Overview
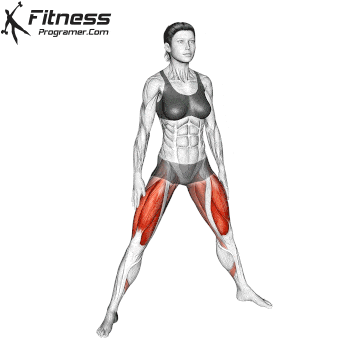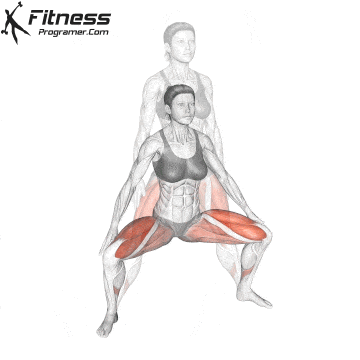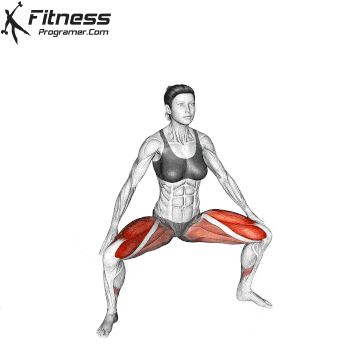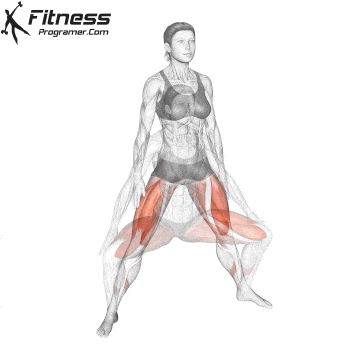
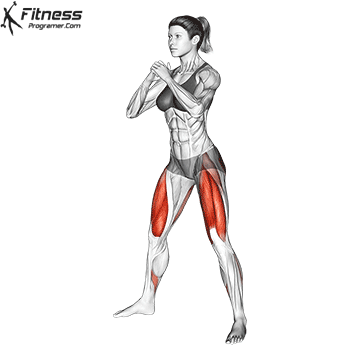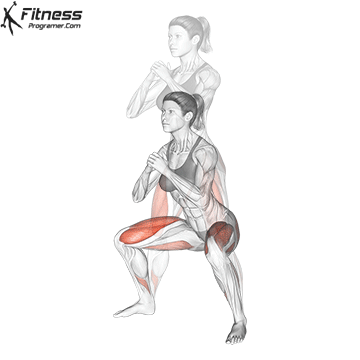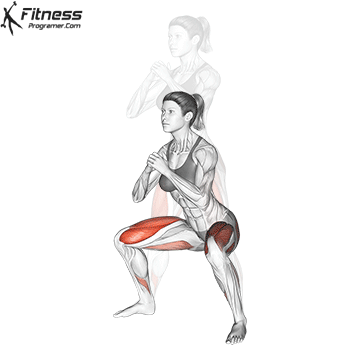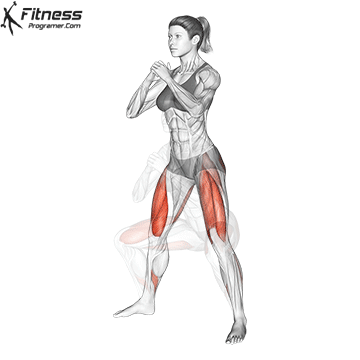
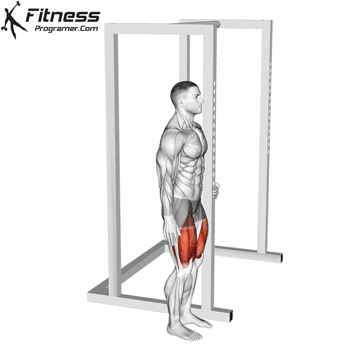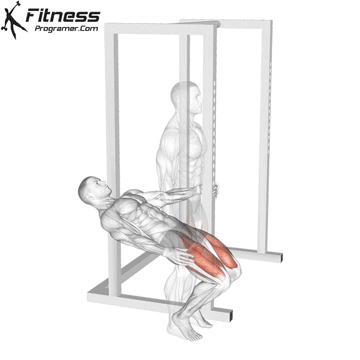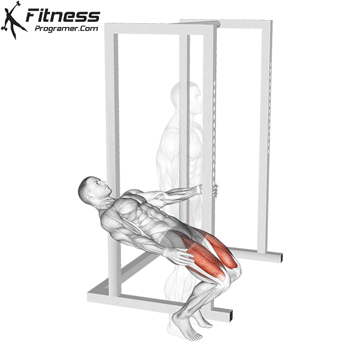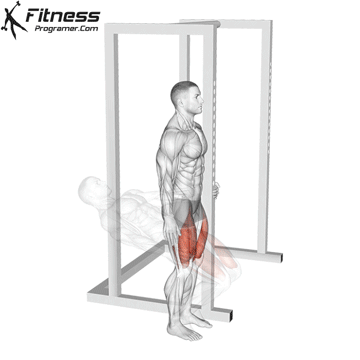
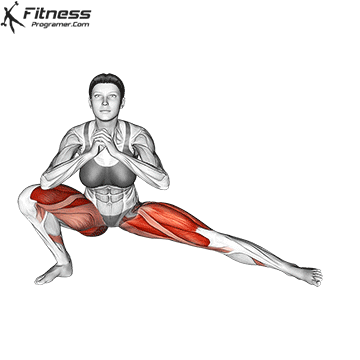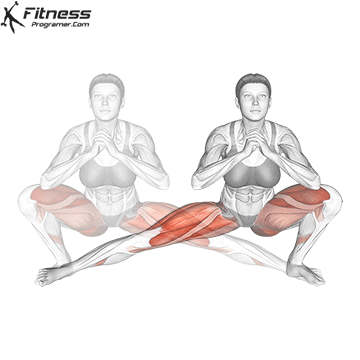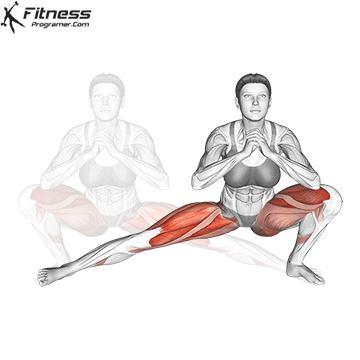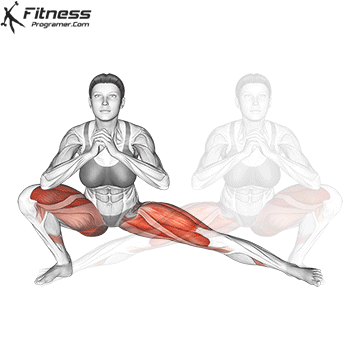
