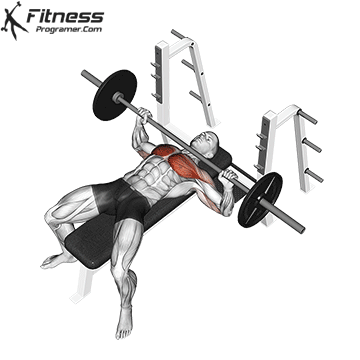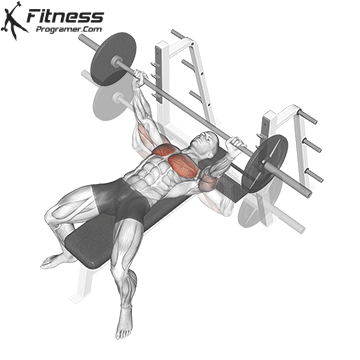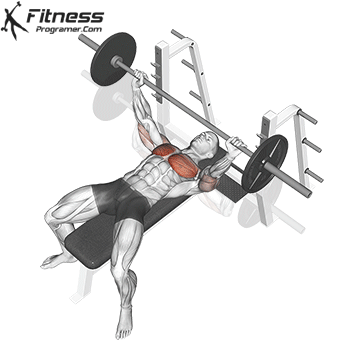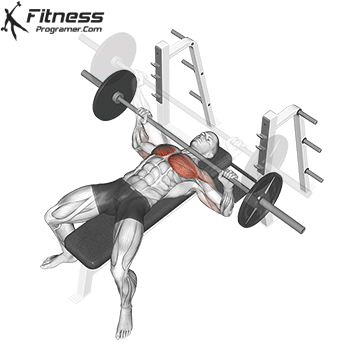
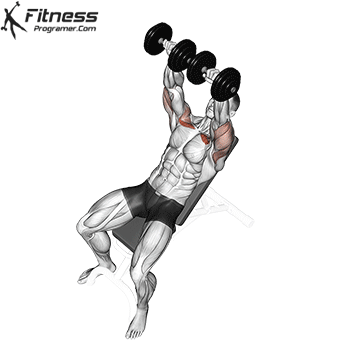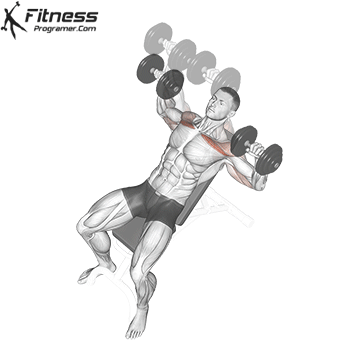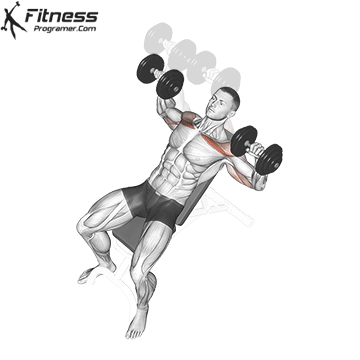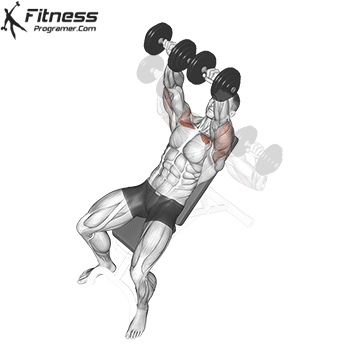
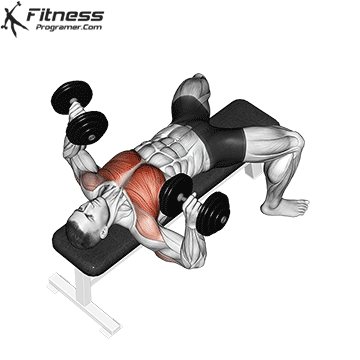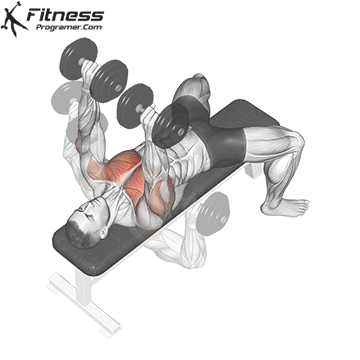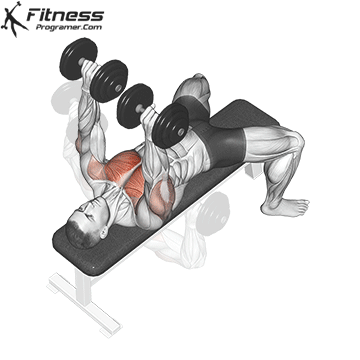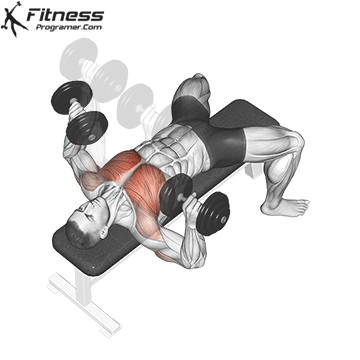
