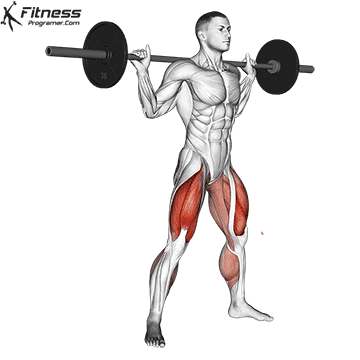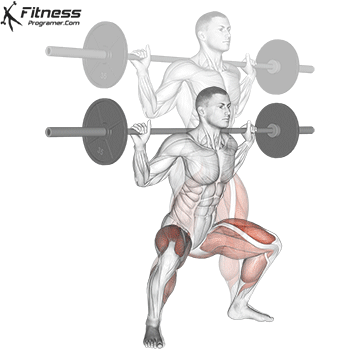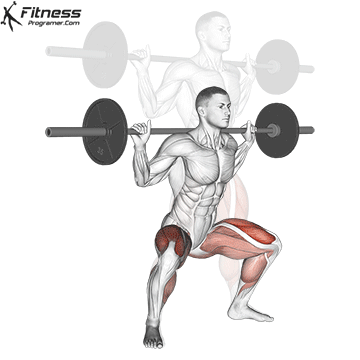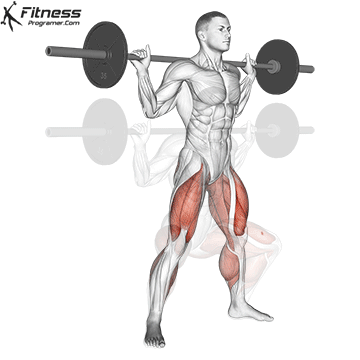
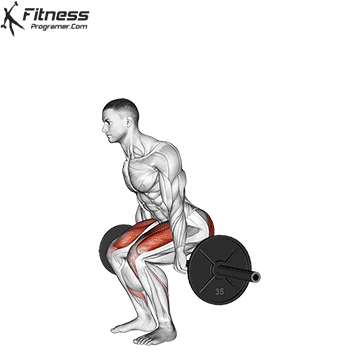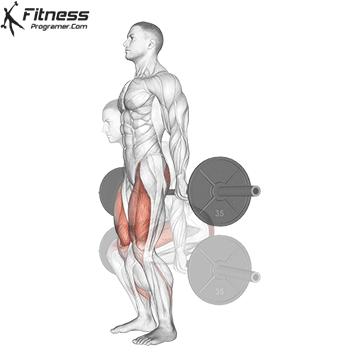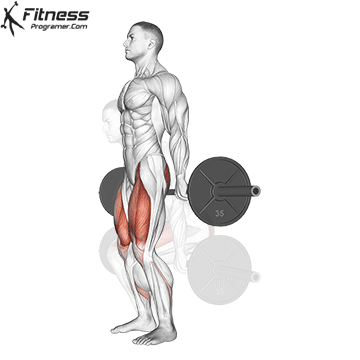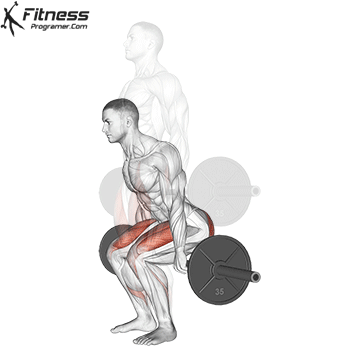
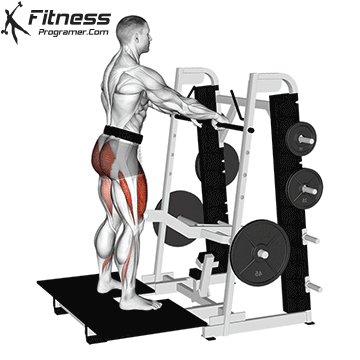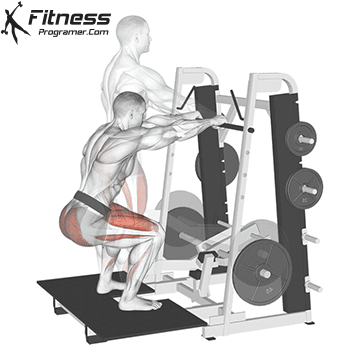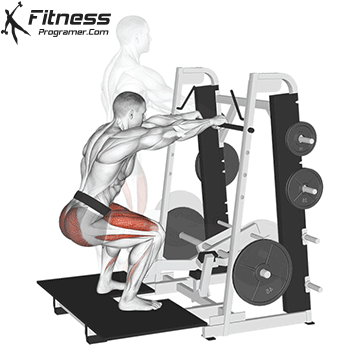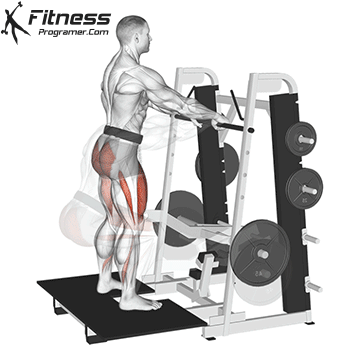
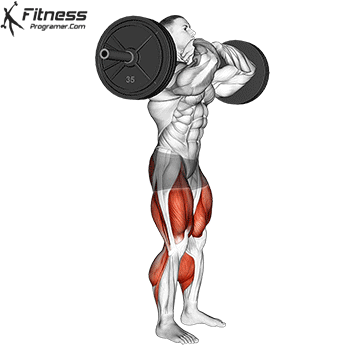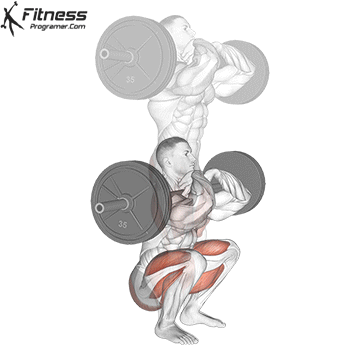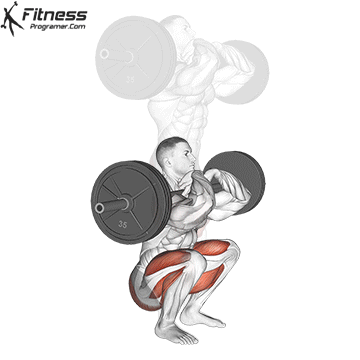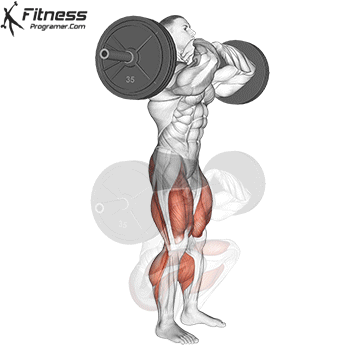
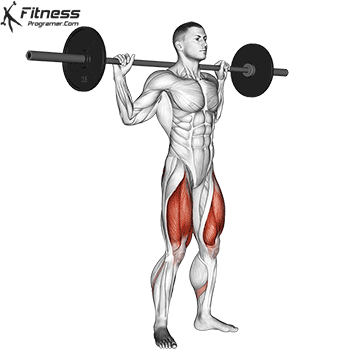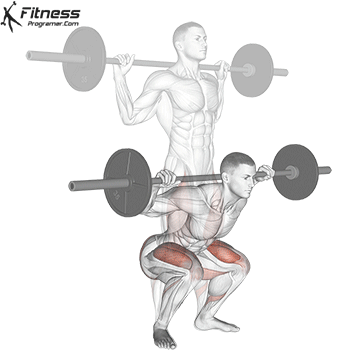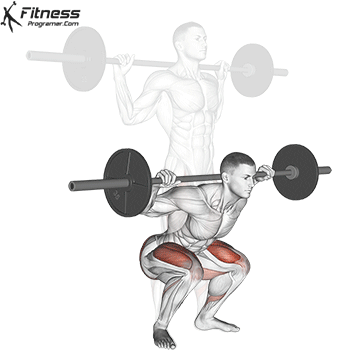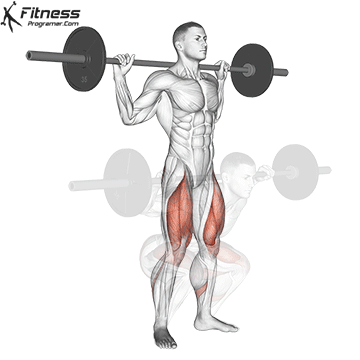
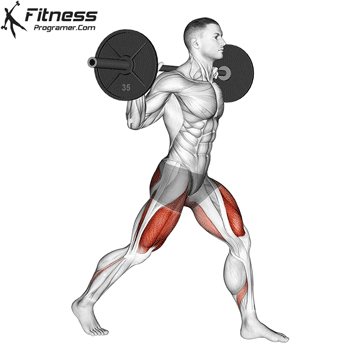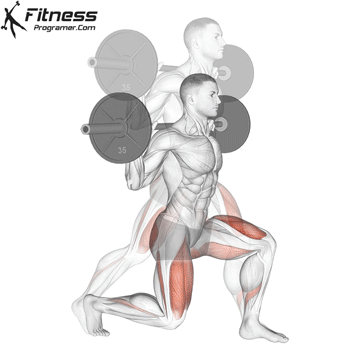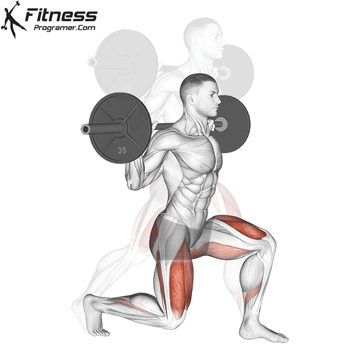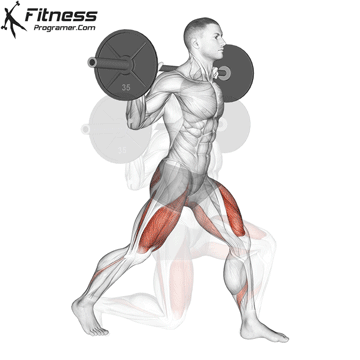