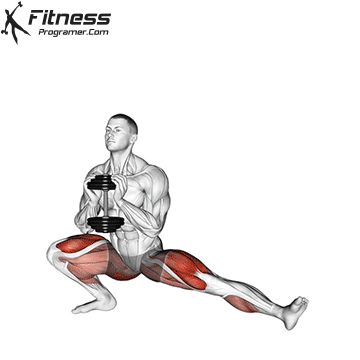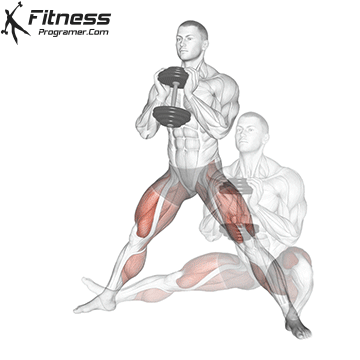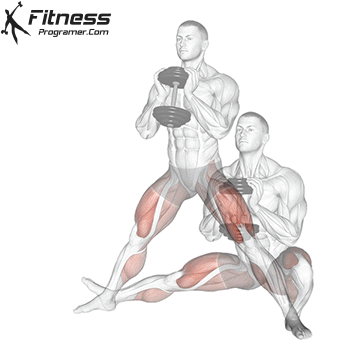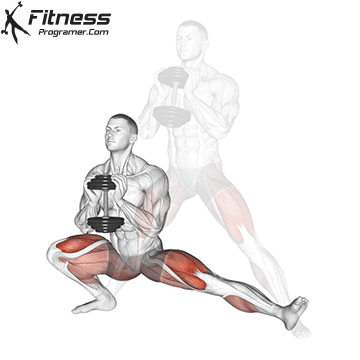
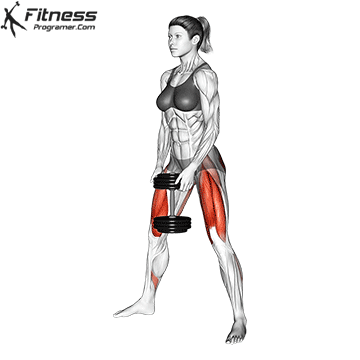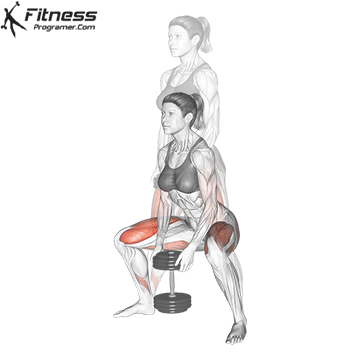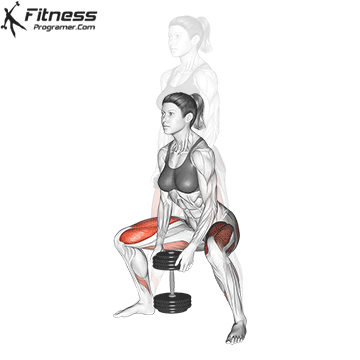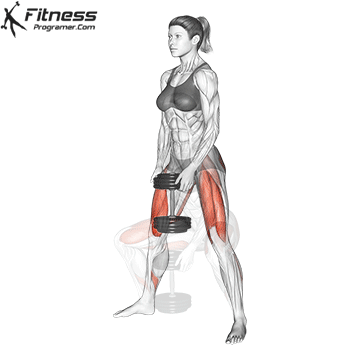
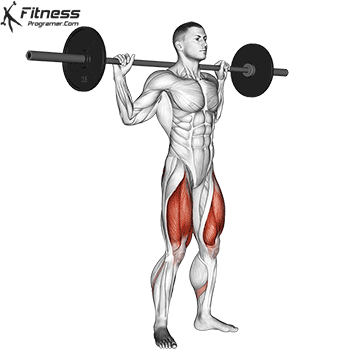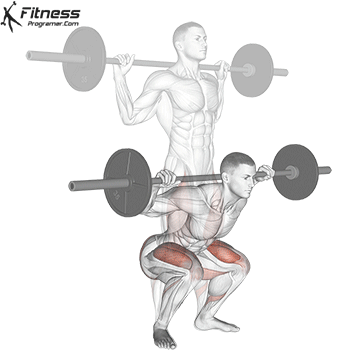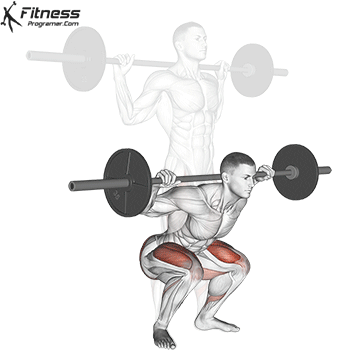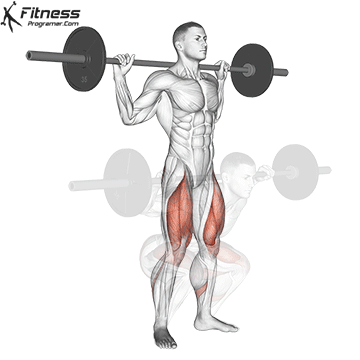
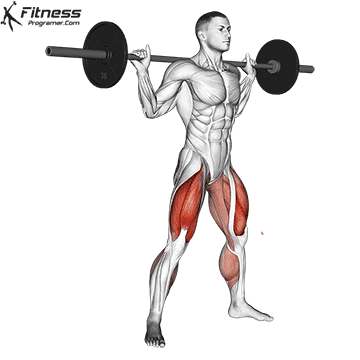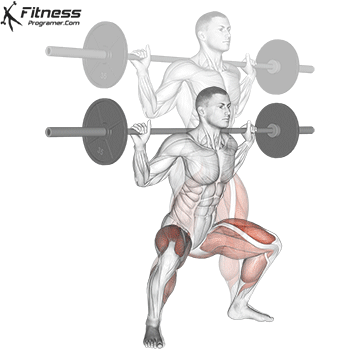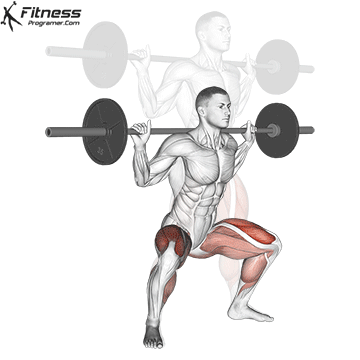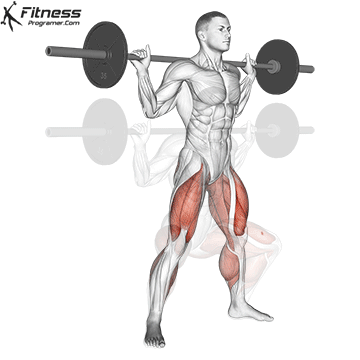
