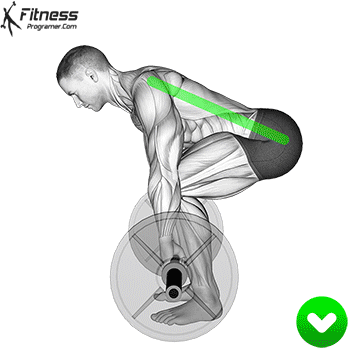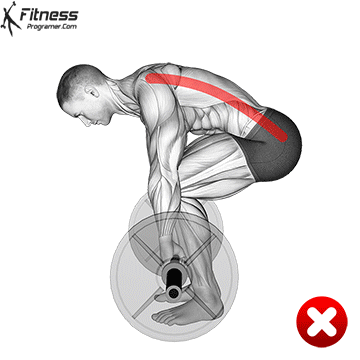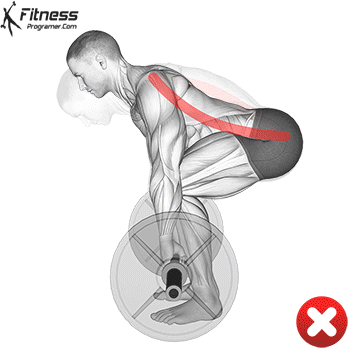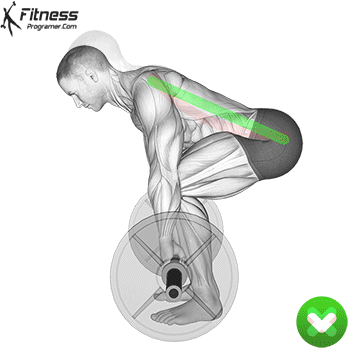
Deadlift
The deadlift is a compound exercise that involves lifting a weight from the ground to a standing position. It is often considered one of the best exercises for building overall strength and power, as it works multiple muscle groups throughout the body.
How To Do:
Here are the steps to perform a conventional deadlift:
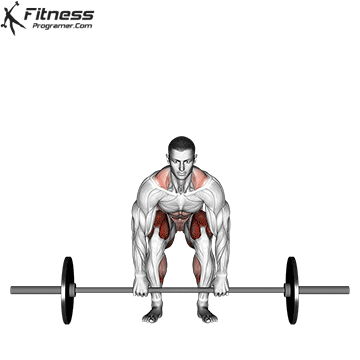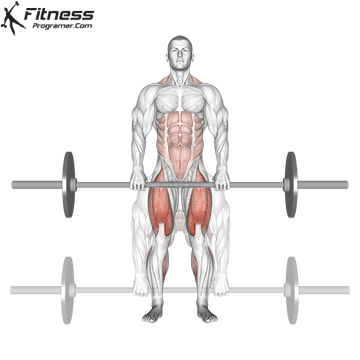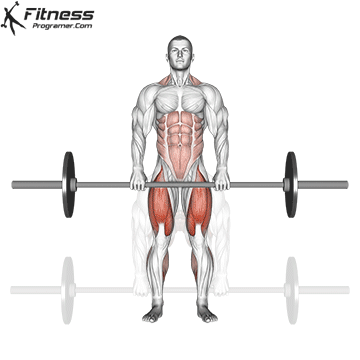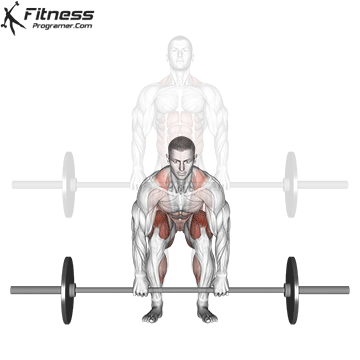
- Begin by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, with your toes pointed straight ahead. The barbell should be on the ground in front of you.
- Bend down and grasp the bar with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, using an overhand or mixed grip (one hand overhand, one hand underhand).
- Bend your knees and lower your hips, keeping your back straight and your chest up. Keep your head and neck in a neutral position, and focus on looking forward.
- Take a deep breath and brace your core muscles. This will help to stabilize your spine and protect your lower back.
- Keep the bar close to your body as you lift, and use your legs, glutes, and back muscles to power the lift.
- Once you have lifted the bar to a standing position, pause for a moment, then lower it back down to the ground, keeping your back straight and your core engaged.
It is important to maintain proper form throughout the lift, as improper technique can lead to injury. Some key points to keep in mind include:
- Keep your back straight and your chest up throughout the lift.
- Keep the bar close to your body, and use your legs and glutes to power the lift.
- Brace your core muscles to stabilize your spine and protect your lower back.
- Avoid rounding your back or allowing your shoulders to hunch forward.
- Use a weight that allows you to perform the exercise with proper form and technique.
Deadlift Benefits
- Increased overall strength: Deadlifts are a compound exercise that work multiple muscle groups throughout the body, making them an excellent way to build overall strength and power. It allows you to grasp an object more firmly when you hold it. In addition, studies show that deadlift is an effective exercise for improving explosive strength and vertical jumping performance.
- Improved posture: Deadlifts work the muscles of the back, including the spinal erectors and traps, which can help to improve posture and reduce the risk of back pain.
- Stronger legs and glutes: Deadlifts primarily target the muscles of the lower body, including the hamstrings, glutes, and quadriceps, making them an excellent way to build strength and size in these muscle groups.
- Increase in testosterone: Deadlifts are a challenging exercise that require a high level of effort and intensity, which can help to stimulate the release of growth hormone and testosterone. As muscle mass increases, testosterone levels tend to increase as well. This can help to maintain healthy testosterone levels as men age.
- Improved grip strength: Holding onto a heavy barbell during a deadlift requires strong grip strength, which can be improved through regular deadlifting. It allows you to grasp an object more firmly when you hold it.
- Improved athletic performance: Deadlifts are a highly challenging exercise that can help to boost your metabolism and burn calories, making them a great addition to any fat-loss program. Also, Deadlifts can help to improve overall power and explosiveness, making them a valuable exercise for athletes in a range of sports.
- Increased bone density: Deadlifts are a weight-bearing exercise that can help to improve bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Overall, the deadlift is an excellent exercise that offers a range of benefits for anyone looking to improve their strength, fitness, and overall health. However, it is important to use proper form and technique to avoid injury, and to gradually increase the weight over time to avoid overloading the body.
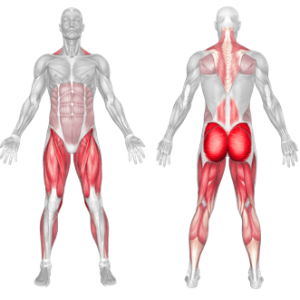
Deadlift Muscles Worked
The deadlift primarily targets the muscles of the lower body, including the glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps, as well as the muscles of the back, including the spinal erectors, lats, and traps. It also works the muscles of the arms, including the biceps and forearms.