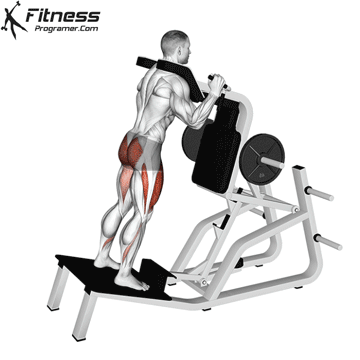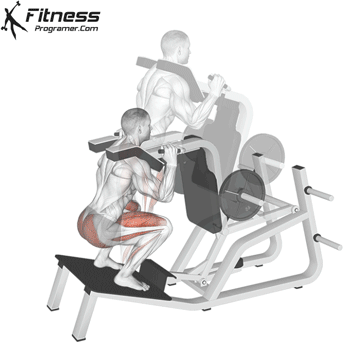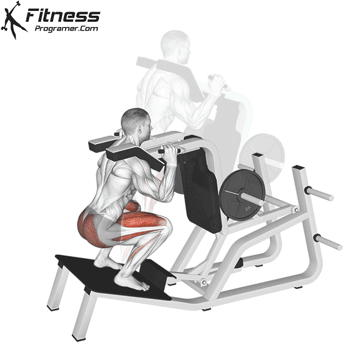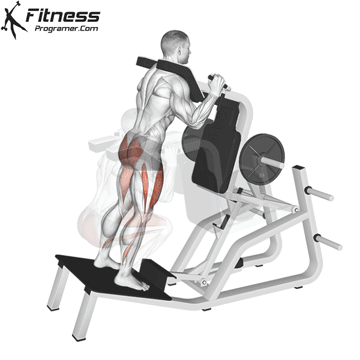
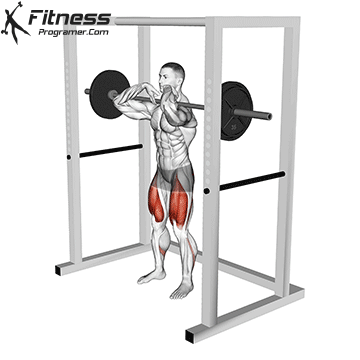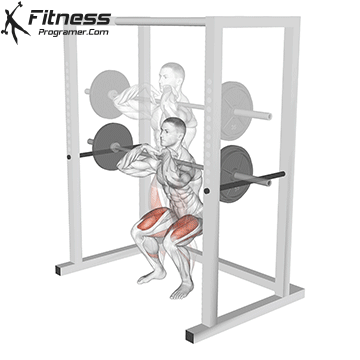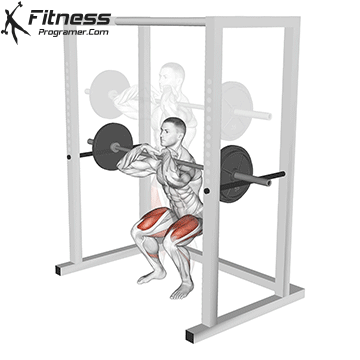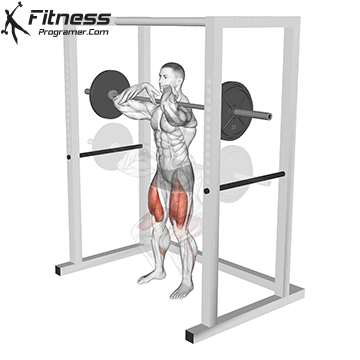
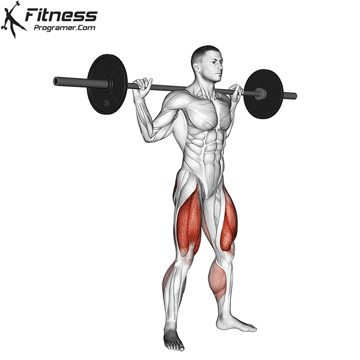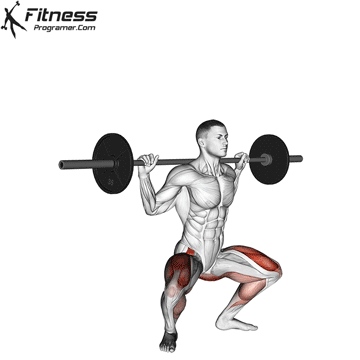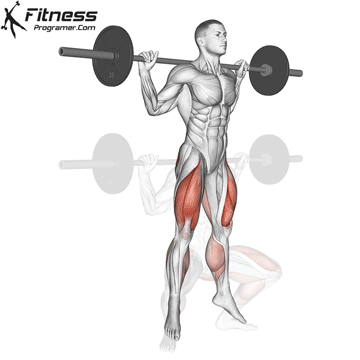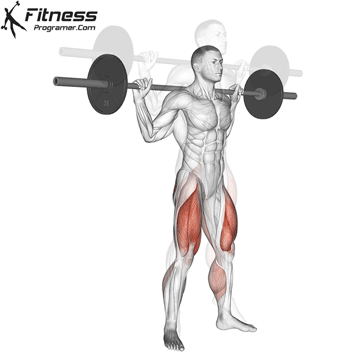
How To: Long Jump
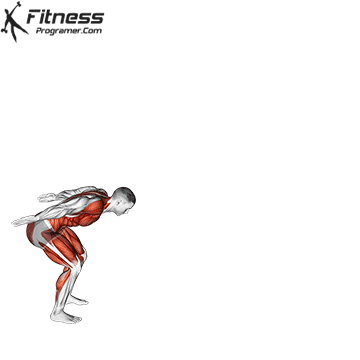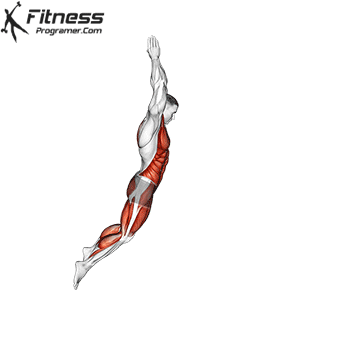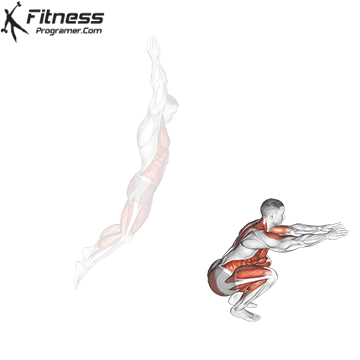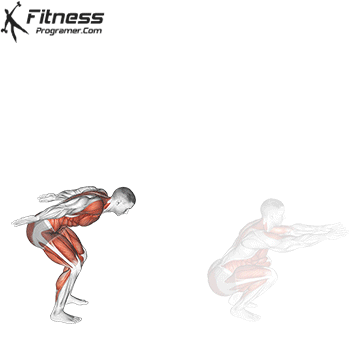
Dumbbell Burpees
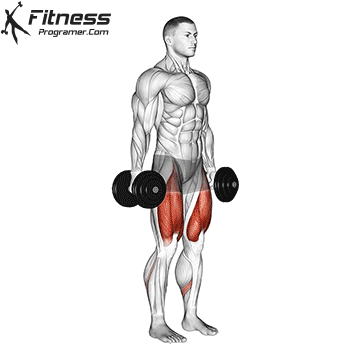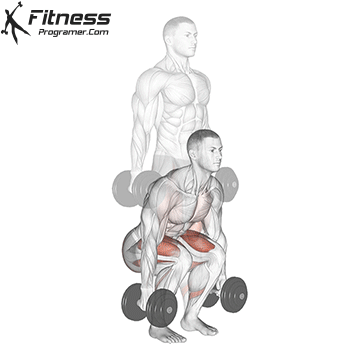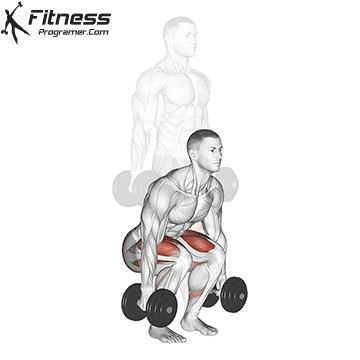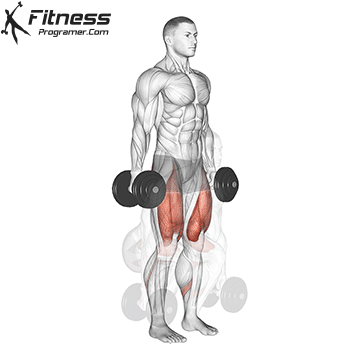