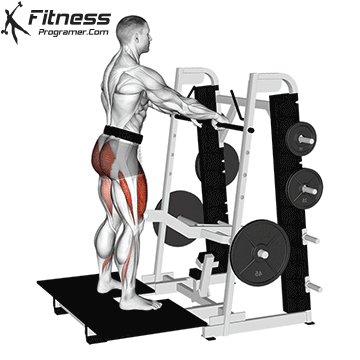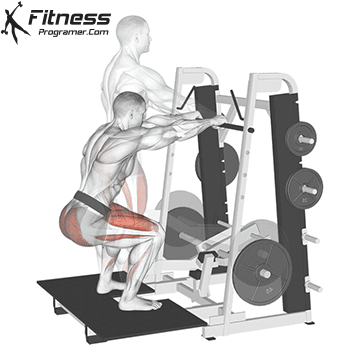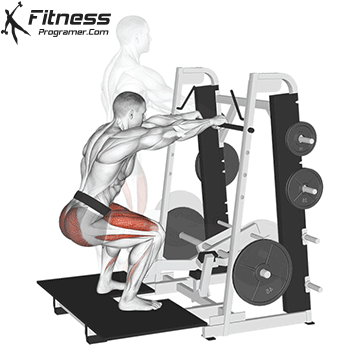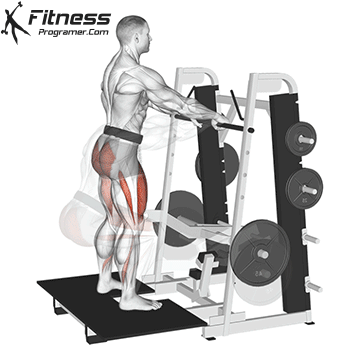
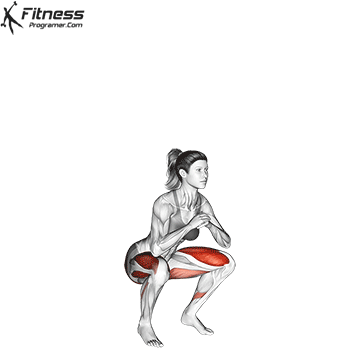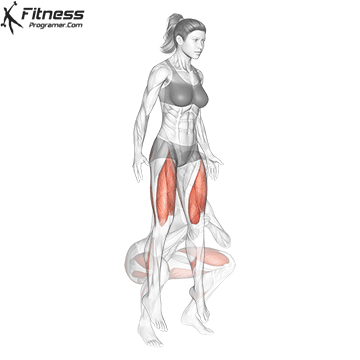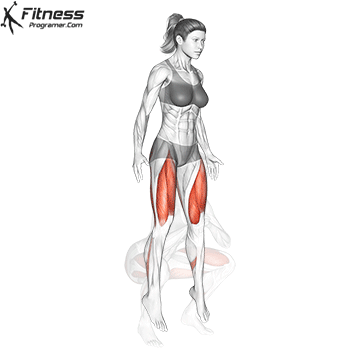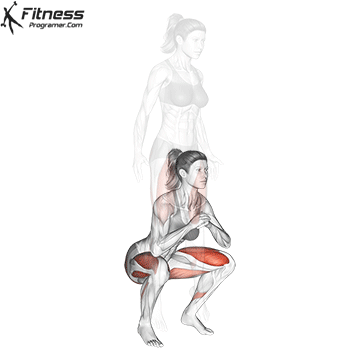
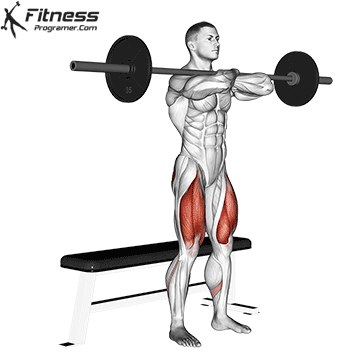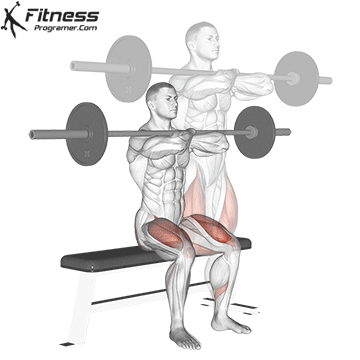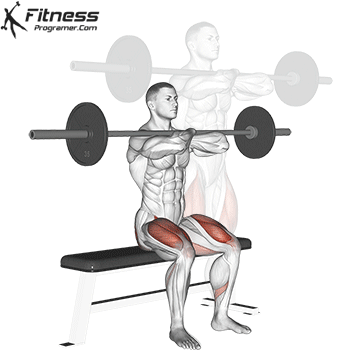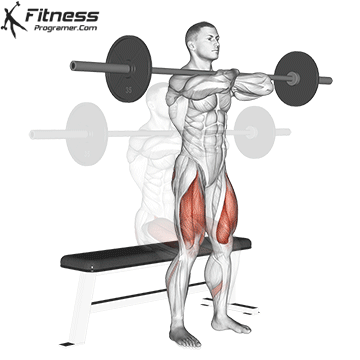
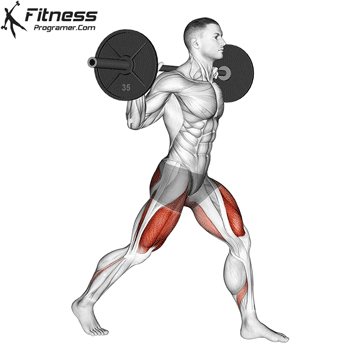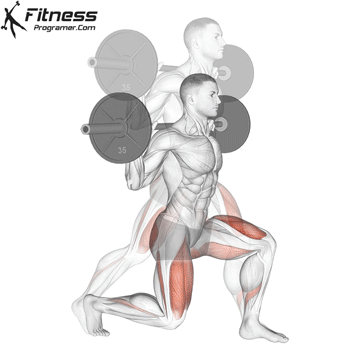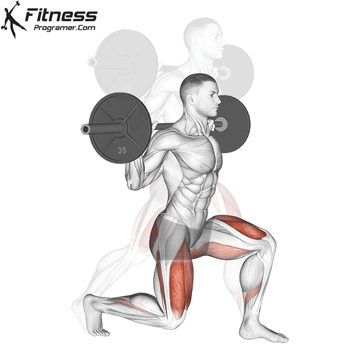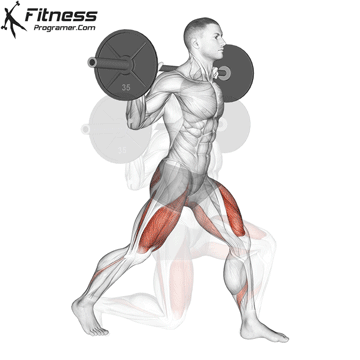
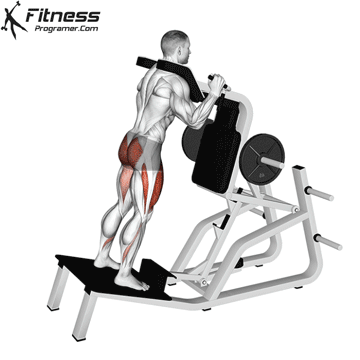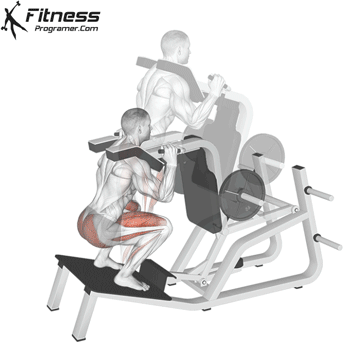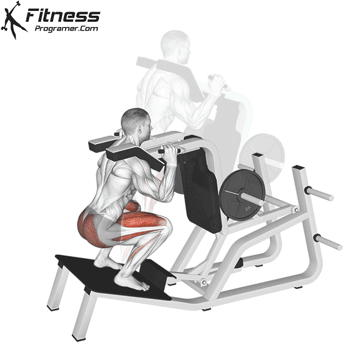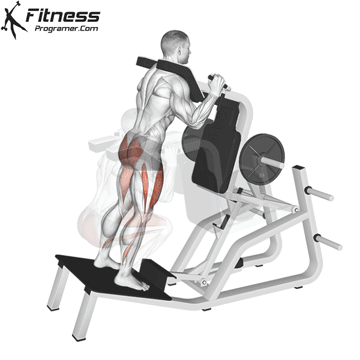
