Overview
The rowing machine is a cardio and strength-training exercise tool that simulates rowing. By engaging both upper and lower body muscle groups, it improves stamina, strength, and calorie expenditure simultaneously. It provides a full-body workout, engaging muscles in the legs, core, back, and arms while offering low-impact cardiovascular conditioning. It is widely used for fat loss, aerobic endurance, and sport-specific conditioning.
How to Use the Rowing Machine
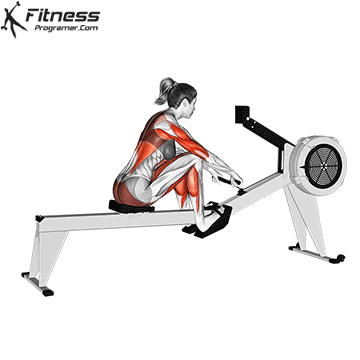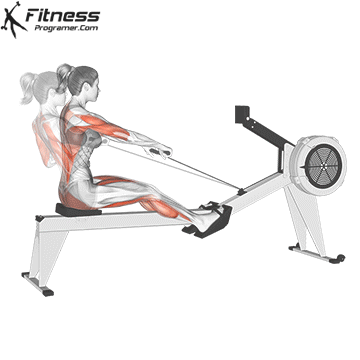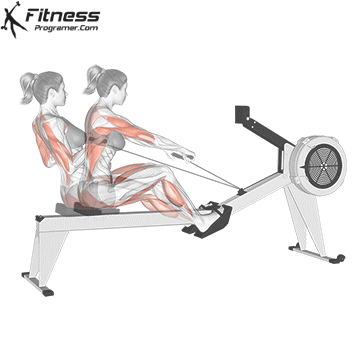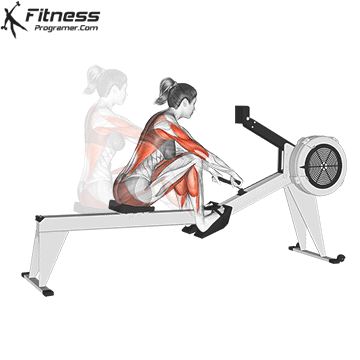
Start Position (The Catch): Sit on the seat with feet strapped in. Bend your knees, lean slightly forward at the hips, and hold the handle with an overhand grip.
Drive Phase: Push explosively through the legs, extend hips, then pull the handle toward your upper abdomen while keeping elbows close to the body.
Finish Position: Legs fully extended, torso leaning slightly back, handle pulled just below the chest.
Recovery Phase: Extend arms forward first, then hinge at the hips, and finally bend knees to return to the catch.
Maintain a steady rhythm, coordinating legs, core, and arms smoothly.
Tips for Proper Form
Keep your back straight and avoid rounding during the drive.
Push with your legs first, then follow with the upper body pull.
Maintain a controlled pace; don’t rush the recovery.
Keep elbows tucked close to the ribcage at the finish.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Leading with the arms instead of pushing with the legs.
Overextending the lower back at the finish.
Letting knees splay outward during the drive.
Rushing the recovery phase instead of keeping rhythm.
Benefits of the Rowing Machine
Full-Body Workout: Engages legs, core, back, and arms simultaneously, promoting balanced muscular development.
Low-Impact Conditioning: Gentle on joints while still delivering high-calorie burn and cardiovascular benefits.
Builds Endurance and Stamina: Improves both aerobic capacity and muscular endurance, making it suitable for athletes and general fitness.
Enhances Posture and Core Strength: Strengthens posterior chain muscles, supporting better posture and spinal health.
Efficient Calorie Burn: A time-efficient way to combine strength and cardio training in one workout.
How to Incorporate Into Your Routine
Begin your training with a 5 minute warm up (to gradually increase heart rate). It should be performed at a light intensity to warm up your body. Light perspiration is an indicator that your body has warmed up and is ready for an increase in intensity.
For Beginners: Start with 10–15 minutes at a moderate pace, focusing on learning proper technique.
For Endurance Training: Row for 20–40 minutes at a steady pace, maintaining consistent rhythm and breathing.
For Interval Training: Perform high-intensity intervals (e.g., 1 minute fast, 1–2 minutes slow) for 15–20 minutes.
For Strength and Power: Use higher resistance and shorter bursts, rowing hard for 250–500 meters, followed by rest.
For General Fitness: Include rowing sessions 2–3 times per week as part of a balanced cardio and strength program.
The duration of your exercise depends on your fitness level; generally it is recommended that you maintain your heart rate in the training zone for at least 15-20 minutes to realize an aerobic benefit. Beginners should always start slowly and bring their workout sessions up to 15 minutes or more. As your fitness level increases, you will be able to maintain your heart rate in the training zone for longer periods: usually between 20 and 30 minutes.
Rowing Machine Muscles Worked
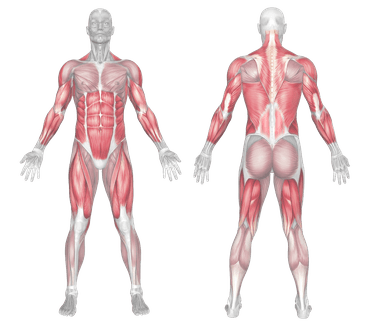
- Deltoids
- Triceps
- Trapezius
- Serratus Anterior
- Erector Spinae
- Rectus Abdominus
- Hamstrings
- Tibialis Anterior
- Gastrocnemius
| Legs Emphasis | Body Swing Emphasis | Arm Pull Through |
|
|
|
- Biceps
- Brachialis
- Brachioradialis
- Forearm Extensors
- Latissimus Dorsi
- Trapezius
- Quadriceps
- Posterior Deltoid
- Gluteus Maximus
- Trapezius
- Rectus Abdominus
- Hamstrings
- Anterior Deltoid
- Triceps
- Wrist Extensors
- Gastrocnemius
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is the rowing machine good for weight loss?
Yes, it is excellent for calorie burning while building strength and endurance.
How long should beginners row?
Start with 10–15 minutes, focusing on form before increasing duration or intensity.
Is rowing safe for people with knee or joint issues?
Yes, it’s low-impact, but proper form is essential to avoid strain.
How many times per week should I row?
Two to four sessions per week is effective for most fitness goals.
What type of resistance is best—air, water, or magnetic?
All are effective; air and water rowers mimic natural rowing feel, while magnetic rowers are quieter and smoother.
Can rowing replace weight training?
Rowing builds muscular endurance and strength but should complement, not replace, resistance training.
