Overview
The Full Planche is an advanced bodyweight exercise that challenges both strength and balance. It requires tremendous upper body and core strength to maintain a horizontal position with only the hands touching the ground. Achieving a Full Planche is a remarkable feat in bodyweight training, showcasing a high level of control and muscular coordination.
This exercise tests a combination of strength, flexibility, and stability, making it an impressive skill in calisthenics and bodyweight training.
How to Perform the Full Planche
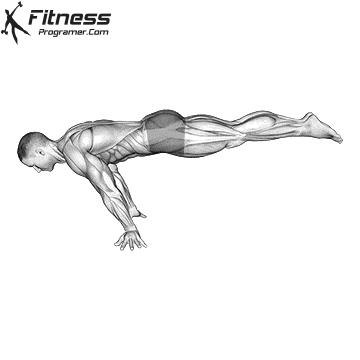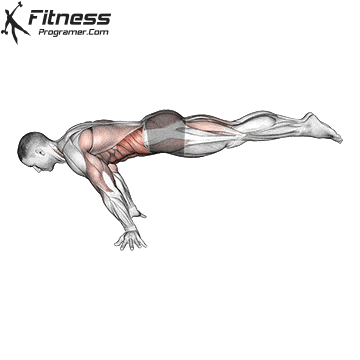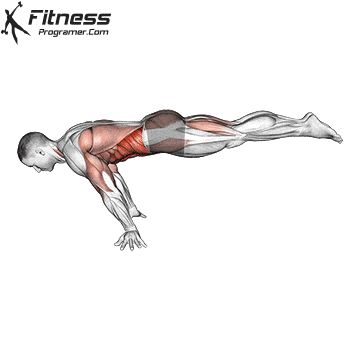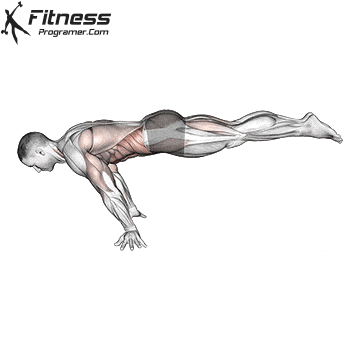
To successfully perform the Full Planche, follow these steps:
Start in a Push-Up Position: Begin in a push-up stance, with your hands placed slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
Engage Core and Shoulders: Push your shoulders forward and engage your core to prevent sagging in the lower back. Your arms should be straight and fully locked out.
Lift Your Feet Off the Ground: Slowly raise your legs off the floor, keeping them straight, until your body forms a straight line from head to toes.
Balance and Hold: As you lift your legs, use your hands and shoulders to help balance your body in a horizontal position. Keep your gaze forward and focus on maintaining the hold.
Maintain the Position: Hold the Full Planche as long as possible, focusing on balance and proper alignment of the body. As you build strength, aim to hold for longer durations.
Tips for Proper Form
Keep the arms straight: Ensure your arms are fully extended and locked at the elbows to avoid strain.
Engage the core: Tighten your abs and lower back muscles to maintain a straight body position.
Push through your hands: Press your hands into the ground to stabilize your shoulders and maintain balance.
Focus on your gaze: Keep your gaze forward to help with body alignment and to avoid excessive neck strain.
Work on wrist mobility: Wrist flexibility is crucial in performing the Full Planche without discomfort.
Common Mistakes
Lack of core engagement: Not engaging the core can lead to a sagging lower back and instability in the movement.
Elbows bending: Bending the elbows compromises the position and puts excess strain on the arms and shoulders.
Incorrect hand placement: Placing hands too far forward or backward can affect balance and make it harder to hold the position.
Not keeping legs straight: Bending the knees reduces the intensity of the exercise and makes the position unstable.
Rushing the progression: Skipping progressions can lead to injuries and difficulty mastering the Full Planche.
Benefits of the Full Planche
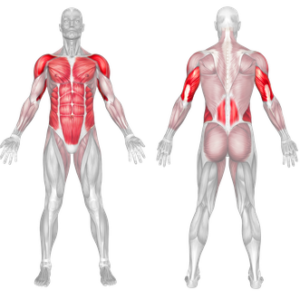
Builds upper body strength: The Full Planche strengthens the shoulders, arms, and wrists, as they support your entire body weight.
Engages the core: The exercise requires intense core activation, improving overall core strength and stability.
Improves body control and balance: Holding the Full Planche enhances your proprioception and ability to balance under pressure.
Increases muscular endurance: Holding the Full Planche for extended periods builds muscular endurance in both the upper body and core.
Enhances flexibility and mobility: The position encourages mobility in the wrists, shoulders, and hips as you work toward mastering it.
How to Incorporate Into Your Routine
Incorporating the Full Planche into your routine requires gradual progression. Start with basic core and shoulder strengthening exercises like planks, push-ups, and planche leans. Once you’ve built enough strength and balance, begin working on progressions like the frog stand or tuck planche. As you develop your ability, gradually extend your hold times and focus on form to eventually achieve the Straddle Planche Full Planche.
Full Planche Muscles Worked