Reaction Ball Throw / Agility Ball
The Reaction Ball Throw is a training exercise that focuses on improving your reaction time, hand-eye coordination, and agility. This exercise involves throwing a reaction ball against a wall and reacting quickly to its unpredictable bounces. The goal is to react quickly to the ball’s movements and catch or control it. It’s often used in basketball training, fitness routines, and agility-focused workouts.
How to do:
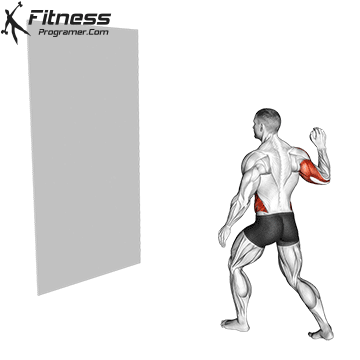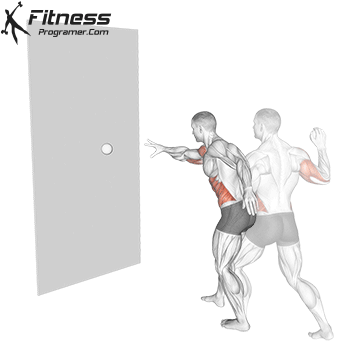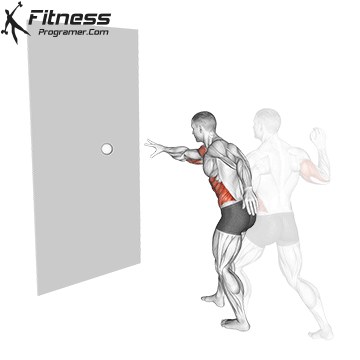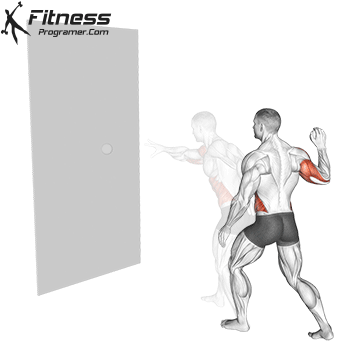
Here’s how you can perform a Reaction Ball Drill:
- Stand facing the wall or chosen surface with the reaction ball in one hand (e.g., your right hand if you’re starting with your dominant hand).
- Assume a comfortable athletic stance with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Hold the reaction ball at chest level with your arm slightly bent.
- Use your wrist, arm, and core muscles to throw the reaction ball against the wall. The goal is to create an unpredictable bounce.
- As the ball bounces back, quickly react to its movement with the same hand and attempt to catch it.
- Focus on tracking the ball’s trajectory and adjusting your hand positioning to catch it accurately.
- Repeat the throws and catches for a set number of repetitions or a specified time period.
Hand Switch:
- After completing the desired number of throws with one hand, switch to the other hand (e.g., your left hand if you started with your right).
- Perform the same single-handed throws and catches with the opposite hand.
- This variation challenges your coordination and reaction time with your non-dominant hand.
What is Reaction Ball Training?
At its core, reaction ball training involves using a specialized ball with uneven surfaces that cause unpredictable bounces when thrown against a solid surface. The irregular rebound of the ball challenges your ability to anticipate its trajectory, requiring quick reflexes and precise hand-eye coordination to catch or control it. Reaction ball training is not only physically demanding but also mentally stimulating, as it sharpens your cognitive skills by forcing you to process information rapidly and make split-second decisions.
Benefits of Reaction Ball Training
Enhanced Reflexes: Reaction ball training conditions your body to respond swiftly to unexpected movements. The rapid adjustments needed to catch or control the ball fine-tune your motor skills. This translates to improved reaction times in various situations, both in sports and daily life.
Agility: Agility is the ability to change direction quickly and gracefully. The rapid movements demanded by reaction ball training bolster your agility by teaching your body to adapt swiftly to changing conditions.
Hand-Eye Coordination: The erratic bounces of the reaction ball require your eyes and hands to work together harmoniously. Regular practice refines your hand-eye coordination, enabling you to react accurately and effectively.
Attention Control and Visual Processing: The unpredictability of the ball’s movement requires intense focus and attention. Tracking the movement of the reaction ball challenges your visual processing abilities. Your brain rapidly processes visual cues, calculates trajectory angles, and predicts where the ball will bounce next.
Muscle Coordination: Your muscles must work together harmoniously to catch the ball. This coordinated effort between different muscle groups improves overall muscle coordination.
Incorporating reaction ball training into your routine not only makes your workouts more dynamic but also stimulates your brain, leading to improved cognitive function in parallel with enhanced physical prowess.
Reaction Ball Throw: Muscle activation
The Reaction Ball Throw works various muscle groups in your upper body, lower body, and core while performing the throwing and catching movements of the ball. Here’s a breakdown of the main muscles worked during the Reaction Ball Throw:
1. Upper Body Muscles:
- Deltoids (Shoulders): The deltoid muscles are actively engaged during the throwing motion as you generate power to propel the reaction ball forward.
- Biceps and Triceps: Both the biceps (front of the upper arm) and triceps (back of the upper arm) are used to control and stabilize your arm during the throw and catch.
2. Core Muscles:
- Rectus Abdominis (Abs): Your core muscles are engaged to stabilize your trunk during the throwing and catching actions, helping maintain your posture and control the movement.
- Obliques: These muscles on the sides of your abdomen also contribute to core stability during the rapid movements.
3. Back Muscles:
- Latissimus Dorsi (Lats): These muscles in your back are involved in the pulling motion during the throw and catching phases.
- Erector Spinae: These muscles run along your spine and help maintain an upright posture during the exercise.
4. Arm and Hand Muscles:
- Forearm Muscles: The muscles of the forearm are engaged in gripping and controlling the reaction ball, especially during catching.
- Wrist Muscles: The muscles of the wrist play a role in controlling the ball’s bounce and your hand’s movement.
5. Lower Body Muscles:
- Quadriceps and Hamstrings: These muscles in the front and back of your thighs, respectively, are involved in stabilizing your lower body and assisting with the throwing and catching movements.
- Calves: Your calf muscles help provide stability and balance during the exercise.
6. Hip Muscles:
- Hip Flexors and Extensors: The hip flexors and extensors play a role in generating power during the throwing motion and maintaining balance.
Overall, the Reaction Ball Throw exercise provides a comprehensive workout for multiple muscle groups in your upper body, core, lower body, and even your hands. Its dynamic nature engages these muscles in various ways, improving not only strength but also coordination, agility, and balance.
References:
