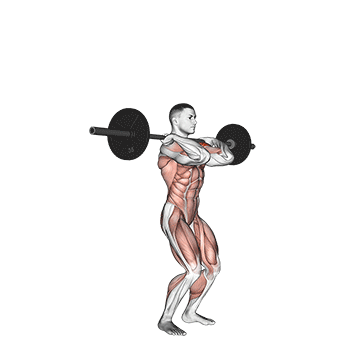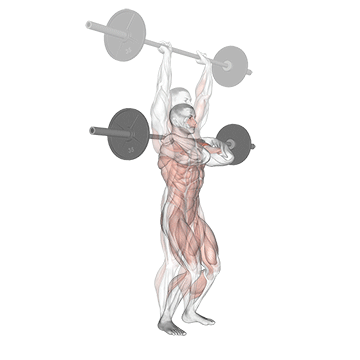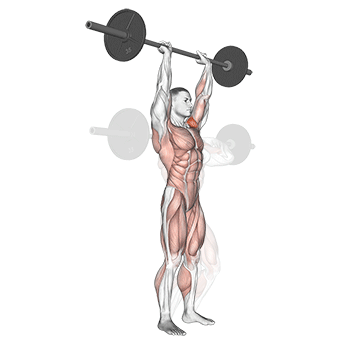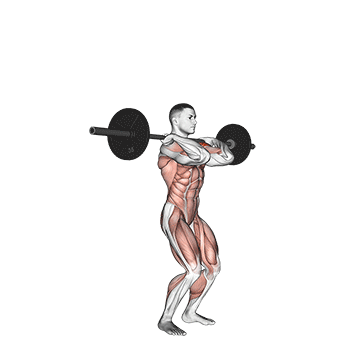Push Press
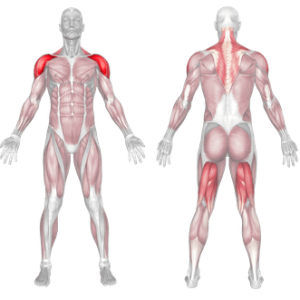
The push press is a explosive weightlifting exercise that targets the shoulders, triceps, and upper body while also engaging the core and legs. The push press is often used in strength training, Olympic weightlifting, and functional fitness workouts. The explosive nature of the push press can benefit athletes in various sports by improving their ability to generate power and strength quickly.
How to do:
- Set Up:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Your toes should be slightly turned out.
- Position the barbell across your upper chest, just below your neck. If using dumbbells, hold one in each hand at shoulder height with palms facing forward.
- Grip:
- For the barbell push press, your grip should be slightly wider than shoulder-width. Grip the bar with your palms facing forward and your elbows pointing downward. Make sure your wrists are aligned with your forearms.
- If using dumbbells, grip them firmly with your palms facing each other.
- Rack Position:
- Lift the barbell off the rack or clean the barbell to your shoulders if starting from the ground.
- Keep your elbows slightly in front of the barbell and your upper arms parallel to the ground. This is your starting position.
- Dip:
- Begin by slightly bending your knees to initiate a dip. Keep your torso upright and your chest lifted.
- As you dip, focus on keeping your weight balanced on the midfoot and heels.
- Drive:
- Explosively extend your hips and knees to generate upward momentum. This movement should be powerful and quick.
- As you drive upward, press the barbell overhead using the strength of your shoulders and triceps. If using dumbbells, press them overhead simultaneously.
- Lockout:
- Fully extend your arms overhead, locking out your elbows. Your head should move slightly forward as the barbell passes your forehead.
- Return:
- Lower the barbell back to the starting position by bending your knees and hips. Allow the weight to descend under control.
- Rack the Barbell:
- If using a barbell, rack it back on the supports or the ground.
Tips:
- Maintain a tight core throughout the movement to stabilize your spine.
- Use a slight bounce from your dip to aid in the upward drive, but avoid turning it into a full squat.
- Engage your glutes and quads during the drive phase for maximum power.
- Keep the barbell or dumbbells close to your body during both the upward and downward phases of the movement.
- Always warm up before attempting heavy weights and start with a weight you can comfortably handle to practice your form.
Push Press Benefits
Increased Upper Body Strength: The push press primarily targets the shoulders, triceps, and upper back muscles. By pushing heavy weights overhead, you can develop substantial upper body strength.
Enhanced Muscle Mass: Engaging multiple muscle groups during the push press stimulates muscle growth. This exercise can contribute to broader shoulders, a stronger upper chest, and more defined triceps.
Improved Power and Explosiveness: The explosive drive from the hips and legs to lift the weight overhead develops power in the lower body and transfers it to the upper body, resulting in improved overall explosiveness.
Functional Strength: The push press simulates movements that involve lifting objects overhead, making it a functional exercise for daily activities or sports that require pushing or lifting.
Metabolic Conditioning: The high-intensity nature of the push press engages multiple muscle groups, leading to an increased heart rate. This can contribute to improved cardiovascular fitness and fat burning.
Joint Stability: The push press requires proper joint alignment and stability, promoting healthy shoulder and elbow joints when performed correctly.
Muscles Worked in the Push Press