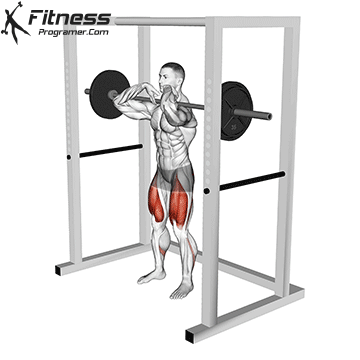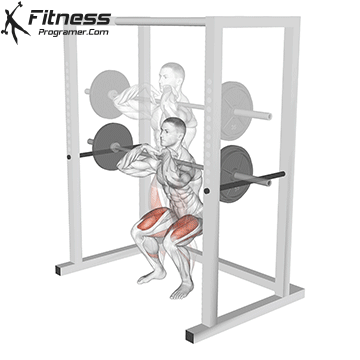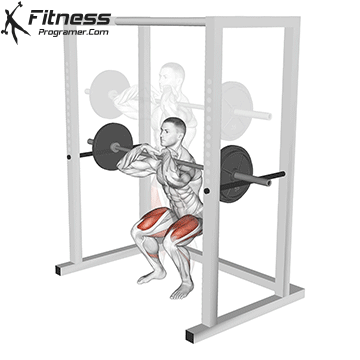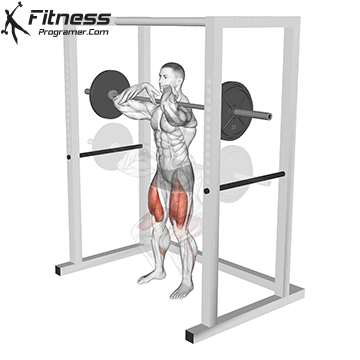
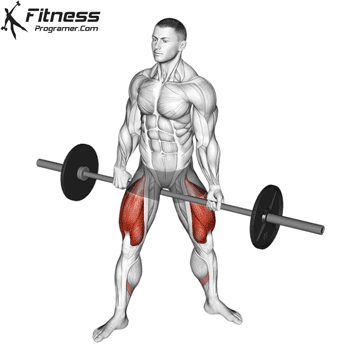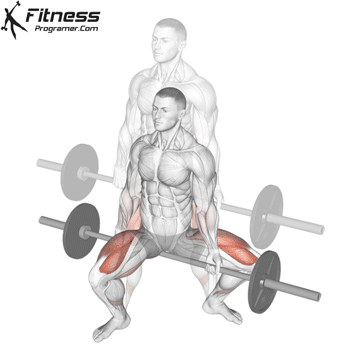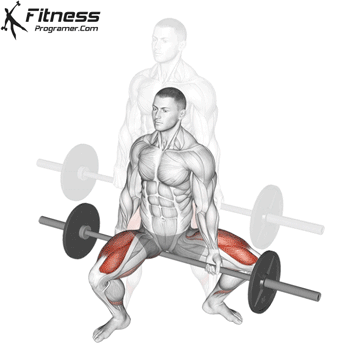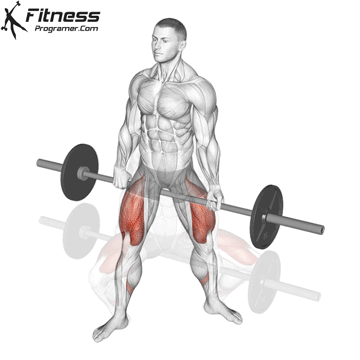
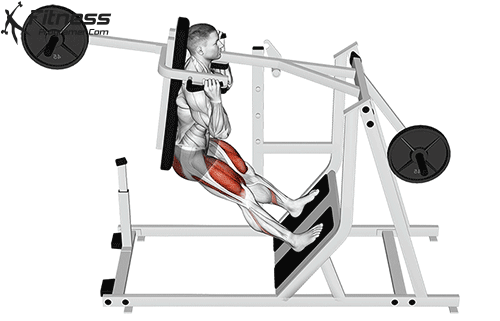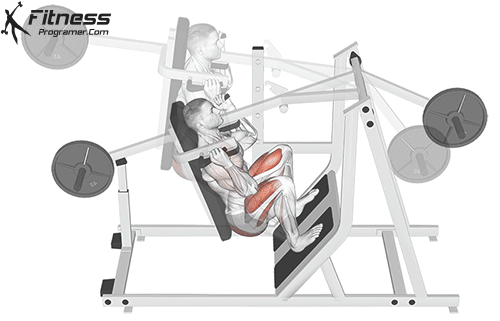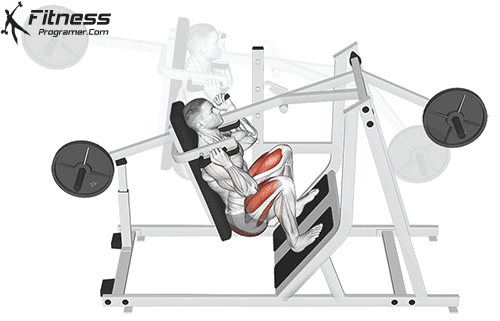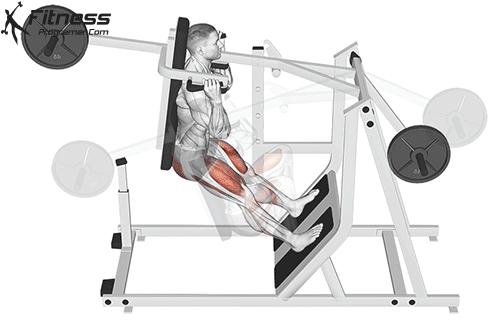
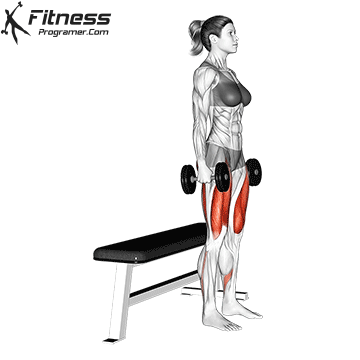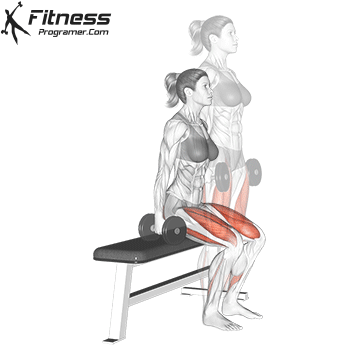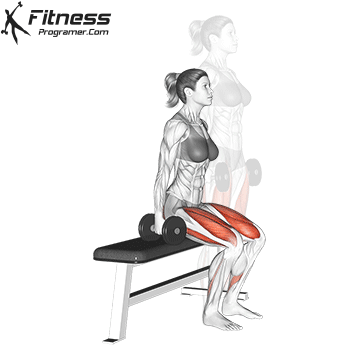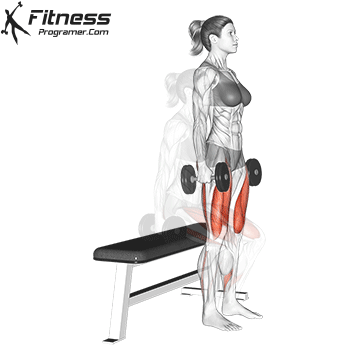