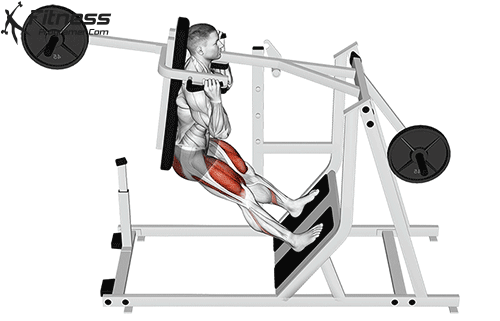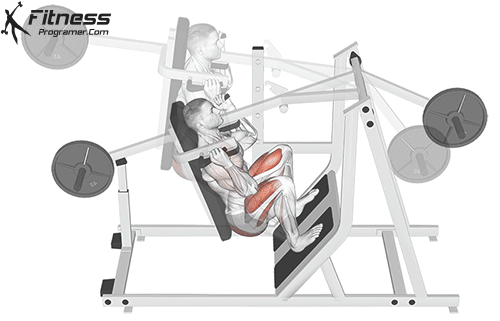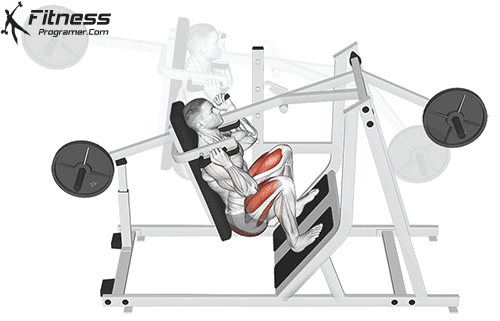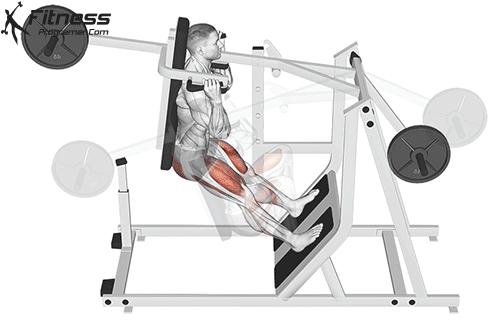
The Dumbbell Burpee is a dynamic and challenging full-body exercise that combines the elements of a traditional burpee with the added resistance of dumbbells. It targets the abs, hips, thighs, and legs, providing a cardiovascular and strength workout in one. This exercise can offer various benefits to your overall fitness and health.
How to do:
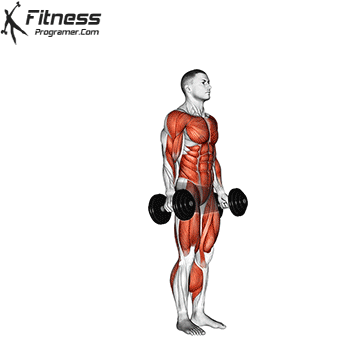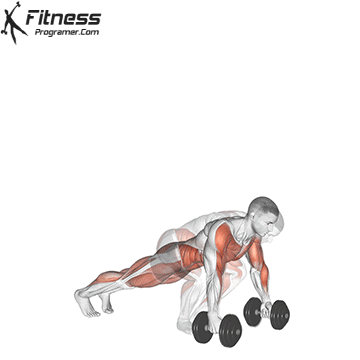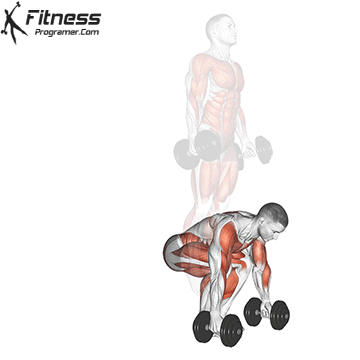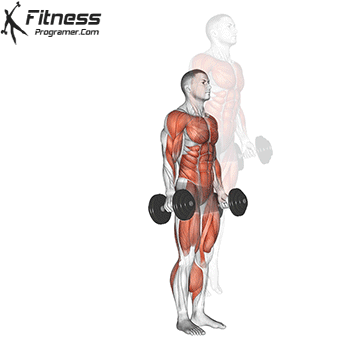
- Starting Position:
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand, standing with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Squat and Place Dumbbells:
- Lower into a squat position while holding the dumbbells at your sides.
