Overview
The dumbbell push press is a strength training exercise that targets the shoulders, triceps, and upper body, while also engaging the core and lower body for stability and support. It’s commonly used in athletic training, CrossFit, and general strength routines to develop shoulder strength and explosiveness.
How to Perform Dumbbell Push Press
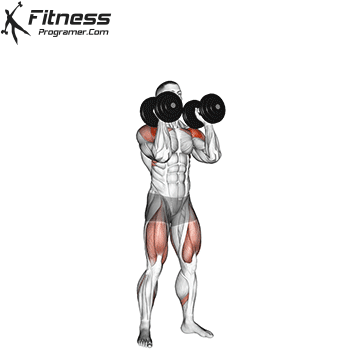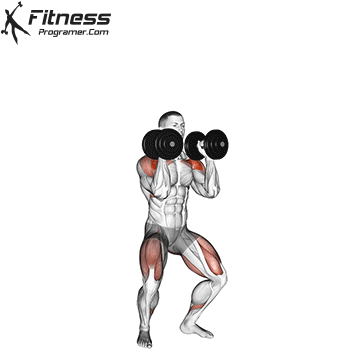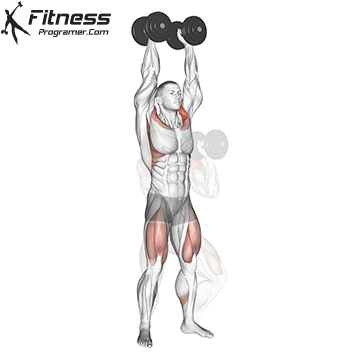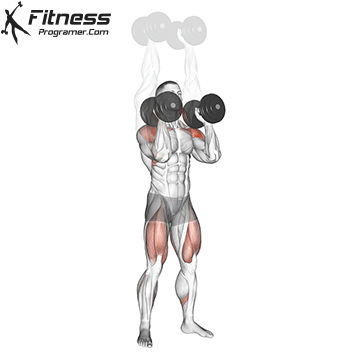
- Starting Position:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand, with your arms bent at a 90-degree angle, and your palms facing each other.
- The dumbbells should be positioned just outside your shoulders. This is your starting position.
- Dip Your Knees:
- Begin the movement by slightly bending your knees, initiating a small dip.
- Explosive Push (Drive Phase):
- Explosively push up with your legs. This leg drive generates the force needed to lift the dumbbells overhead.
- Simultaneously, press the dumbbells straight over your shoulders, extending your arms fully at the top of the movement.
- Top Position:
- At the top of the movement, your arms should be fully extended overhead.
- Your wrists should be stacked over your shoulders, and your palms should still be facing each other.
- Lower the Dumbbells:
- Lower the dumbbells back to the starting position by bending your elbows and controlling the descent.
- Maintain good form and control as you bring the dumbbells down.
- Repeat:
- Perform the desired number of repetitions, typically within a specific rep range based on your fitness goals and the weight you’re using.
Tips:
- Ensure proper form: Maintain a stable core, keep your back straight, and avoid arching or rounding your spine.
- Use an appropriate weight: Start with a weight that allows you to perform the exercise with good technique. Gradually increase the weight as you get stronger.
- Controlled Tempo: Maintain a controlled and steady tempo during both the ascent (pressing the dumbbells) and descent (lowering the dumbbells) phases of the exercise. Avoid jerky movements.
- Warm up: Prioritize shoulder warm-up exercises and mobility work to prepare your shoulders for the demands of the push press.
Ensure you have adequate shoulder and hip mobility before attempting the push press. Limited mobility can compromise your form and effectiveness. As you become more proficient, gradually increase the weight to challenge yourself. However, prioritize maintaining good form over heavy weights.
Benefits of Dumbbell Push Press
- Upper Body Strength: The dumbbell push press primarily targets the muscles of the upper body, including the shoulders (deltoids), triceps, and chest. It’s an effective exercise for building upper body strength.