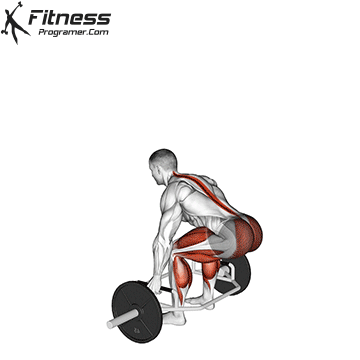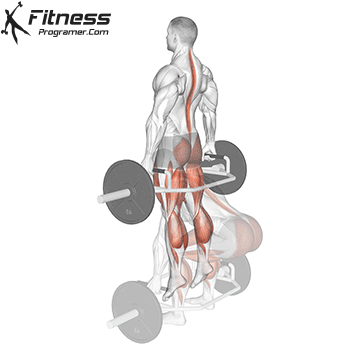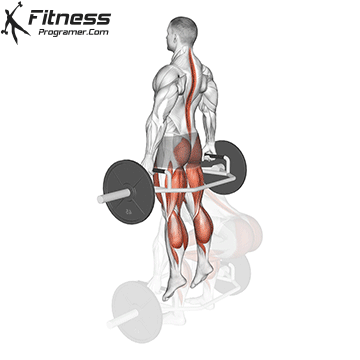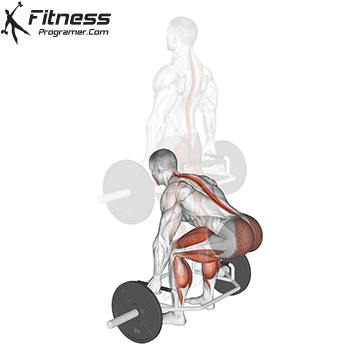
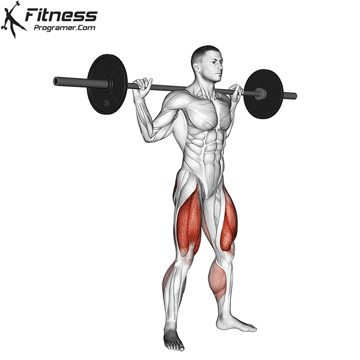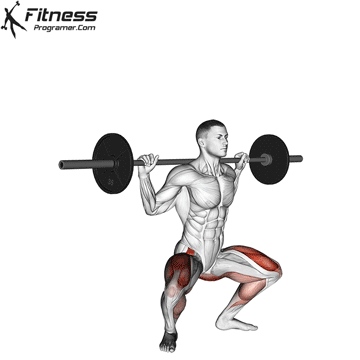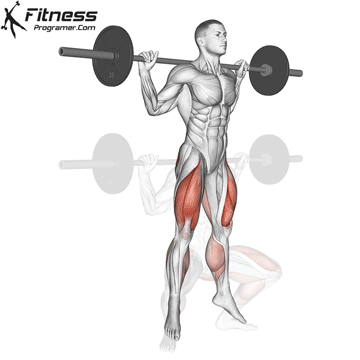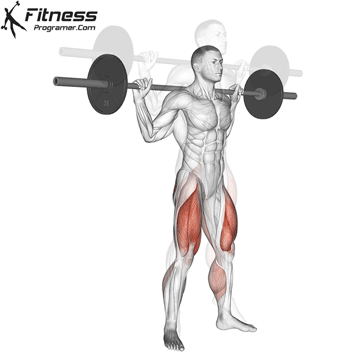
The cable goblet squat is a front-loaded lower body exercise performed using a cable machine. By holding the cable attachment at chest height, you perform a squat with resistance that pulls forward, which enhances core activation and encourages upright posture. It’s an effective squat variation for all levels of training.