- Plank Position:
- Place the dumbbells on the floor in front of you and jump or step your feet back into a plank position, keeping your body in a straight line.
- Push-Up (Optional):
- Perform a push-up while maintaining a straight back. This step is optional but can be included for an additional challenge.
- Jump or Step Forward:
- Jump or step your feet back toward your hands, returning to the squat position.
- Stand and Press:
- Explosively stand up from the squat position and press the dumbbells overhead.
- Repeat:
- Return to the starting position and repeat the sequence for the desired number of repetitions.
Dumbbell Burpees: Benefits
- Full-Body Workout: Dumbbell burpees engage multiple muscle groups, including the chest, shoulders, arms, core, and legs. This makes it an effective full-body exercise that can help improve overall strength and muscle tone.
- Cardiovascular Endurance: Burpees, in general, are known for their cardiovascular benefits. Adding dumbbells increases the intensity, making it an excellent way to improve cardiovascular endurance, burn calories, and enhance your aerobic fitness.
- Strength Building: The addition of dumbbells provides resistance, promoting strength development in the upper body (especially the arms and shoulders). This can contribute to improved functional strength for everyday activities.
- Caloric Burn: Dumbbell burpees are a high-intensity exercise, leading to an increased calorie burn. This can be beneficial for weight management and fat loss when combined with a proper diet.
- Functional Movement: Dumbbell burpees involve a combination of movements, including squatting, jumping, push-ups, and lifting weights. These functional movements mimic real-life activities, helping to improve overall coordination and movement patterns.
