Overview
The cable side triceps extension is an effective isolation exercise that targets the triceps brachii, particularly the long head. Using a cable machine provides constant resistance, ensuring maximum muscle engagement throughout the movement. This exercise is a great alternative to free-weight extensions, offering improved control and reduced strain on the joints.
How to Perform the Cable Side Triceps Extension
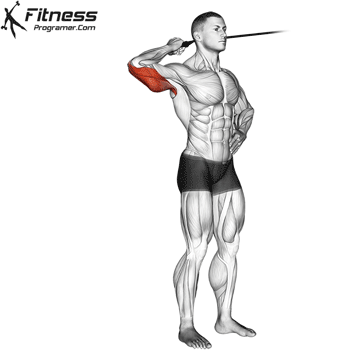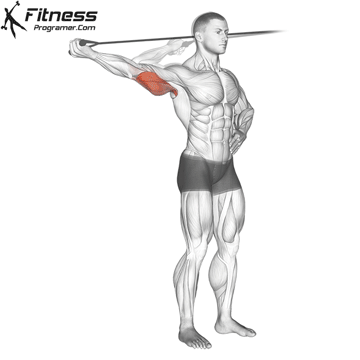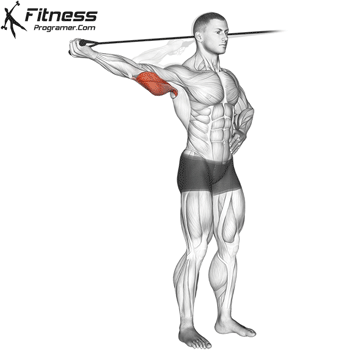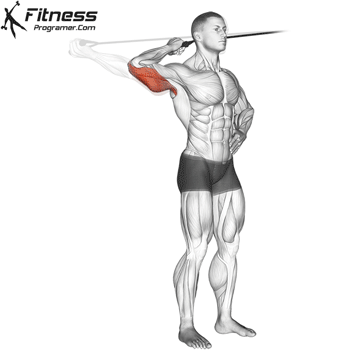
Step 1: Setup and Starting Position
- Attach a single-handle grip to a high cable pulley.
- Stand sideways to the cable machine, with your working arm closest to the cable.
- Grab the handle with an overhand grip and position your elbow at shoulder height, bent at 90 degrees.
- Place your opposite hand on your hip or stomach for stability.
Step 2: Execution
- Extend your arm outward, straightening the elbow until your arm is fully extended.
- Keep your upper arm stationary, moving only your forearm.
- Pause for a brief contraction at the top, squeezing your triceps.
- Slowly return to the starting position, maintaining control throughout.
- Repeat for 8 to 12 reps per arm, completing 3 to 4 sets.
Tips for Proper Form
- Keep your elbow at shoulder height throughout the movement.
- Engage your core for stability.
- Use a controlled motion, avoiding momentum.
- Do not overextend your arm to prevent joint strain.
- Ensure your wrist remains neutral to avoid discomfort.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Dropping the elbow, reducing triceps activation.
- Using too much weight, compromising form.
- Relying on momentum, decreasing muscle engagement.
- Not fully extending the arm, limiting the range of motion.
- Twisting the torso, reducing focus on the triceps.
Benefits of the Cable Side Triceps Extension
Targets the Long Head of the Triceps: The side extension angle emphasizes the long head, which contributes to overall arm size and strength.
Provides Constant Tension: The cable machine ensures continuous resistance, maximizing muscle activation.
Enhances Muscle Symmetry: Working one arm at a time helps correct imbalances between the left and right triceps.
Reduces Wrist and Elbow Stress: The controlled movement and smooth resistance minimize joint strain, making it safer than free weights.
Improves Lockout Strength: Strengthening the triceps helps improve performance in pressing movements like the bench press and overhead press.
Muscles Worked