How to do Perform Cable Goblet Squat
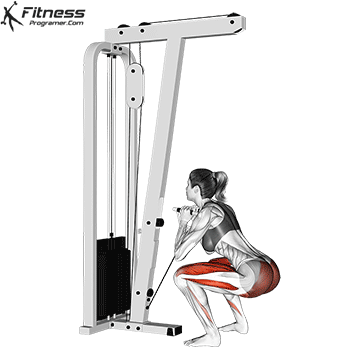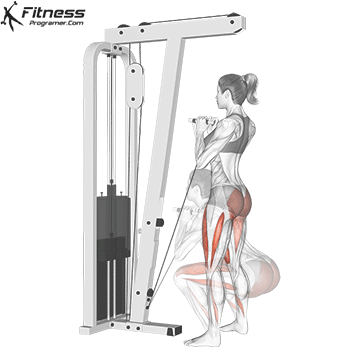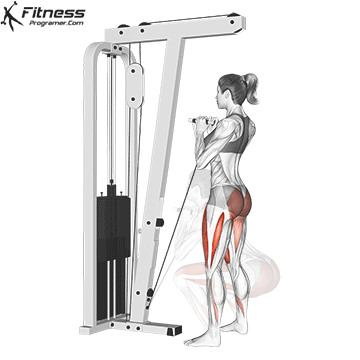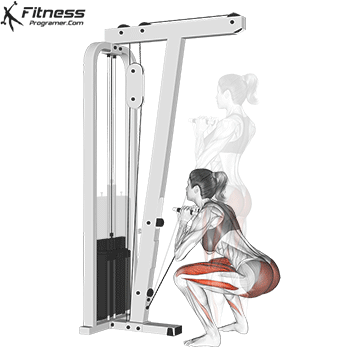
Attach a straight bar or rope handle to the low pulley of a cable machine.
Stand facing the machine and grip the handle with both hands, holding it at chest height.
Step back slightly so the weight pulls forward, then stand with feet shoulder-width apart.
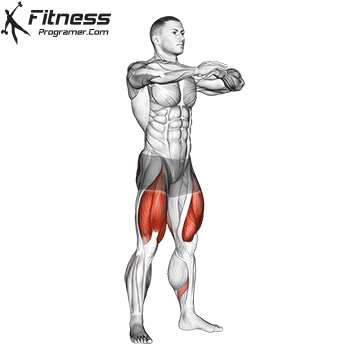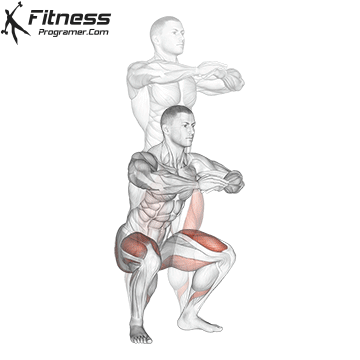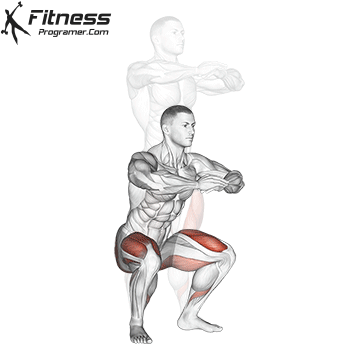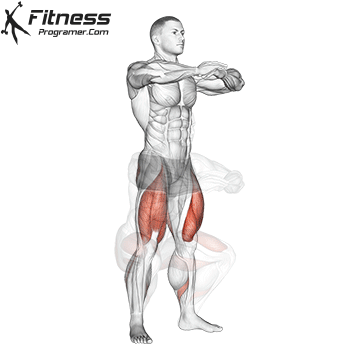
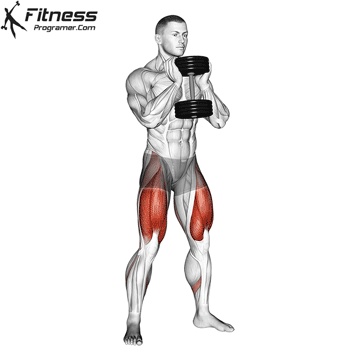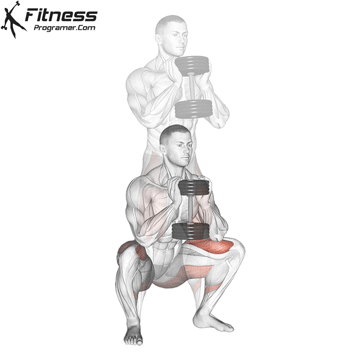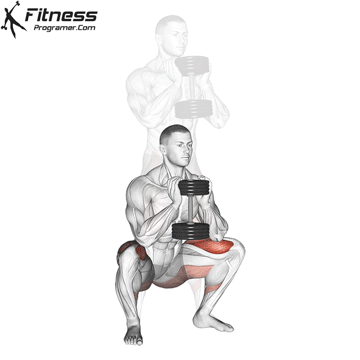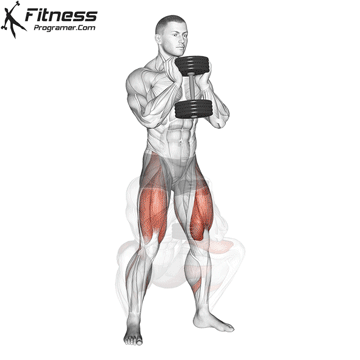
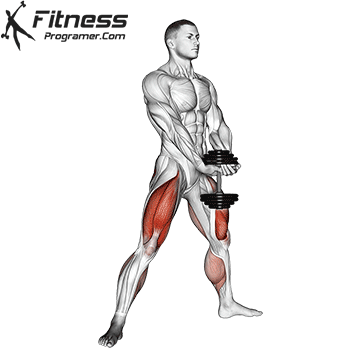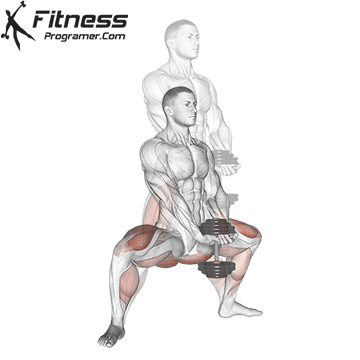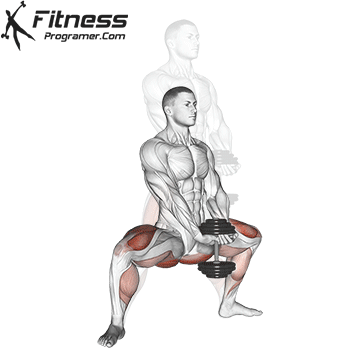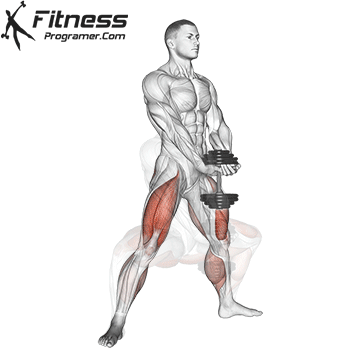