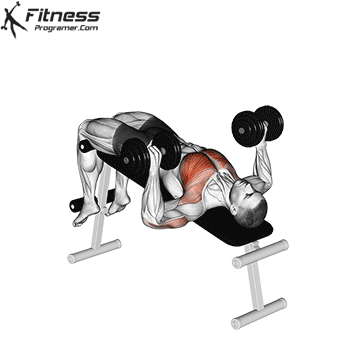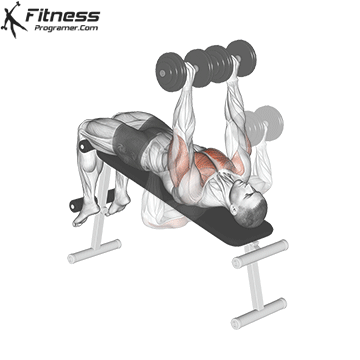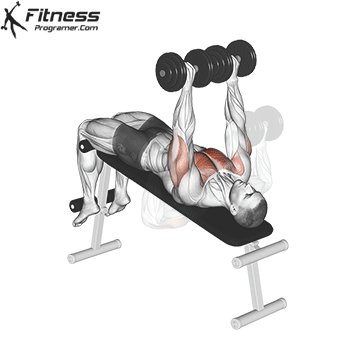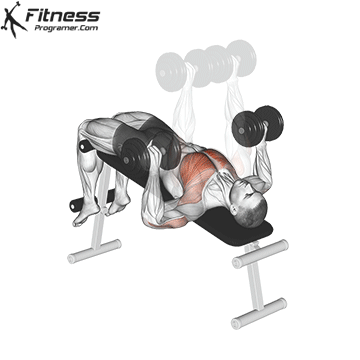
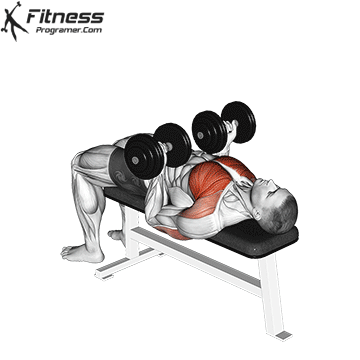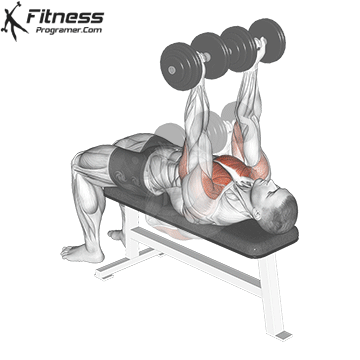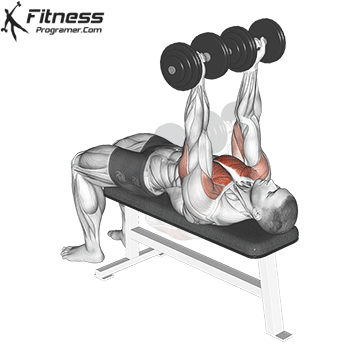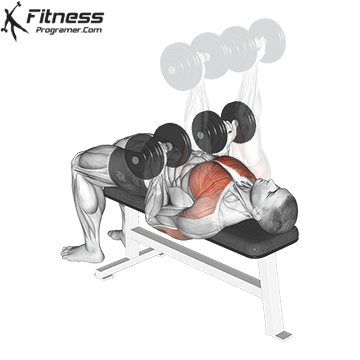
Overview
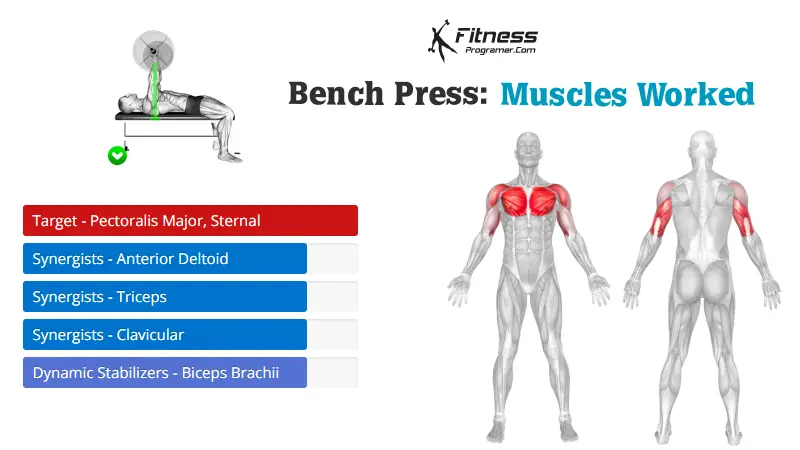
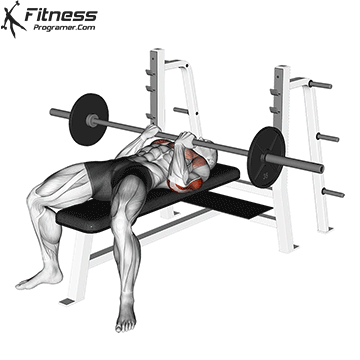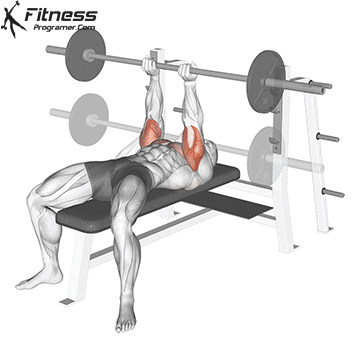