- Time Efficiency: Dumbbell burpees are a compound exercise that targets multiple muscle groups simultaneously. This makes them a time-efficient option for those looking to get a challenging workout in a short amount of time.
- Variety in Workouts: Adding dumbbells to burpees introduces variety to your workout routine. This can be important for preventing boredom and keeping your fitness routine interesting and challenging.
- Adaptability: Dumbbell burpees can be adapted to different fitness levels by adjusting the weight of the dumbbells or modifying the intensity. This makes them suitable for both beginners and advanced exercisers.
- Core Engagement: The burpee component of the exercise involves a plank position and jumping, which engages the core muscles. This can contribute to improved core strength and stability.
- Increased Metabolism: High-intensity exercises like dumbbell burpees can lead to an increased post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), also known as the afterburn effect. This means your body continues to burn calories at an elevated rate even after you’ve finished exercising.
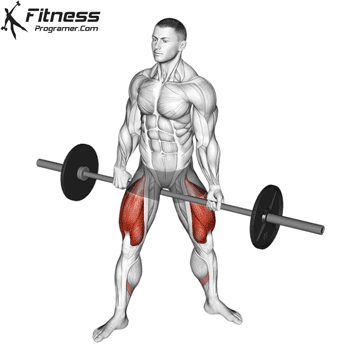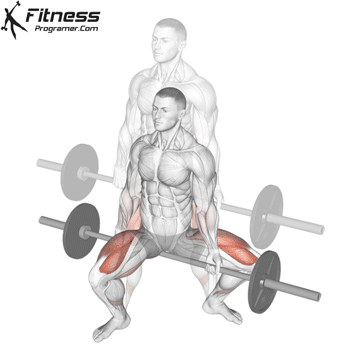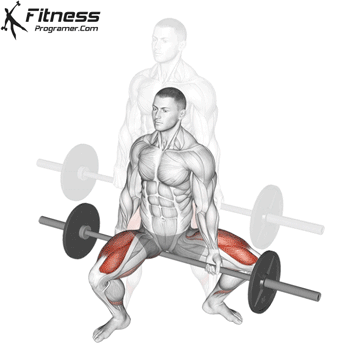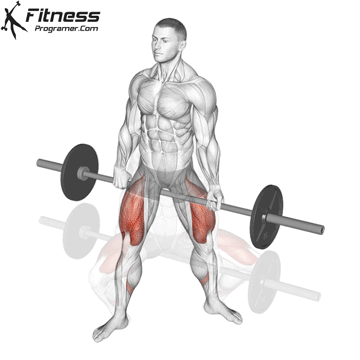
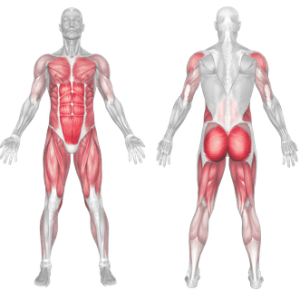
Dumbbell Burpees: Muscles Worked
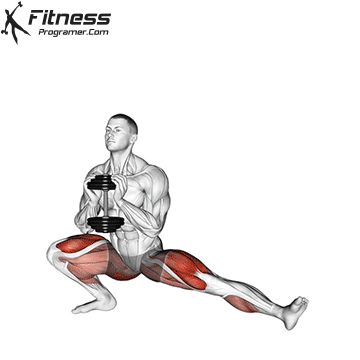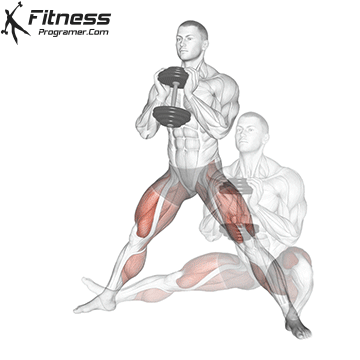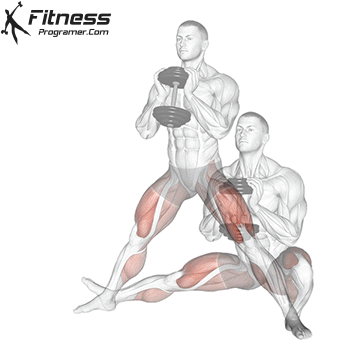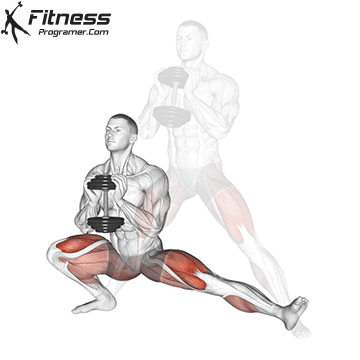
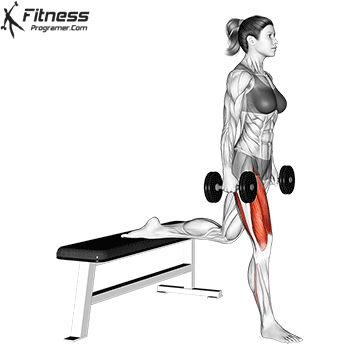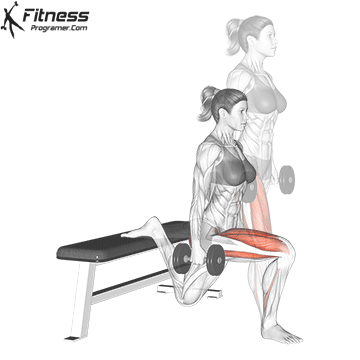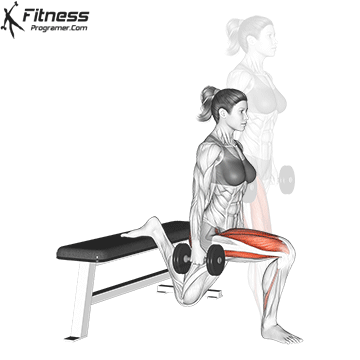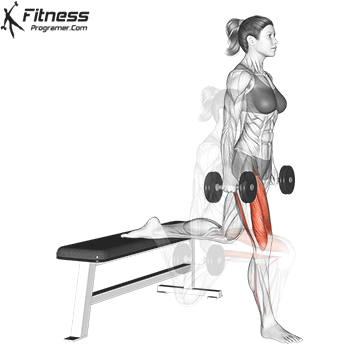