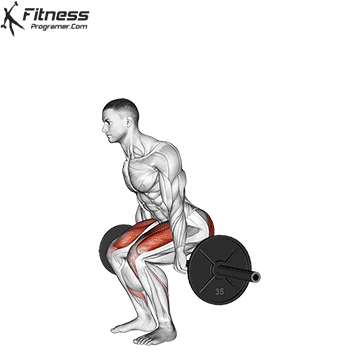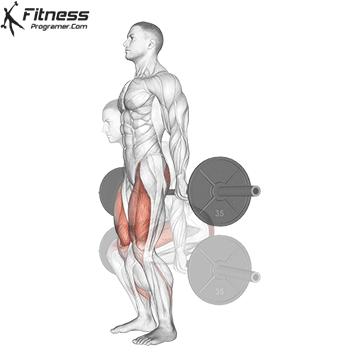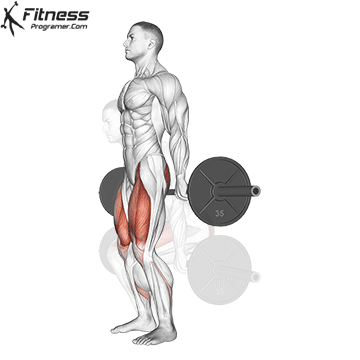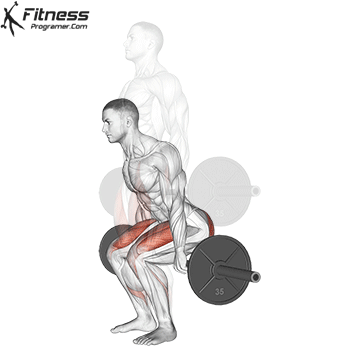
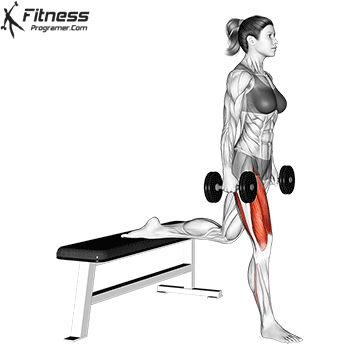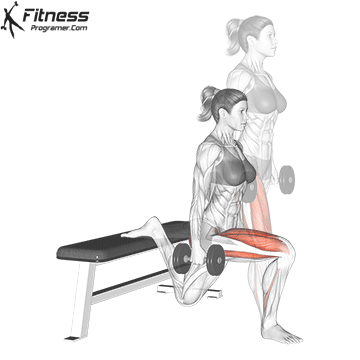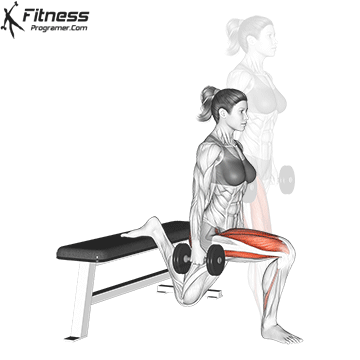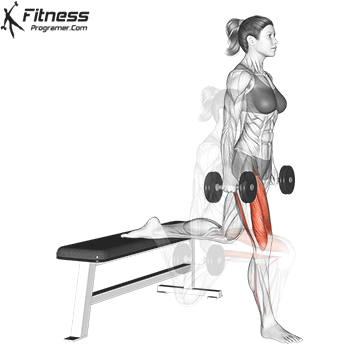
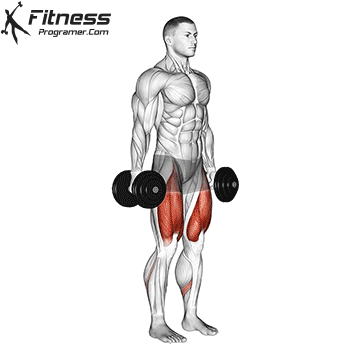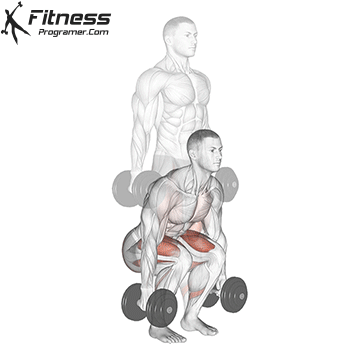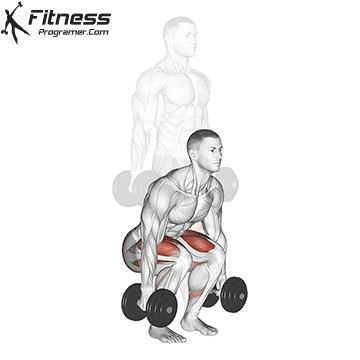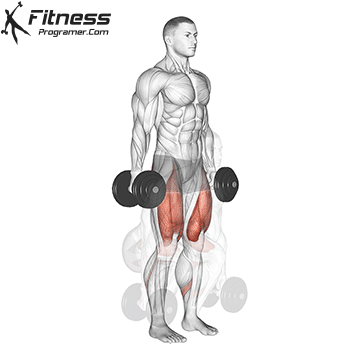
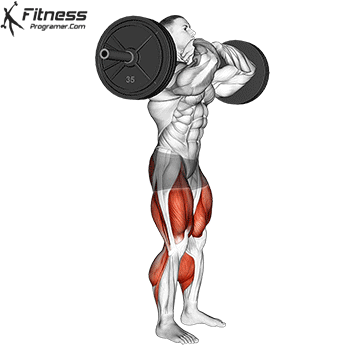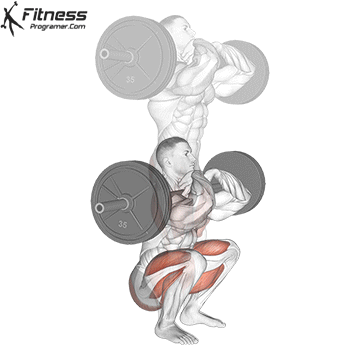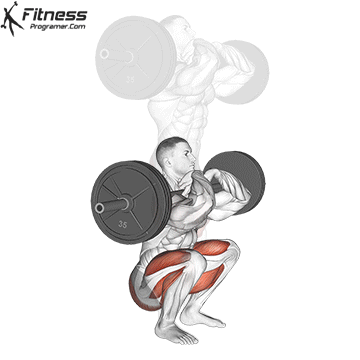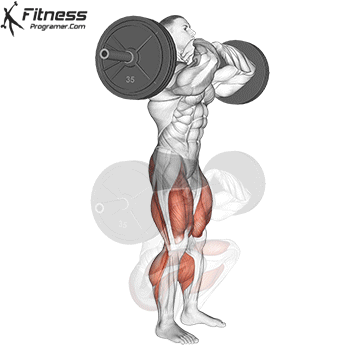
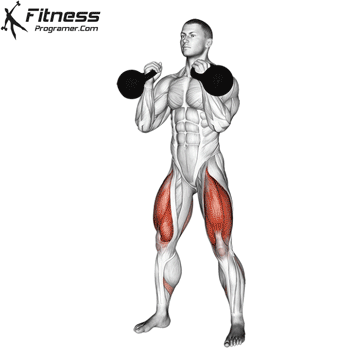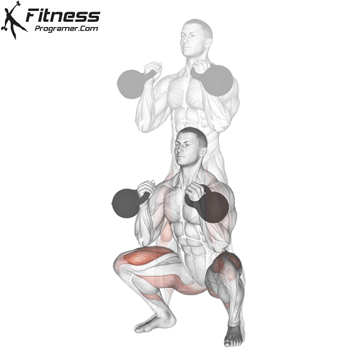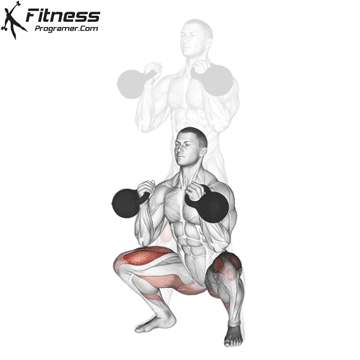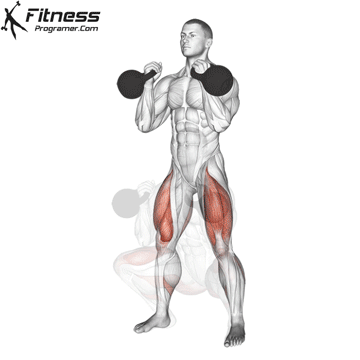
Brace your core and begin the squat by bending your hips and knees simultaneously.