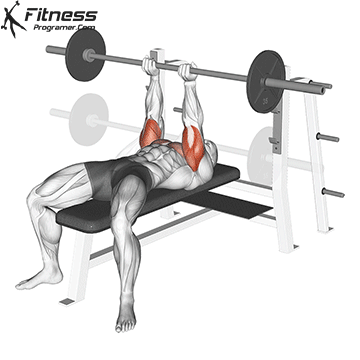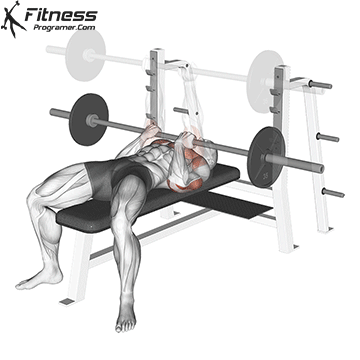
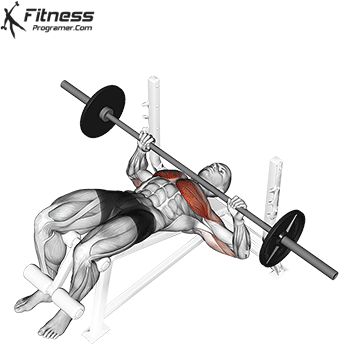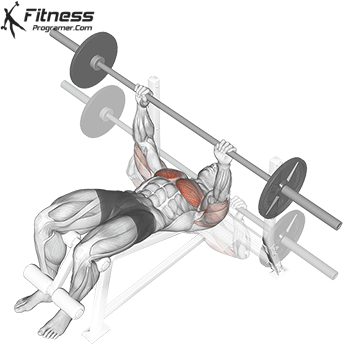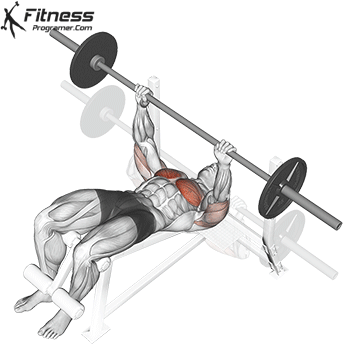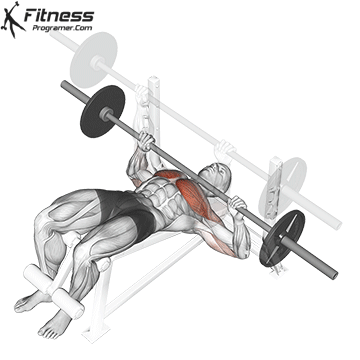
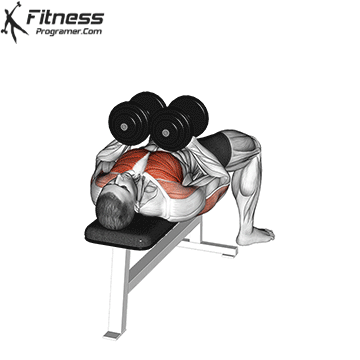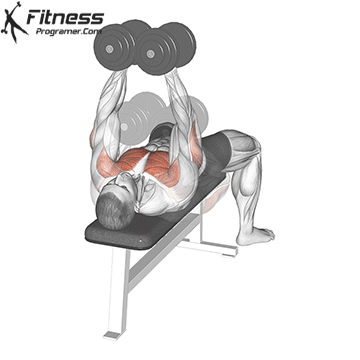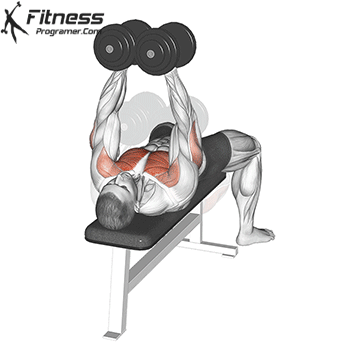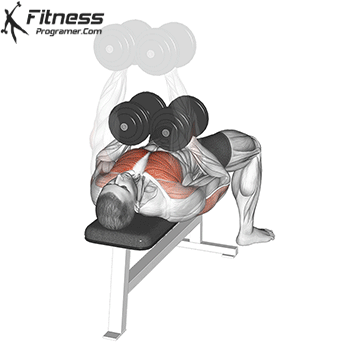