How to do Ski Step
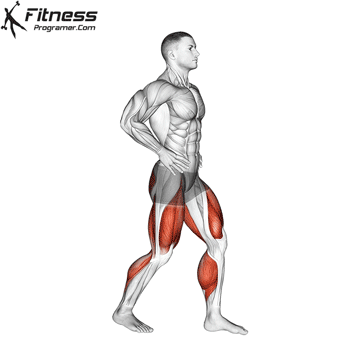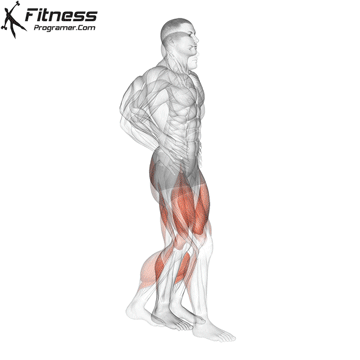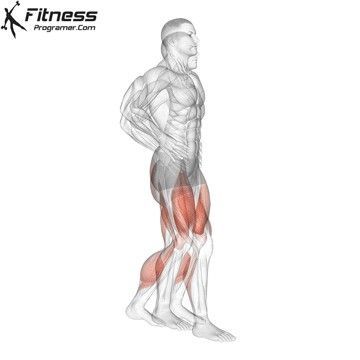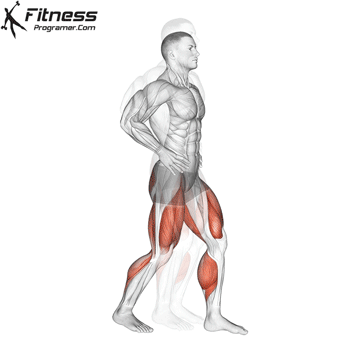
how to do Dumbbell Split Jump
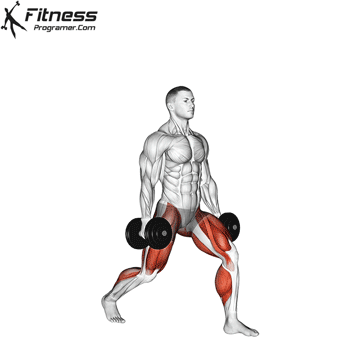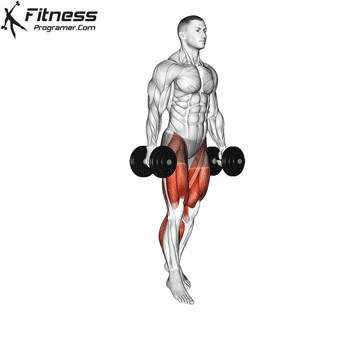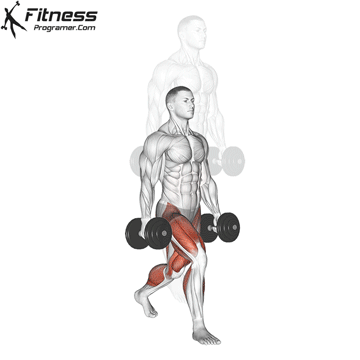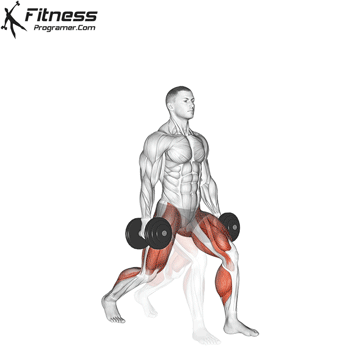
Overview
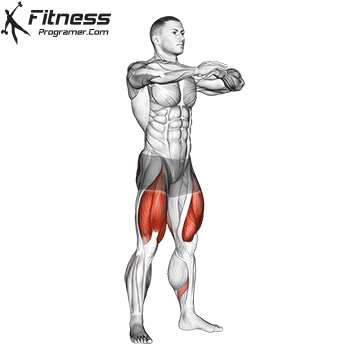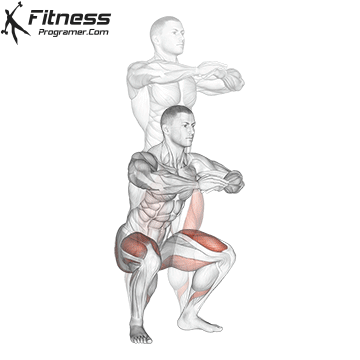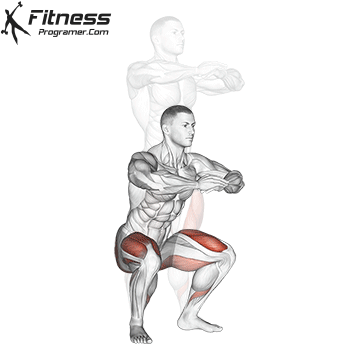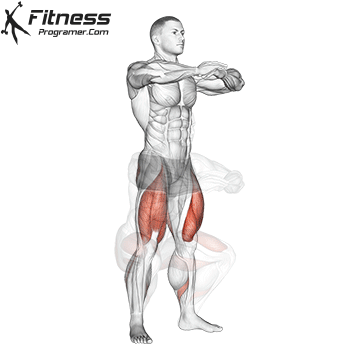
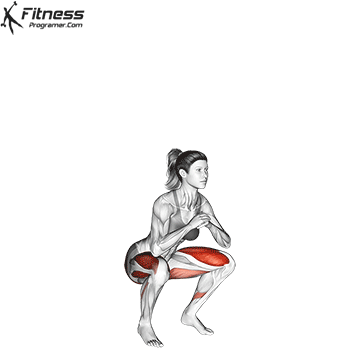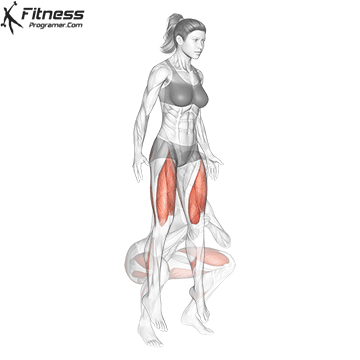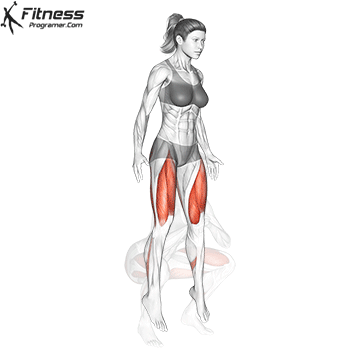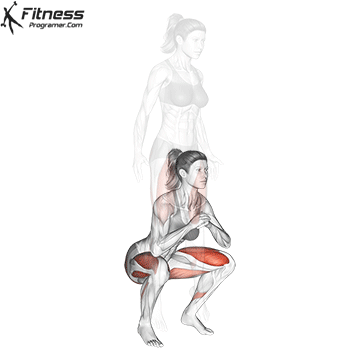
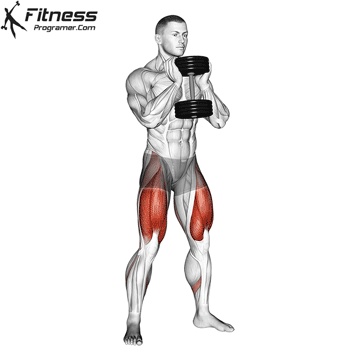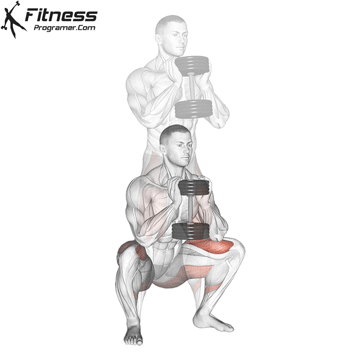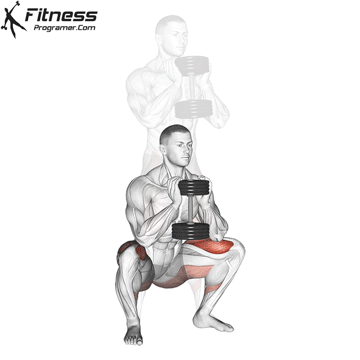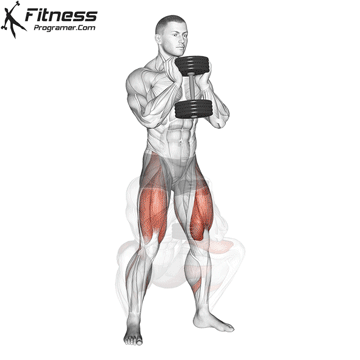
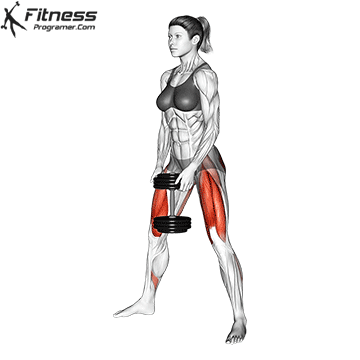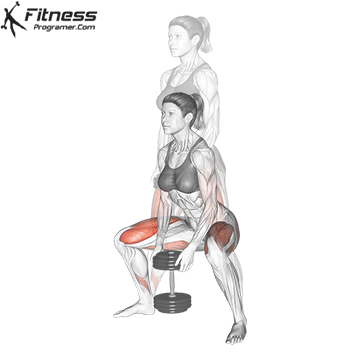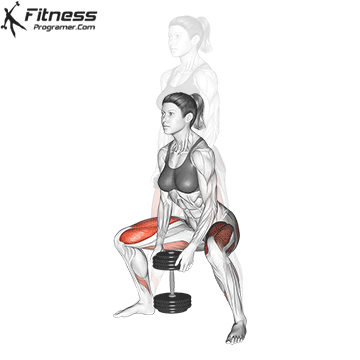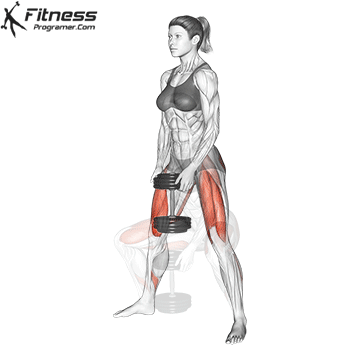
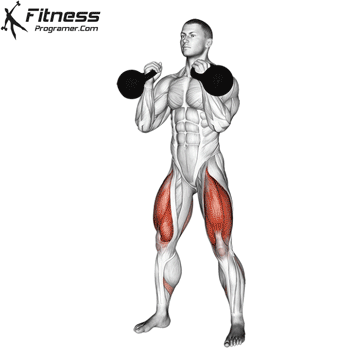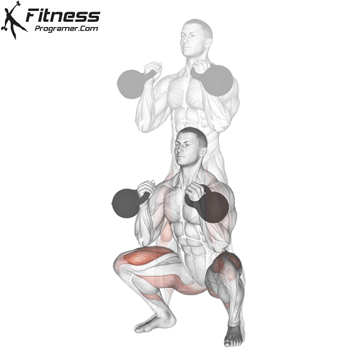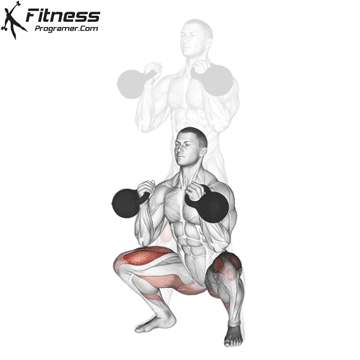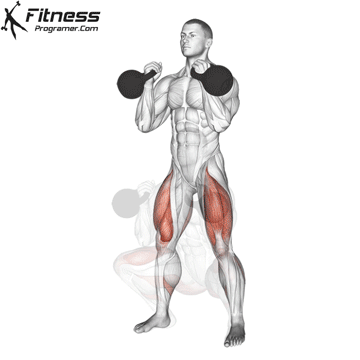
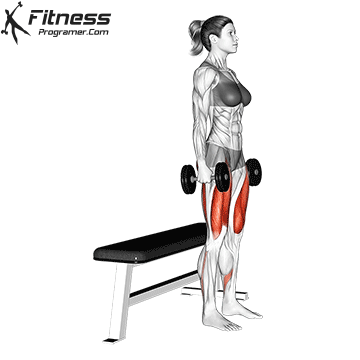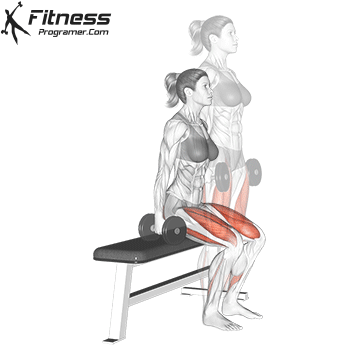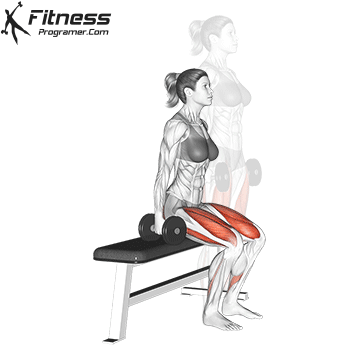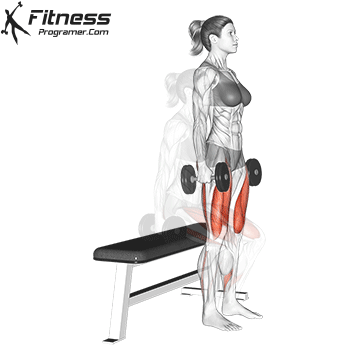
The dumbbell jump squat is a weighted plyometric exercise where you perform a vertical jump while holding dumbbells at your sides. This variation increases loading on the quads, glutes, and calves, and enhances fast-twitch muscle fiber recruitment. It is used to build power, speed, and agility in a functional and efficient way.