Lower your body until your thighs are parallel to the floor or slightly below, keeping your chest up.
Drive through your heels to return to the starting position, maintaining cable tension throughout.
Repeat for reps, ensuring control and an upright torso during the movement.
Tips for Proper Form
Keep your chest upright and elbows close to your body to maintain balance.
Push through your heels to avoid excess pressure on your knees.
Engage your core throughout the movement to counter the forward pull of the cable.
Use a full range of motion, lowering your hips to parallel or just below.
Step far enough back from the machine to keep constant tension on the cable.
Common Mistakes
Leaning too far forward, reducing glute and quad engagement.
Letting the elbows drop, which shifts the load awkwardly.
Standing too close to the machine, decreasing tension on the cable.
Allowing the knees to cave in, risking poor alignment.
Using momentum rather than controlled movement through the squat.
Benefits of the Cable Goblet Squat
Enhanced Core Activation: The forward-pulling resistance forces your core to stabilize, strengthening the abs and lower back.
Improved Squat Form: The cable assists in maintaining an upright torso, reinforcing better posture in other squat variations.
Constant Muscle Tension: The cable provides resistance throughout the entire range of motion, increasing muscle time under tension.
Joint-Friendly Setup: The guided path and upright positioning reduce pressure on the spine and knees.
Better Mind-Muscle Connection: The cable allows for smooth, controlled reps that help focus on muscle activation in the quads and glutes.
Versatile for All Levels: Adjustable weight and minimal setup make it beginner-friendly yet scalable for advanced users.
Functional Strength Gains: Encourages coordination between the upper and lower body, improving balance and movement control.
How to Incorporate Into Your Routine
- For Beginners: Perform 2 to 3 sets of 10 to 12 reps with light resistance to build form and confidence.
- For Hypertrophy: Use 3 to 4 sets of 12 to 15 reps with moderate tension, focusing on controlled movement.
- For Strength: Aim for 4 sets of 6 to 8 reps using a heavier load while maintaining posture and cable tension.
- For Functional Training: Perform 3 sets of 8 to 10 reps using a moderate load to build posture, mobility, and control.
- For Circuit Training: Add 10 to 12 reps into a full-body circuit for endurance and muscular fatigue.
- For General Fitness: Do 2 to 3 sets of 8 to 12 reps as part of a lower-body or total-body routine.
- For Mobility or Recovery: Use light weight for 2 to 3 sets of 12 to 15 reps to improve range of motion and muscle engagement.
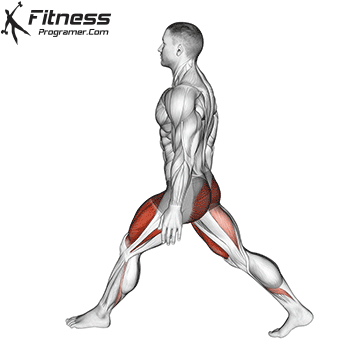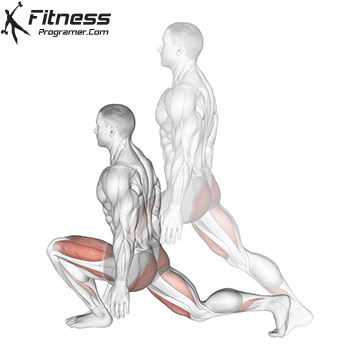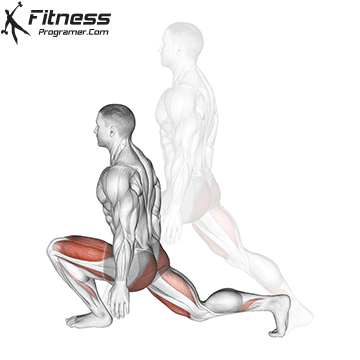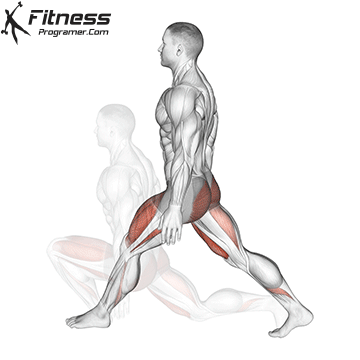
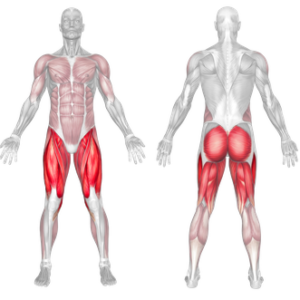
Cable Goblet Squat Muscles Worked
Frequently Asked Questions
Is the cable goblet squat good for beginners?
Yes, it is beginner-friendly and helps reinforce proper squatting mechanics with added stability.
How does it differ from the dumbbell goblet squat?
The cable version maintains constant resistance and activates the core more due to forward tension.
Can I use any handle for this exercise?
Yes. Straight bars, rope handles, or even a single D-handle can work, depending on your grip preference.
Does this help with posture?
Yes. The upright position it encourages makes it useful for reinforcing proper posture and alignment.