Kettlebell Deadlift
The kettlebell deadlift is a fundamental exercise that targets the posterior chain muscles, including the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back. The kettlebell deadlift is similar to the conventional barbell deadlift but using a kettlebell instead, which allows for a more comfortable grip and can be more accessible for beginners.
how to do:
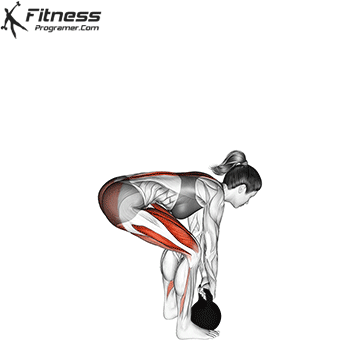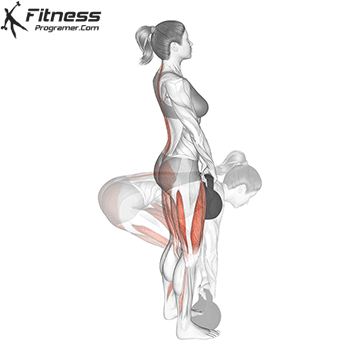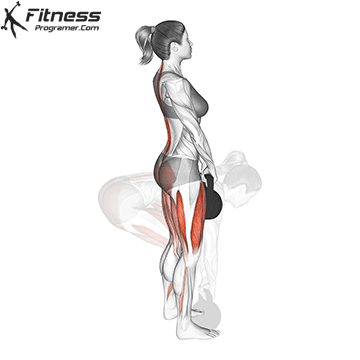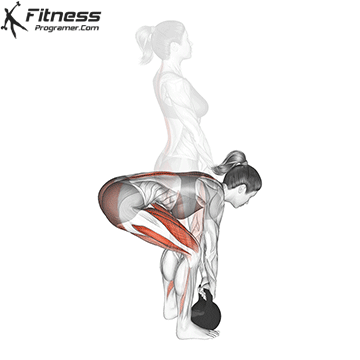
- Set Up: Begin by standing with your feet hip-width apart or slightly wider. Place the kettlebell on the ground between your feet.
- Grip: Bend at the hips and knees, reaching down to grip the kettlebell handle with both hands. Your palms should be facing your body, and your hands should be just outside your knees.
- Positioning: Keep your back flat and chest up as you hinge at the hips, pushing your hips backward while bending your knees slightly. Your shins should remain vertical, and your weight should be centered over your midfoot.
- Lift: Drive through your heels and engage your glutes and hamstrings to lift the kettlebell off the ground. As you stand up, keep the kettlebell close to your body to maintain balance and control.
- Full Extension: At the top of the movement, stand tall with your hips and knees fully extended. Your body should form a straight line from head to heels, and your shoulders should be pulled back.
- Lowering: To lower the kettlebell back down, hinge at the hips and push your hips backward as you bend your knees. Lower the kettlebell back to the starting position with control.
Tips:
- Maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement. Avoid rounding or arching your back to prevent injury.
- Keep the kettlebell close to your body at all times to reduce stress on the lower back.
- Focus on using your hips, glutes, and hamstrings to lift the kettlebell, rather than relying on your lower back or arms.
- Breathe out as you lift the kettlebell and breathe in as you lower it back down.
Kettlebell Deadlift – Benefits
- Strengthens the Lower Body: The kettlebell deadlift primarily targets the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back muscles. It helps build strength and muscular endurance in these areas, which are essential for everyday activities like lifting, bending, and walking.
- Hip Hinge Mechanics: Performing kettlebell deadlifts reinforces the hip hinge movement pattern. Learning and mastering this movement pattern is crucial for lifting objects safely and efficiently, reducing the risk of lower back injuries.
- Core Stabilization: During the kettlebell deadlift, the core muscles are engaged to stabilize the spine and maintain a neutral posture. This helps develop core strength and improves overall stability.
- Grip Strength: Since you need to hold the kettlebell throughout the movement, the kettlebell deadlift also improves grip strength. A stronger grip can be beneficial for various activities, including sports and daily tasks.
- Increased Range of Motion: The hip hinge motion in the kettlebell deadlift requires good hip flexibility. Regular practice can lead to improved hip mobility and range of motion.
- Less Impact on the Spine: Compared to some other exercises like traditional barbell deadlifts, kettlebell deadlifts typically put less stress on the spine. The load is centered closer to your body, which can be more forgiving for those with lower back issues.
- Improved Posture: By strengthening the posterior chain muscles and the core, kettlebell deadlifts can help improve posture and reduce the likelihood of rounded shoulders and a slouched back.
- Functional Fitness: The hip hinge movement pattern used in the kettlebell deadlift mimics many real-life activities, making it a functional exercise that can enhance your performance in daily tasks and sports.
- Scalability: Kettlebell deadlifts can be easily adjusted for different fitness levels. You can start with a lighter kettlebell and gradually increase the weight as you progress.
- Efficiency: Kettlebell deadlifts are relatively simple to learn and can be incorporated into various workout routines. They are an efficient exercise for building strength and engaging multiple muscle groups in a short amount of time.
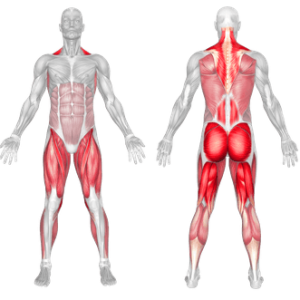
Kettlebell Deadlift – Muscles Worked