Dumbbell Iron Cross
The dumbbell iron cross is a combination of squats and lateral raises. This exercise is performed with a pair of dumbbells, and it requires a high level of stability, balance, and coordination.
How to do:
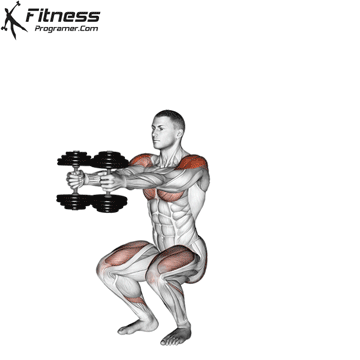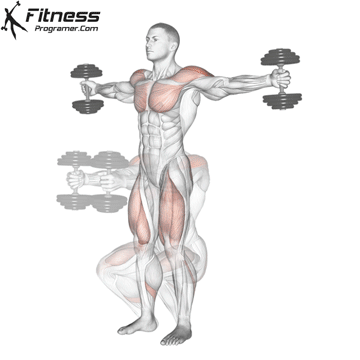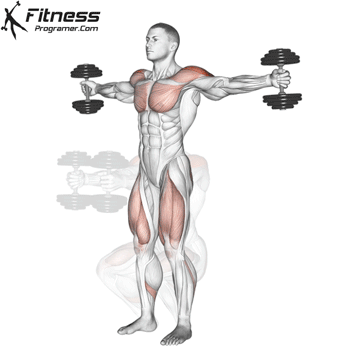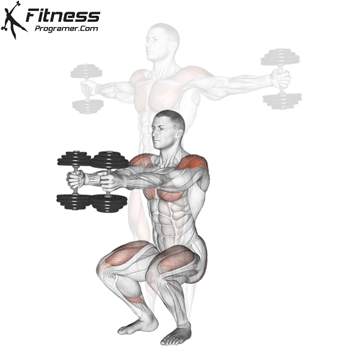
Benefits:
The dumbbell iron cross is a strength training exercise that targets the shoulders and legs. It offers several benefits for those who work multiple muscle groups and incorporate it into their workout routine;
The dumbbell iron cross requires a significant amount of stability and control, particularly in the shoulders, hip and legs, leading to improved strength in these areas. As you progress with the dumbbell iron cross, you will find that it requires a significant amount of endurance to perform multiple reps. By consistently incorporating it into your workout routine, you can improve your overall endurance levels.
High intensity: The dumbbell iron cross can be considered a high-intensity exercise, depending on how it is performed, making it a challenging exercise that can increase heart rate and build muscle. To make the exercise more intense, you can use heavier weights, perform it at a faster pace, or incorporate it into a circuit training routine. However, it is important to make sure you have proper form and control before increasing the intensity, as improper form can lead to injury. It’s also a good idea to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the weight as you build up your strength.