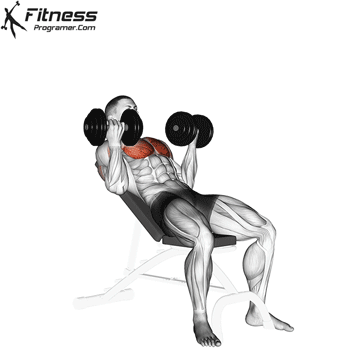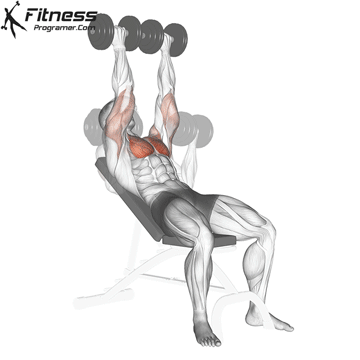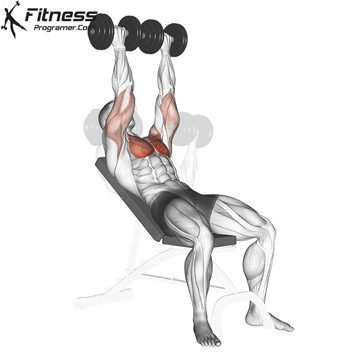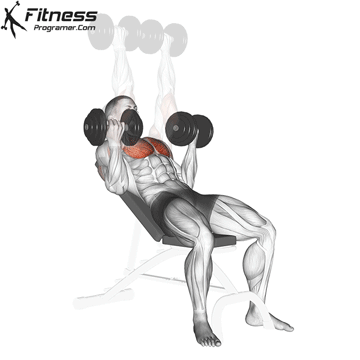
The bench press is a compound strength training exercise that primarily targets the chest muscles (pectoralis major and minor). It can be performed using various grips and angles to target different areas of the chest, with variations such as the incline, decline, or flat bench. This exercise is fundamental in bodybuilding, powerlifting, and general fitness training.