- Shoulder Strength: During the dumbbell push press, the deltoid muscles in the shoulders are heavily engaged to lift the weights overhead. The exercise requires a powerful extension of the shoulder joint, particularly during the “drive” phase when you explosively push the dumbbells upward. This movement effectively strengthens the shoulder muscles, making them more capable of handling resistance.
- Shoulder Stability: To perform the push press correctly, you must stabilize the dumbbells overhead once they’re raised. This requires your shoulder stabilizer muscles to work actively. Improved shoulder stability not only aids in lifting heavier weights but also enhances your ability to control and stabilize your shoulders during various activities and sports, reducing the risk of injuries.
- Size and Hypertrophy: The dumbbell push press, when performed with sufficient resistance and volume, can lead to muscle hypertrophy or muscle growth in the deltoids. Over time, this can contribute to broader and more defined shoulders, which many individuals find aesthetically appealing.
- Full Body Engagement: While the emphasis is on the upper body, the dumbbell push press also engages the lower body. The legs play a crucial role in generating power to drive the dumbbells overhead, making it a compound exercise that involves multiple muscle groups.
- Explosive Movement: The push press is characterized by a dynamic and explosive movement pattern. This exercise begins with a powerful initiation from the lower body, involving an explosive triple extension of the hips, knees, and ankles. During this phase, your lower body generates a significant amount of force. This force is then efficiently transferred to the upper body, where it is used to propel the dumbbells or barbell overhead. As you gradually increase the resistance, the challenge intensifies, compelling your muscles to produce maximum power for a rapid upward movement of the weights. This heightened rate of force development plays a direct role in enhancing your overall power output.
- Core Activation: To stabilize the weights overhead, your core muscles, including the abdominals and lower back, play a crucial role. They work to prevent excessive arching or rounding of the spine, ensuring proper posture during the exercise.
- Athletic Performance: Athletes in sports such as basketball, football, volleyball, and many others can benefit from the increased upper body strength and power that the dumbbell push press provides. It can enhance performance in activities that involve pushing or lifting.
Incorporating the dumbbell push press into your training routine can provide a comprehensive full-body workout, combining upper body strength and power development with lower body explosiveness.
How to Incorporate Into Your Routine
- For Beginners: Start with 2–3 sets of 6–8 reps using light dumbbells to learn timing and control.
- For Hypertrophy: Perform 3–4 sets of 8–10 reps with moderate weights and strict rest periods.
- For Strength: Use 4–5 sets of 4–6 reps with heavier loads, focusing on explosive drive and full lockout.
- For Functional Training: Add to total-body movement circuits to build athletic strength and movement economy.
- For Circuit Training: Pair with squats or kettlebell swings in high-intensity formats (30 sec on, 30 sec off).
- For General Fitness: Use in upper-body strength workouts 2x/week to develop pressing capacity and coordination.
- For Fat Loss and Conditioning: Include in metabolic circuits with 3–4 rounds of 8–10 reps using moderate weights.
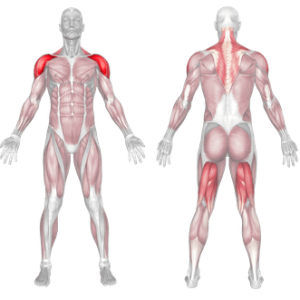
Dumbbell Push Press Muscles Worked
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a push press and a strict press?
The push press uses leg drive to assist the overhead press, while the strict press relies solely on upper-body strength.
Can I use the Dumbbell Push Press for cardio?
Yes, when used in circuits or high-rep conditioning formats, it significantly elevates the heart rate.
Should I use neutral or pronated grip?
Both are acceptable. A neutral grip (palms facing in) may be more shoulder-friendly for some lifters.
How heavy should I go?
Choose a weight that challenges you but still allows clean technique and full lockout. Prioritize form over load.
