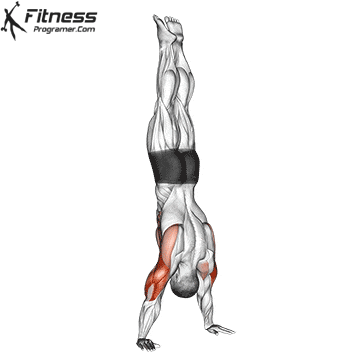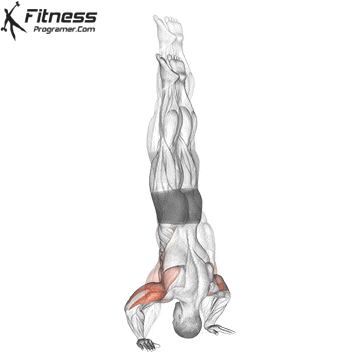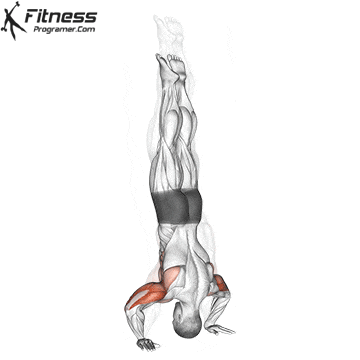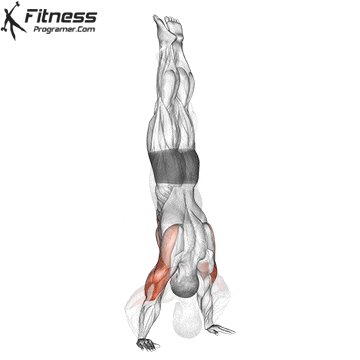
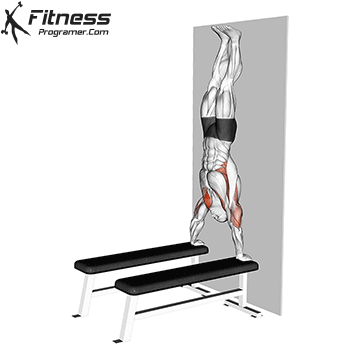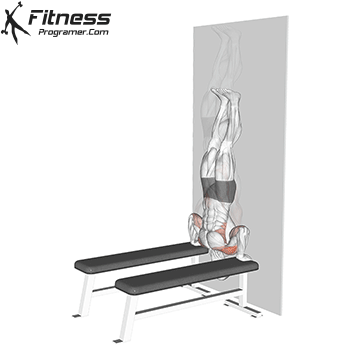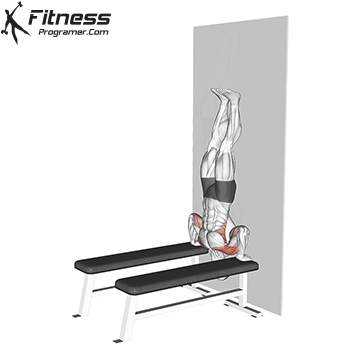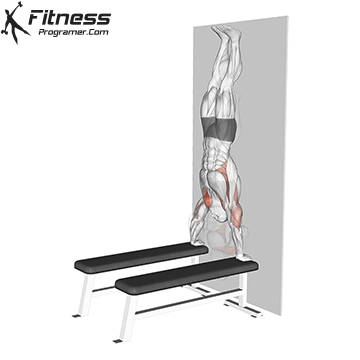
Handstand Overview
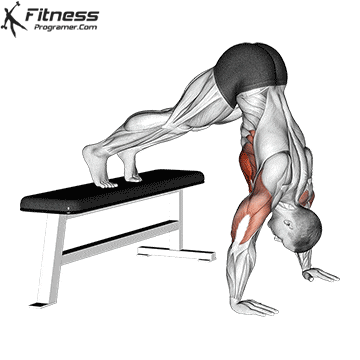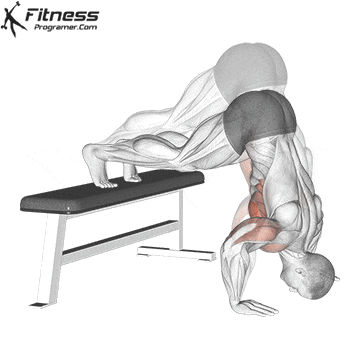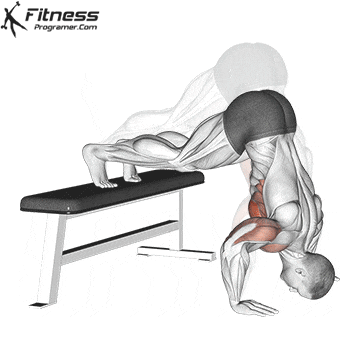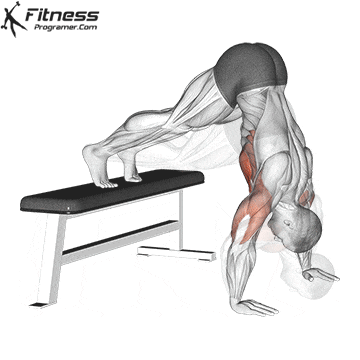
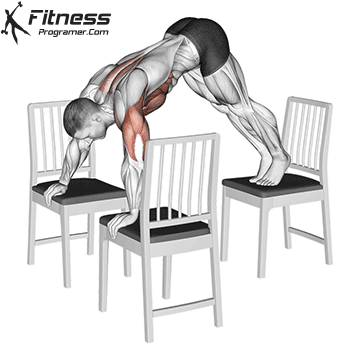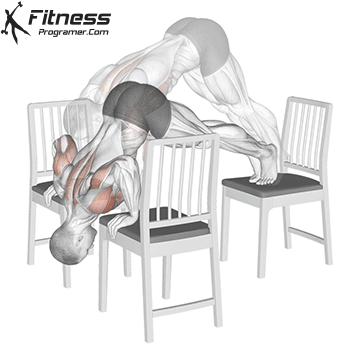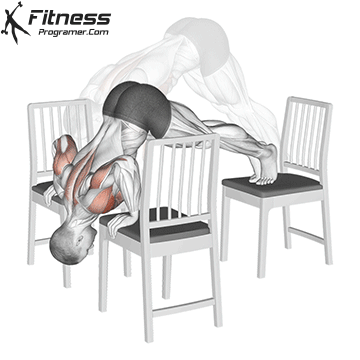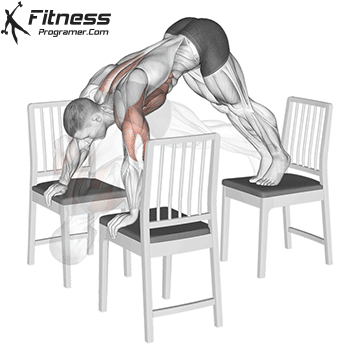
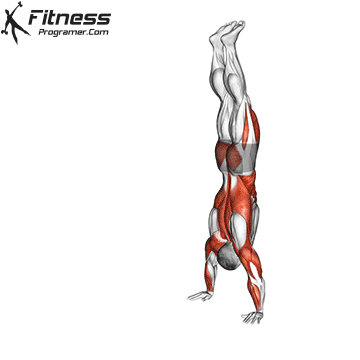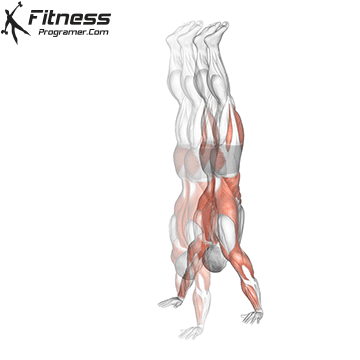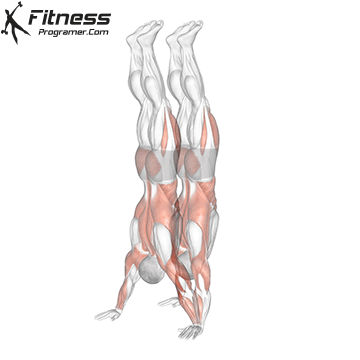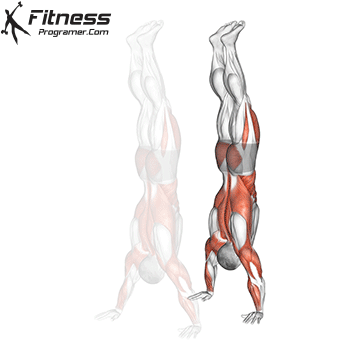
The handstand is a bodyweight exercise that requires strength, balance, and coordination. It involves holding your entire body weight on your hands in an inverted, stable, vertical position. Mastering this skill takes time and practice, but it offers significant benefits, including improved body awareness, increased upper-body strength, and endurance.
How to Perform a Handstand

Step 1: Warm Up Properly
- Stretch and mobilize the wrists, shoulders, and core.
- Perform plank holds, pike push-ups, and shoulder shrugs to activate key muscles.
Step 2: Choose Your Starting Position
- Wall-Assisted Handstand: Face a wall, kick up, and use the wall for balance.
- Freestanding Handstand: Kick up into a handstand and balance without assistance.