How to do Perform Dumbbell Jump Squat
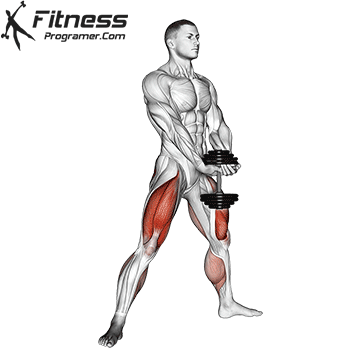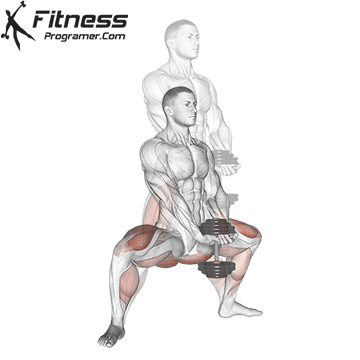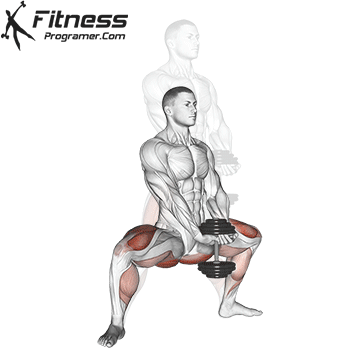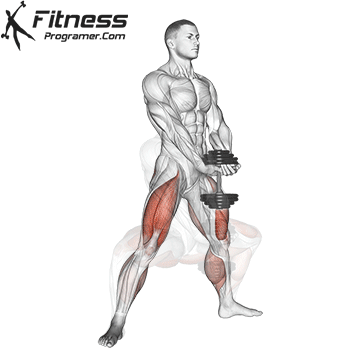
- Stand tall with feet shoulder-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand at your sides.
- Brace your core and lower into a squat, keeping your chest up and back neutral.
- Explode upward, jumping off the ground as high as you can while holding the dumbbells.
- Land softly on the balls of your feet, immediately lowering back into a squat for the next rep.
- Repeat for reps, maintaining control during both the takeoff and landing.
Tips for Proper Form
- Use light dumbbells to maintain jump height and avoid compromising form.
- Land softly with bent knees to absorb impact and protect your joints.
- Keep your chest lifted and core engaged to avoid rounding your back.
- Maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement.
- Control your descent to avoid slamming down on your joints.
Common Mistakes
- Using too much weight, which reduces jump height and increases injury risk.
- Landing with stiff legs, placing stress on the knees and ankles.
- Losing posture, such as rounding the back or leaning too far forward.
- Jumping without control, resulting in poor form or imbalance.
- Skipping the squat phase, turning the movement into a bounce rather than a squat jump.
Benefits of the Dumbbell Jump Squat
Builds Explosive Power: Jump squats with weight train fast-twitch muscle fibers for quicker, more explosive movements.
Strengthens Lower Body Muscles: Targets the glutes, quads, hamstrings, and calves with added resistance.
Improves Athletic Performance: Enhances vertical jump, sprinting ability, and acceleration.
Boosts Cardiovascular Conditioning: High-intensity bursts elevate heart rate and improve endurance.
Increases Core Engagement: Holding weights requires stability and activates the core throughout the jump.
Enhances Coordination and Balance: Forces you to control body positioning through rapid, dynamic motion.
Burns More Calories: Plyometric resistance training increases post-exercise oxygen consumption, aiding fat loss.
Highly scalable for all levels: From beginners to advanced lifters, weights and depth can be adjusted.
How to Incorporate Into Your Routine
- For Beginners: Use 2 to 3 sets of 6 to 8 reps with light dumbbells to learn landing mechanics and control.
- For Hypertrophy: Try 3 to 4 sets of 8 to 10 reps with moderate weight to combine power with muscle-building.
- For Strength: Use 3 sets of 4 to 6 reps with explosive intent, focusing on maximal jump height and good form.
- For Functional Training: Add 2 to 3 sets of 6 reps to drills that mimic sport-specific movements or agility.
- For Circuit Training: Include 8 to 10 reps in a total-body circuit to increase intensity and caloric burn.
- For General Fitness: Use 2 to 3 sets of 8 to 10 reps as part of a conditioning or athletic workout.
- For Speed and Power: Pair with sprints or box jumps for contrast training to build dynamic lower-body explosiveness.
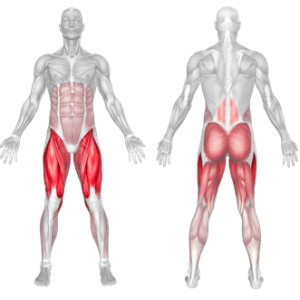
Dumbbell Jump Squat Muscles Worked
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use heavy dumbbells for jump squats?
No, using too much weight reduces explosiveness and increases injury risk. Stick to light to moderate dumbbells to maintain jump quality.
Is this exercise suitable for beginners?
Beginners should master bodyweight jump squats first, then progress to light dumbbells as control improves.
How often should I perform dumbbell jump squats?
One to two times per week is enough to build power without overtraining your joints and central nervous system.
Do dumbbell jump squats build muscle or power?
They do both, especially when performed with moderate weight and explosive intent. The primary benefit is improved power output.
Dumbbell Jump Squat Variations
Burpees
Burpee is a full-body exercise that combines elements of strength training and cardiovascular conditioning. It is generally considered a high-intensity, plyometric exercise.
The explosive and dynamic nature of burpees engages the fast-twitch muscle fibers, enhancing muscular power and agility. Plyometric exercises like burpees are particularly beneficial for athletes involved in sports that require quick bursts of energy, such as basketball, soccer, and sprinting.
How to do
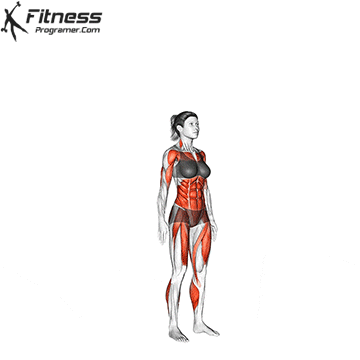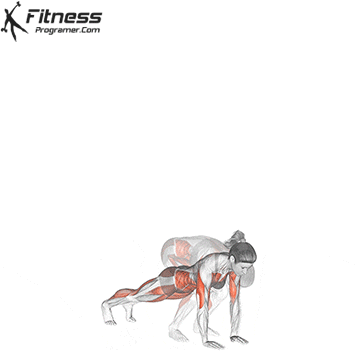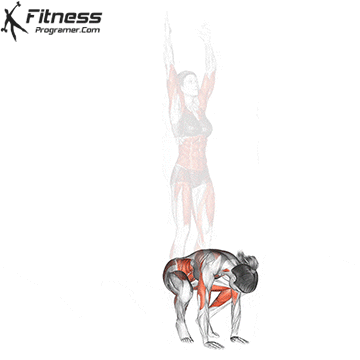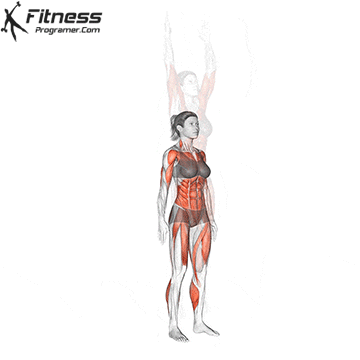
Benefits of Burpees
- Cardiovascular fitness: Burpees elevate your heart rate quickly, providing an effective cardiovascular workout. This helps improve your cardiovascular health, stamina, and endurance.