Overall, the bench press effectively targets multiple muscle groups in the upper body and is a valuable addition to any strength training routine.
How to Perform the Barbell Bench Press
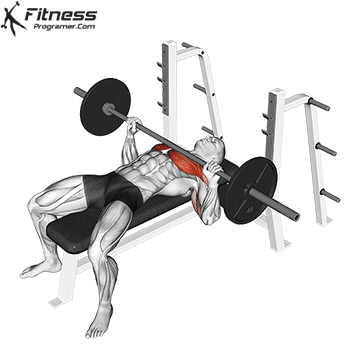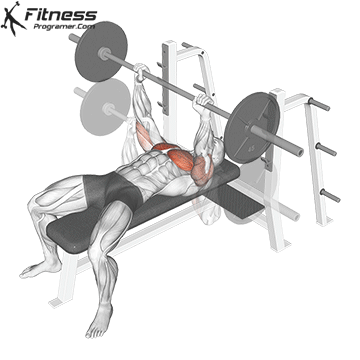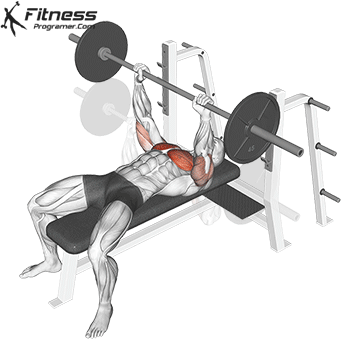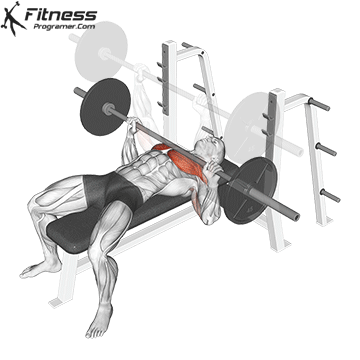
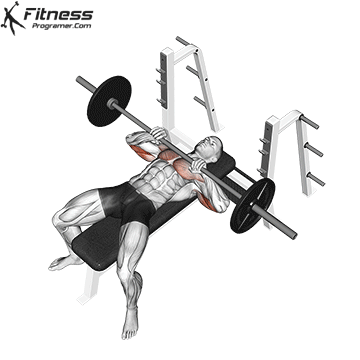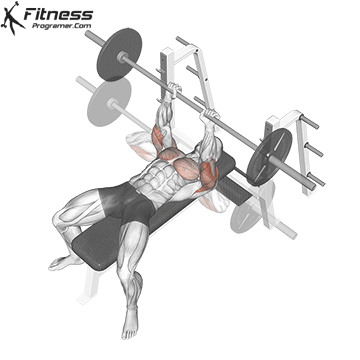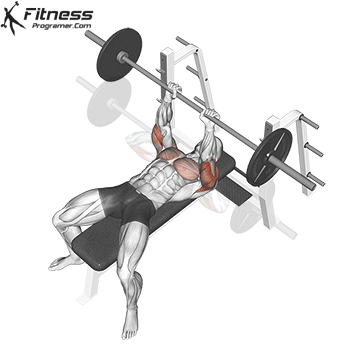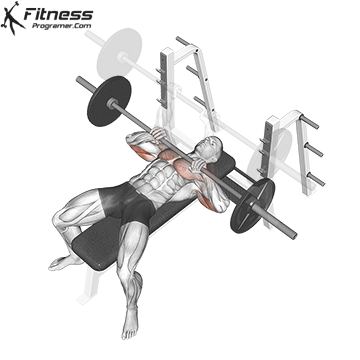
Setup
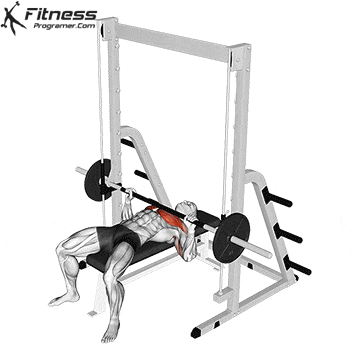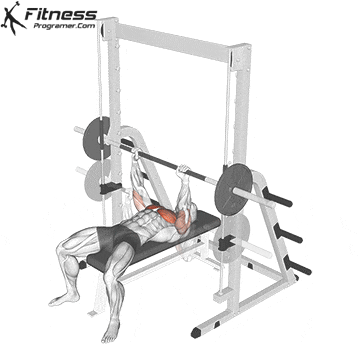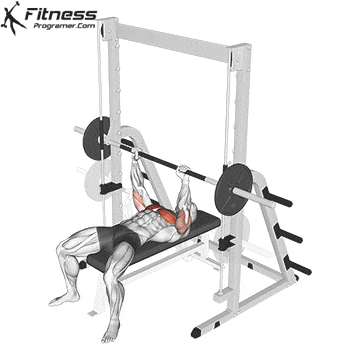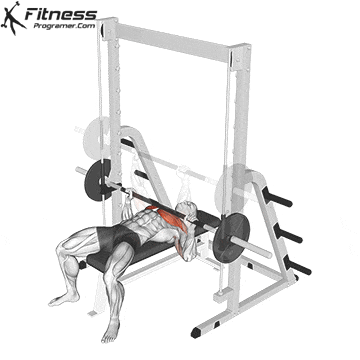