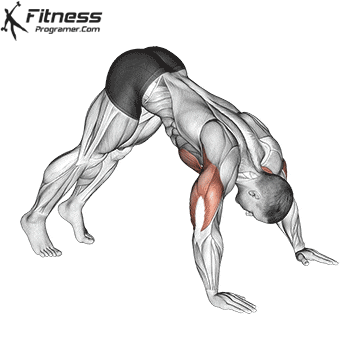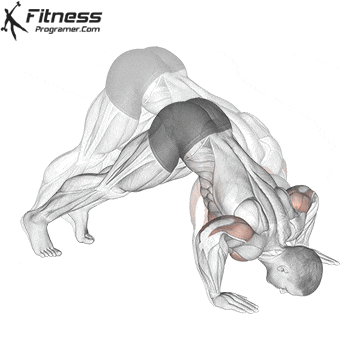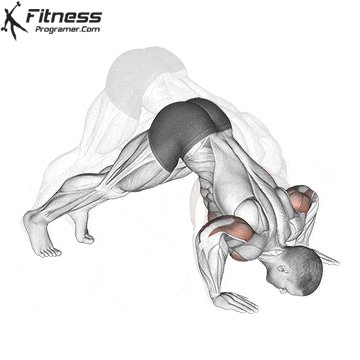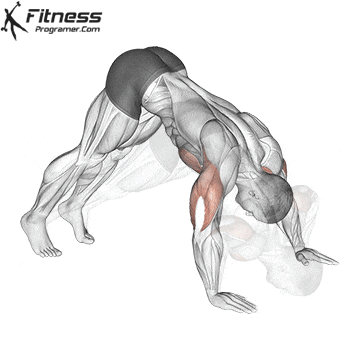
Step 3: Kick Up into Position
- Place your hands shoulder-width apart on the ground.
- Kick one leg up while keeping your core tight and arms straight.
- Engage your shoulders, core, and glutes to stabilize the position.
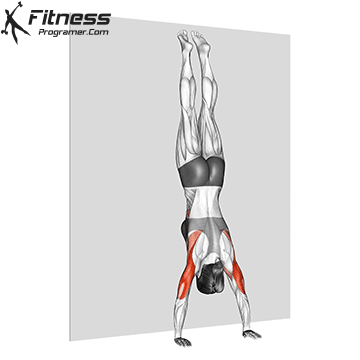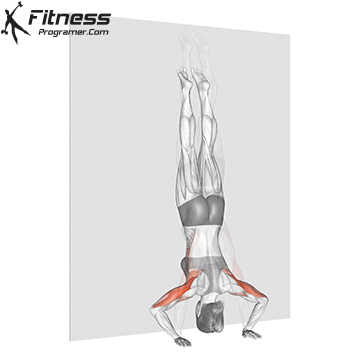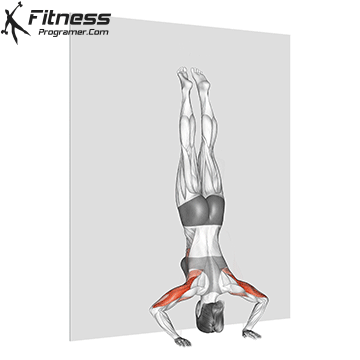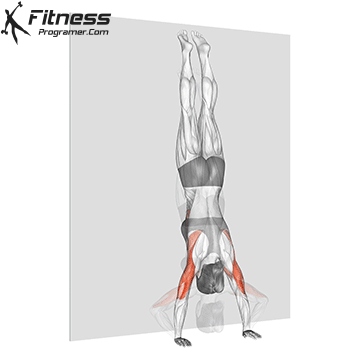
Step 4: Maintain the Hold
- Keep your legs straight and toes pointed.
- Balance by making small hand adjustments if necessary.
- Focus on slow, controlled breathing to stay relaxed.
Step 5: Safely Exit the Handstand
- Lower one leg at a time back to the ground.
- If you lose balance, tuck your chin and roll forward to avoid injury.
Tips for Proper Form
- Keep Your Core Engaged – Prevents lower back arching and maintains alignment.
- Stack Your Shoulders Over Your Hands – Ensures stability and balance.
- Point Your Toes and Squeeze Your Glutes – Helps maintain a straight line.
- Use Your Fingers for Balance – Pressing into the floor with your fingertips helps control movement.
- Train Against a Wall First – Builds confidence and endurance before progressing to freestanding handstands.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Arching the Lower Back – Can cause loss of balance and strain the spine.
- Bending the Arms – Reduces stability and increases the risk of collapsing.
- Not Engaging the Core – Leads to poor alignment and balance issues.
- Kicking Up Too Hard – Increases the chance of falling over.
- Neglecting Wrist Strength – Weak wrists may struggle to support body weight.
Benefits of the Handstand
1. Builds Upper Body Strength
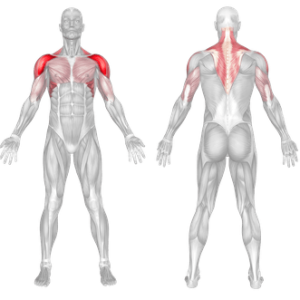
Holding a handstand strengthens the shoulders, arms, and upper back, improving overall body control.
2. Develops Core Stability
A strong core is essential for maintaining balance in a handstand, improving overall athletic performance.
3. Enhances Balance and Coordination
Practicing handstands improves body awareness and motor control, essential for gymnastics and calisthenics.
4. Improves Shoulder Mobility
Regular handstand training enhances shoulder flexibility and joint stability, reducing the risk of injury.
5. Boosts Confidence and Mental Focus
Balancing in an inverted position requires concentration and patience, improving mental resilience.
6. Strengthens Wrist and Forearm Muscles
Supporting body weight on the hands builds wrist strength, reducing the risk of strain.
Handstand Muscles Worked