- Full-body workout: Burpees engage multiple muscle groups, including the chest, arms, shoulders, core, glutes, and legs. This comprehensive activation makes it a time-efficient exercise for working various muscle groups simultaneously.
- Calorie burn: Due to their high-intensity nature, burpees can help burn a significant number of calories in a short amount of time. This makes them beneficial for those looking to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight.
- Strength building: Burpees require you to move from a plank position to a squat and then jump, incorporating both upper and lower body strength. This helps build muscular strength and endurance over time.
- Improved agility and coordination: The dynamic movements involved in burpees enhance agility and coordination, as you transition through different positions quickly.
- No equipment required: Burpees can be done with just your body weight, making them a convenient and accessible exercise that can be performed anywhere without the need for equipment.
- Time-efficient: Burpees are a time-efficient exercise that can be included in high-intensity interval training (HIIT) routines, providing an effective workout in a short period.
- Metabolic boost: The intense nature of burpees can elevate your metabolism, leading to increased calorie burning even after you’ve finished your workout. This is known as the afterburn effect or excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC).
- Versatility: Burpees can be modified to suit different fitness levels. Beginners can start with basic variations and gradually progress to more challenging versions as their strength and stamina improve.
- Functional fitness: The movements in burpees mimic everyday activities, making them valuable for developing functional fitness. This can improve your ability to perform daily tasks with ease.
Burpees Muscles Worked

Single Leg Hip Thrust Jump
This explosive movement targets your glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps while enhancing your balance, strength, and overall athletic performance.
How to do:
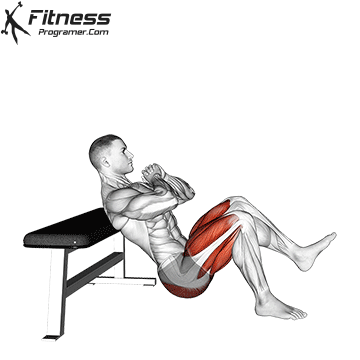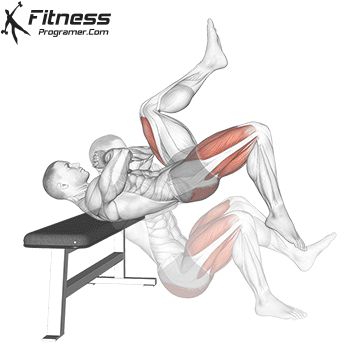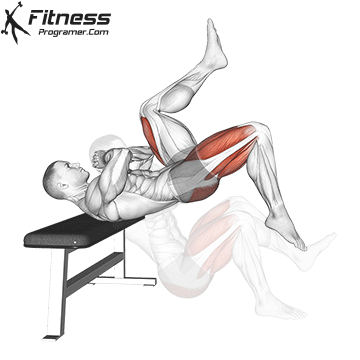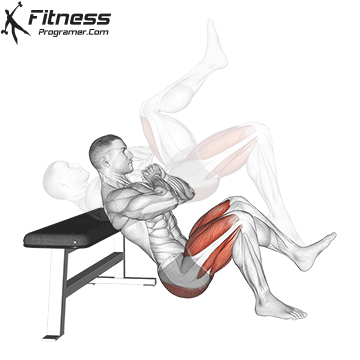
- Begin by sitting on the ground with your back firmly against a bench or platform.
- Lift your hips slightly off the ground. Place your hands together in front of your chest. This position will provide you with stability and support throughout the exercise.
- Now, lift your left foot into the air while ensuring that your right foot remains firmly planted on the floor. This is your starting position for the explosive jump to come.
- Push forcefully through your right foot, using your glute muscles to propel yourself into the air.
- As you ascend during the jump, concentrate on squeezing your buttocks to maximize power and height.
- The descent is just as crucial as the jump. Focus on making a soft landing on the floor with your right foot. Keep a slight bend in your right knee to absorb the impact and maintain balance.
- After landing, smoothly lower your hips back to the starting position, ensuring they remain elevated throughout the exercise.
- Complete the desired number of repetitions on your right leg before switching to your left leg.
How to: Trap Bar Jump Squat
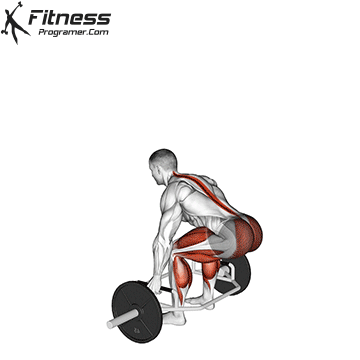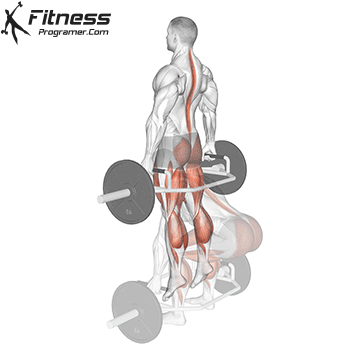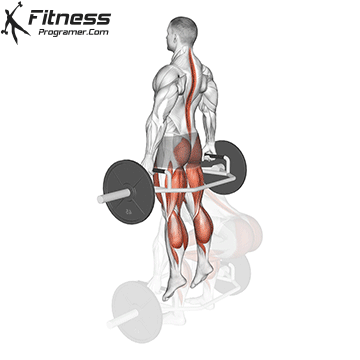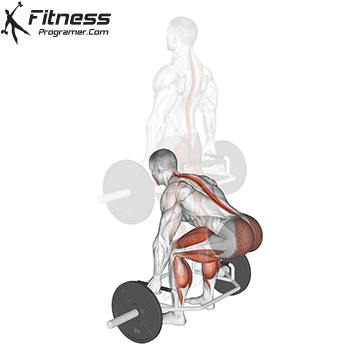
How to: Box Jump to Pistol Squat
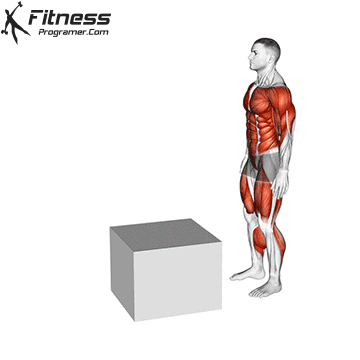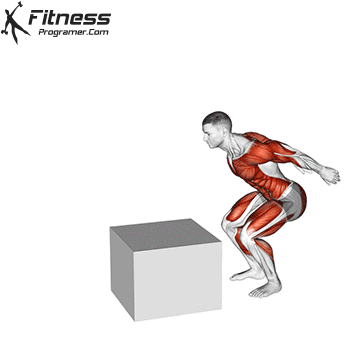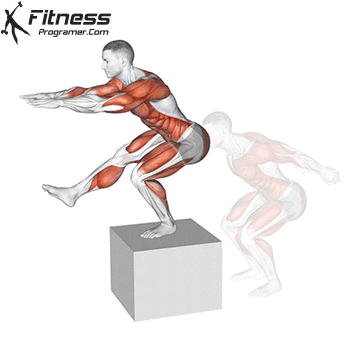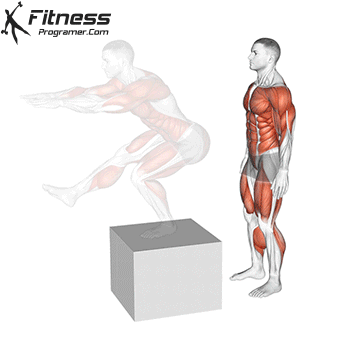
How to: Box Jump 2 to 1