Lie on a flat bench with eyes directly under the bar.
Feet flat on the ground, knees bent at ~90°.
Grip the bar with a slightly wider than shoulder-width grip (wrists stacked over elbows).
Retract and depress the scapulae to stabilize the upper back.
Maintain a natural arch in the lower back.
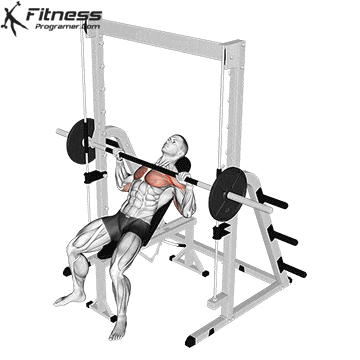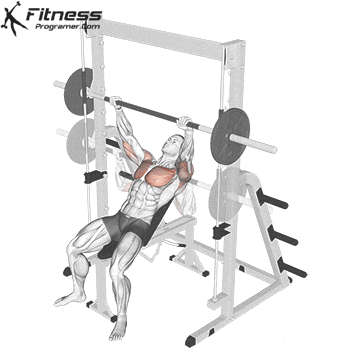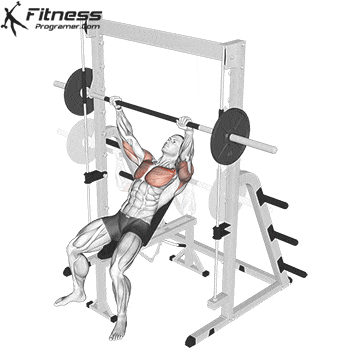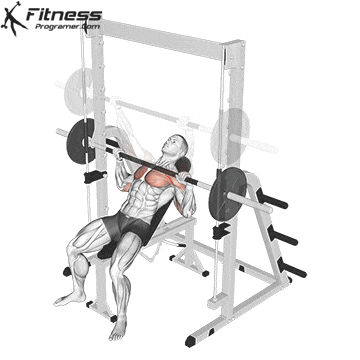
Unrack and Descent
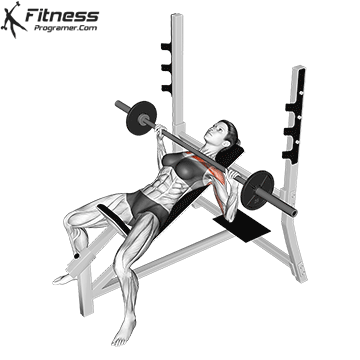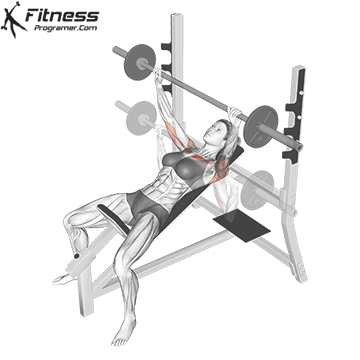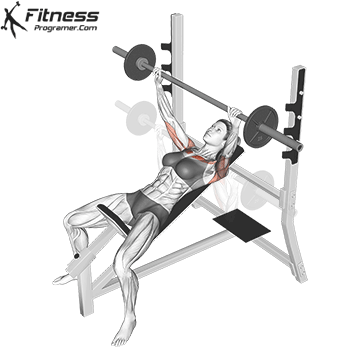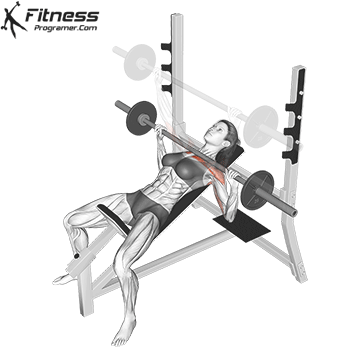
Unrack the bar and bring it over your chest, elbows fully extended.
Inhale, brace your core, and lower the bar slowly to the lower portion of your chest (around nipple level), keeping elbows at ~45° from the torso.
Press Phase
Push the bar upward in a slight arc back toward your eyes.
Exhale as you drive through the chest and triceps, locking out the elbows at the top.
Reset and Repeat
Maintain upper back tightness and repeat for prescribed reps.
Tips for Proper Form
By following these tips and tricks for perfect form, you can maximize your gains while minimizing your risk of injury. Remember to always start with light weights and gradually increase the load as your strength and technique improve. Here are the steps to perform a bench press:
Keep your shoulder blades retracted throughout the lift for better joint stability.
Do not flare your elbows excessively—aim for ~45°–60° from the body.
Maintain a tight glute and leg drive to anchor your base.
Keep wrist alignment neutral to avoid strain.
Lower the bar under control; don’t bounce it off the chest.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Letting the elbows flare too far out, which increases shoulder joint stress.
Lifting the feet off the ground, reducing base stability.
Allowing the lower back to over-arch excessively, risking lumbar stress.
Bouncing the bar off the chest for momentum.
Inconsistent bar path, which reduces mechanical efficiency.
Benefits of the Bench Press
Maximal Upper Body Strength: Essential for strength athletes and widely tested in powerlifting.
Chest Hypertrophy: Efficiently loads the pectoral muscles through a full range of motion.
Triceps and Shoulder Development: Builds pressing capacity across both arm and shoulder joints.
Functional Horizontal Pushing Strength: Translates to athletic tasks requiring upper body force production.
- Burns Calories: Strength training exercises like the bench press can help you burn calories, increase your metabolic rate and lose weight.
- Increases Bone Density: Bench press, as a strength training exercise, has been shown to increase bone density.
Measurable Progression: Easily tracked with load, rep, and volume increases over time.
How to Incorporate Into Your Routine
| Goal | Prescription |
|---|---|
| Beginner Strength | 2–3×8–10 reps, moderate weight, 2–3×/week |
| Hypertrophy | 3–4×8–12 reps, moderate to heavy weight, controlled tempo |
| Max Strength | 4–6×3–5 reps at 80–90% 1RM, long rest, programmed progression |
| Powerlifting Prep | 3–5×1–3 reps, 85–95% 1RM with peaking strategies |
| Functional Training | Paired with upper-body pull (e.g., row), lighter reps for movement quality |
| Fat Loss Circuit | High-rep (15–20) sets, lighter load, part of upper-body metabolic conditioning |
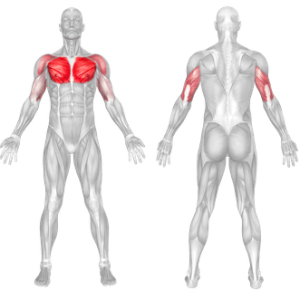
Bench Press – Muscles Worked
Bench Press Variations
Each of the following bench press variations are exercises that work your chest muscles at different angles. Here are the most effective bench press variations.